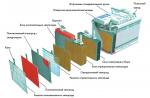
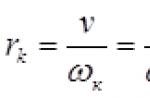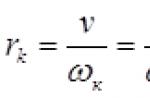Built according to a similar scheme for building all-terrain vehicles Uvat and Asterix. The machine is based on a frame of a fracture type design. The all-terrain vehicle was conceived to transport two people, and it also had to have a kung, with sleeping places for two people, so that it would be possible to spend the night right in the forest if the hunt dragged on.
The name of the all-terrain vehicle TT stands for push-pull.
Materials and parts used by the author to build this all-terrain vehicle:
1) Engine Chinese made 14 hp
2) variator
3) Gearbox from classic VAZ
4) chain reducer
5) bridges from the vase classics
6) encourage KrAZ
7) sheets of aluminum and polycarbonate.
8) profile pipe
9) steering rack from vaz 2108
Let us consider in more detail the stages of construction and the main components of the structures of the all-terrain vehicle.
Frame manufacturing and installation of the main elements:


The bridge was set at a slight angle, had to be set to remove the corners of the driveshafts, which cannot be aligned by raising due to the gearbox. Such an installation cannot have a strong effect on reliability, since the gearboxes are also turned over.

Sprockets with 24 and 16 teeth were used, so the gear ratio is 1.5. To install the star, a clutch disc was used, where the spline for the landing star was machined. Then the star was installed and fixed by welding.
The wheels, like the wheels of the all-terrain vehicle, were made by the author independently, following the instructions in the topics for making wheels on sites dedicated to the construction of such equipment.
The wheels were stripped using an electric winch, which the author assembled on his own. After all four wheels from KrAZ were ready, the author began to think about the design of the frame and transmission as a whole. it was decided to use bridges from a vase, although it would be better to use bridges from a Muscovite, as they are stronger.
After the main part of the all-terrain vehicle was assembled, the author began testing. At the first start of the system, a serious drawback was revealed in the form of strong noise at 3600 engine speeds. To begin with, the author changed tensioners, bearings, a star, but this did not bring results. Therefore, it was decided to abandon the bushings on the rollers in favor of the motor chain in an oil bath. But then you will also have to replace the gearbox drive.
A 42 tooth star was installed on the gearbox, so as not to make much noise, the author tries not to bring the engine speed to the maximum. Speed mode is selected on the gearbox and the engine runs at medium speed. there is enough traction due to the regulator. Since the design of the system does not allow shifting gears on the go, you have to stop the all-terrain vehicle and the variator is suspended through a special device, and then the speed on the gearbox changes. The ability to suspend the operation of the variator is by pressing the pedal right in the cabin of the all-terrain vehicle. But this is not strong problem, since gear shifting is required very rarely, due to the variator, the car drives perfectly.

To connect the driven variator to the gearbox from the VAZ 2108, the author used the following scheme:

And below is a diagram of the transmission of an all-terrain vehicle:

A steering rack from the VAZ 2108 was installed on the all-terrain vehicle, which will give long traction. the main thing is to strengthen it so that the threads do not break.

Since the author nevertheless decided to abandon chain drives, the all-terrain vehicle has undergone a number of upgrades. In particular, it was set manual box gears, and a differential was brewed on the gearbox from the VAZ 2108. On old design the gear ratio excluding the variator was 88.26, after modernization it decreased to 69. manual gearbox allows you to reduce the gear ratio when you turn on low gear. Another useful property consists in unloading the transmission when driving on a primer and bumps. the downside of such an upgrade is an increase in weight by 80 kilograms.
This shows the installation of acceptable cardan shafts from the RCP:


And here is the already installed manual gearbox:

You can immediately see how the gearbox from the VAZ 2108 and the engine are connected:

The engine weighs 36 kilograms, the gearbox from the VAZ 2108 is another 40 kilograms. RCP weighs another 26 kilograms plus 10 kilograms of weight cardan shaft. And the frame of the all-terrain vehicle was also strengthened.
However, with respect to the traction of the all-terrain vehicle, this did not affect much. in first gear at a 25-degree exit, the rover handles just fine, even with a passenger on board.
Shown here engine compartment with engine removed:

The driven variator assembly is shown in more detail:

The design of the drive shaft with crosses:

And here is the engine compartment with the engine installed:

Rear of the vehicle:

Then the author proceeded to test the all-terrain vehicle on rough terrain, where the engine is 14 hp. performed excellently. the power is completely enough, the variator does not reach the maximum speed, thanks to the choice of speeds in the gearbox. Max speed car equals 25 kilometers per hour.
A lot has been said about the benefits of a walk-behind tractor in the subsidiary farm. If funds allow, they buy it. If you want to save money, make your own.
At first glance, it's complicated. technical device, which can only be done in the factory. In fact, homemade walk-behind tractor with a gearbox from the "Ant", quite often found in the yards of homegrown farmers.
If you understand the design, and have an elementary set of a locksmith in the house:

- welding machine;
- Bulgarian;
- drilling tool.
then you can build a self-propelled iron horse literally from past materials. To do this, you need to understand how the design works.
Motoblock device. Basic structural elements

- Frame or bed. The engine, the system for transmitting torque to the wheels, the suspension and traction device for attachments;
- Power unit. Its power can be small, from 5 to 10 horsepower. Engines from mopeds, motorcycles, compressors and even chainsaws are used;
- Suspension. Usually primitive. Comprises homemade wheels or ready from agricultural machinery. Sometimes automobile or motorcycle ones are used. Can be axial or portal;
- Gearbox for motoblock. One of the most important parts of the design. Designed to reduce revs drive shaft with a simultaneous linear increase in torque. Quite often, a gearbox from a car or scooter is used as a gearbox.

However the best option there will be a homemade gearbox. It does not need to be paired with a power plant, since the calculation is made for specific tasks, and you are not limited to a ready-made technical solution.
How to make a gearbox for a walk-behind tractor with your own hands
First you need to decide on the parameters power plant. IN technical specifications indicates the number of revolutions of the crankshaft. This is the first value that is needed for calculations. This figure is not constant, with the addition of "gas" the speed increases. Idle speed + 10% is taken as the base value.
You should not start repairing a gearbox on a walk-behind tractor yourself if the operation of the unit and its device for a new user are a complete secret. Since the gearbox is a rather complicated unit, you should not proceed to repairing it yourself immediately after detecting breakdowns. It will be better if the repair of the checkpoint is carried out by professionals.
If an oil leak from the gearbox is detected, it means that the seals of the bearing assemblies were incorrectly installed or worn out. They can be poorly tightened on the lids. Under them, damaged gaskets may appear. If it got clogged air valve(breather), it is necessary to clean it and bring the oil level to normal. Oil leaks can be repaired by replacing or correct installation seals or gaskets. Tightening the cover bolts will also help solve the problem.
Types of violations in the checkpoint and ways to correct them
If the mechanism automatic box gear has ceased to function normally, then the following types of malfunctions may be observed:
- Violation of the kinematic connection inside the gearbox.
- Spontaneous inclusion of gears or lack of their fixation.
- Oil leak on shift shaft.
- Violation of the function of the mechanism of separation of the semiaxes.
- No gear change.
- Gear jamming.
If the kinematic connection inside the gearbox is broken or the sprocket in the block is broken, it is necessary to disassemble the gearbox in order to replace the problem sprocket. The cause of oil leakage on the shift shaft may be excess oil in the gearbox, so the oil level must be checked. When the welding connection of the gear is broken, after disassembling the gearbox, the block shaft is changed. Draining excess oil, you should check the degree of wear of the working edge of the cuff on the shift shaft, disassemble the gearbox and replace the part.
The reason for the lack of fixation of gears or their spontaneous disengagement is a violation of the adjustment of the gear shift mechanism. When making repairs, loosen the screws securing the switching mechanism board.
After that, turn on the first gear and tighten the screws securing the board. For example, having made a minitractor with your own hands, it is imperative to monitor the correct adjustment of the drive by changing the tension of the cable for controlling the separation of the semiaxes. In order to fix the breakage of any element of the axle disengagement drive inside the gearbox, the gearbox should be disassembled, replacing the broken parts.
If a broken spring or worn shift plate retainers are found, replace the damaged parts by performing a shift adjustment. If it is missing, the shift cracker or the threaded piece of the shift knob may be cut off. After disassembling the gearbox, it will be necessary to replace defective parts. If there is no gear shift, the gearbox should be disassembled and the worn shift fork replaced. If the cause of the jamming of the gearbox was an open circuit, then it should be disassembled and the chain replaced.
If the operation of the gearbox is accompanied by increased noise in the gearbox, then the reason for this may be a lack of oil in the gearbox device or a mismatch in quality lubricant necessary parameters. It is necessary to choose oils of the appropriate brand, they must have a certain purity. If there are any problems, you will need to change the oil or add it to the gearbox.
The occurrence of noise in the transmission units of the walk-behind tractor can be caused by a weak tightening of the fasteners, so it is necessary to inspect the fasteners by tightening them properly.
The cause of frequent noise is the wear of gears with bearings. This may lead to more serious damage in the gearbox of the walk-behind tractor. It is not difficult to avoid their appearance if you do timely inspection and repair of the walk-behind tractor. It consists in the usual replacement of worn components and parts.
If the transmission units of the walk-behind tractor are heated, the following main causes of this malfunction are distinguished:
- Lack of gear oil in crankcases.
- Bearing wear.
- The oil condition does not meet the required parameters.
There are two reasons for correcting deficiencies:
- replaced bearings;
- adding or changing oil.
To reduce or homemade box gears could last longer, it is necessary to periodically check the oil level in them, for fear of a sharp change in load.
Signs of violations associated with difficulties in switching speeds, spontaneous shutdown, violation of the process of turning on the unit, arise for the following reasons:
- Depreciation of parts.
- Abrasion of shaft splines.
- Incorrect clutch adjustment.
Rolling (wear) of the ends of the engaging gears causes two problems, leading to self-shutdown or incomplete engagement of speeds.
Conclusion
If the factory or home-made box works with any violations, it will be necessary to disassemble it, as well as edit the gear teeth by grinding. With sufficient wear, new parts must be installed. To adjust the axial position of the shafts, additional installation of locking rings is required. In certain cases, worn bearings and rings should be replaced.
The gearbox clutch for the walk-behind tractor should be adjusted in a timely manner, otherwise it will no longer be squeezed out and difficulties may arise when shifting gears. Difficulties in driving a walk-behind tractor often arise for beginners who, due to inexperience, can lower the clutch lever too early when shifting gears.
Additional related articles:
Do-it-yourself gearbox for a walk-behind tractor - a wide scope for creativity
A lot has been said about the benefits of a walk-behind tractor in the subsidiary farm. If funds allow, they buy it. If you want to save money, make your own.

At first glance, this is a complex technical device that can only be made in the factory. In fact, a home-made walk-behind tractor with a gearbox from Ant is quite common in the yards of homegrown farmers.
If you understand the design, and have an elementary set of a locksmith in the house:

- welding machine;
- Bulgarian;
- drilling tool.
then you can build a self-propelled iron horse literally from pasture materials. To do this, you need to understand how the design works.
Motoblock device. Basic structural elements

- Frame or bed. An engine, a system for transmitting torque to the wheels, a suspension and a traction device for attachments are mounted on it;
- Power unit. Its power can be small, from 5 to 10 horsepower. Engines from mopeds, motorcycles, compressors and even chainsaws are used;
- Suspension. Usually primitive. Consists of homemade wheels or ready-made from agricultural machinery. Sometimes automobile or motorcycle ones are used. Can be axial or portal;
- Gearbox for motoblock. One of the most important parts of the design. Designed to reduce the speed of the drive shaft with a simultaneous linear increase in torque. Quite often, a gearbox from a car or scooter is used as a gearbox.

However, the best option would be a homemade gearbox. It does not need to be paired with a power plant, since the calculation is made for specific tasks, and you are not limited to a ready-made technical solution.
How to make a gearbox for a walk-behind tractor with your own hands
First you need to decide on the parameters of the power plant. The technical specifications indicate the number of revolutions of the crankshaft. This is the first value that is needed for calculations. This figure is not constant, with the addition of "gas" the speed increases. Idle speed + 10% is taken as the base value.
For example, turnover idle move your motor + 10% is 600 rpm. The required wheel axle revolutions for a speed of 3 km/h are 200 rpm. Accordingly, your gearbox for a walk-behind tractor must have gear ratio 3:1.
The speed of rotation of the axis is reduced by 3 times, in relation to the speed of the motor shaft. Accordingly, the torque is tripled.
Determine the type of gearbox:

- Gears use the ratio of the number of teeth of the driving and driven gears. They work on the principle of pairs in a gearbox. The shape of the gears does not matter - the teeth can be oblique or straight. A bevel gear is used when an angular gearbox is needed for a walk-behind tractor. It all depends on the location of the engine. If the alignment between the wheels and the motor shaft is ensured, the angle is not needed;

The advantage of this design is that the gearbox is immediately angular. If the shaft from the engine is perpendicular to the axis of the wheels, this is the best solution;

A lot of torque cannot be transmitted - the belts will simply slip.

But the shock load on the power plant is reduced - this design is more gentle on drive shaft motor, smoothing out jerks. Slippage can be eliminated by setting toothed belt. In this case, you will have to find a pair toothed pulleys, for example, from an automotive timing system;
Important! Whatever design you choose, you must remember the following rules:

- No distortion between the leading and driven part;
- Bushings cannot be used, only bearings.
Any gearbox, except for a belt one, needs constant lubrication. Therefore, it must be placed in a box. The tightness of the housing will protect against the ingress of dirt and dust, inevitable during field work. Shafts must be fitted with seals. An example to follow are factory gearboxes from Soviet-made agricultural machinery.
The chain drive is not as sensitive to lubrication, but the chain must be regularly maintained - cleaned and lubricated.
Manufacturing or selection of finished structures
With access to a wide range of accessories: landfill old technology or ownerless property of a repair shop, it is possible to manufacture a gearbox with an accurate selection of the gear ratio.
However, such a complex structural element requires serious metal processing equipment. You can choose the body right size, drill holes for the shafts on the bearings, and assemble the design no worse than the factory one.
However, experience shows that the selection of finished structures with minor modifications is much more effective. As an example, consider a home-made walk-behind tractor based on a motor from an IZH motorcycle.

Used its own gearbox, with the ability to switch gears. The stock gear ratio is not enough, although the small sprocket on the output shaft of the gearbox, complete with a large star from the drive wheel, already provides a good reduction in speed.
On the shaft, installed in the bearing podium, there is another small sprocket, which, with the help of a second chain, transmits torque to the wheels. In turn, a large-diameter star is installed on the drive axle.
The result is a design with a two-stage reduction in speed and solid torque. Using the gearbox from the motorcycle, you can choose the desired speed, with little or no use of the throttle. The engine is almost always running idling which prolongs its life.

No less popular is the use of a ready-made gearbox from the Ant scooter.
It is not necessary to use the entire wheeled platform, it is enough to install your rollers on the bridge. By applying a gearbox from the selected power plant, you will get the optimal ratio of power and speed.
Video: finalization of the Neva walk-behind tractor gearbox.
Motoblock device
The walk-behind tractor consists of the following main components: engine 1, transmission 2, running gear 3 and controls 4.

Motoblock device Ugra NMB-1
Engine and its support systems
The walk-behind tractor drive is classic engine internal combustion with all the systems necessary for its operation. IN lung machines and the middle class, four-stroke gasoline engines are used (see here about the design and operation of a four-stroke engine). Heavy-duty motoblocks are often equipped with diesel engines. In obsolete and some lightweight models, you can sometimes (rather rarely) find a two-stroke gasoline engine.

The device of a four-stroke gasoline engine (Honda) of a walk-behind tractor: 1 - fuel filters, 2 - crankshaft, 3 - air filter, 4 - part of the ignition system, 5 - cylinder, 6 - valve, 7 - crankshaft bearing.
Most motoblock users have to deal with four-stroke gasoline engines with air-cooled. These engines have the following systems to ensure their operation:
- Fuel supply system designed for cooking air-fuel mixture, consisting of fuel tank with tap, fuel hose, carburetor, air filter.
- Lubrication system that provides lubrication of rubbing parts.
- A starting mechanism (starter) designed to spin the crankshaft. Many engines are equipped with an easy start mechanism that reduces the starting force due to the device by camshaft, opening Exhaust valve during the compression stroke and thereby reducing the compression in the cylinder when the crankshaft is untwisted. Heavy walk-behind tractors are sometimes equipped with battery-powered electric starters. Some models have electric and manual start. The latter is used as a backup.
- A cooling system that removes heat from the engine cylinder block by a stream of air pumped by the flywheel impeller when the crankshaft rotates.
- An ignition system that ensures uninterrupted sparking at the spark plug. A rotating flywheel with a magnetic shoe induces emf in the magneto. transformed with electronic circuit into electrical signals applied to the spark plug. As a result, a spark jumps between the contacts of the latter, igniting the air-fuel mixture.

1 - electronic magneto, 2 - screw, 3 - magnetic shoe.

The starting mechanism and ignition system of the Cascade MB6 walk-behind tractor: 1 - starter handle, 2 - fan housing, 3 - protective casing, 4 - cylinder, 5 - cylinder head, 6 - magneto, 7 - flywheel.
- The gas distribution system responsible for the timely entry of the air-fuel mixture into the engine cylinder and the release of exhaust gases. The composition of the gas distribution system includes a silencer designed for the directed release of exhaust gases and noise reduction.
Note that engines are sold with all its systems, and if there is an idea to make a walk-behind tractor with your own hands, then the purchased engine will already have a gas tank, an air filter, a starter, etc. for example here (only it is better to buy through an online store, because in a regular store of this network the price may be higher).
The figure below shows a widely used in walk-behind tractors domestic production engine Honda series GX models GX200 QX4. The power of the unit is 5.5 hp. It has a horizontal crankshaft and a high compression ratio for efficient fuel combustion and low carbon deposits.


Honda engine used in walk-behind tractors

Honda engine used in walk-behind tractors

Honda engine used in walk-behind tractors
Transmission
The transmission is used to transmit torque from the engine to the wheels and change the speed and direction of movement of the walk-behind tractor. It usually consists of several units connected in series with each other: a gearbox, a differential (in some models), a clutch, a gearbox. These elements can be structurally performed as separate units or combined in one housing. The gearbox serves to switch speeds, which can be of different numbers (up to 6 forward and 2 rear), and at the same time is a gearbox.
By their type, transmission units (reducers and gearboxes) can be gear, belt, chain, or various combinations of both.
classical gear transmission. consisting only of cylindrical and bevel gears, it is mainly used on heavy walk-behind tractors and some models of medium machines. As a rule, it has a reverse and several lowering steps.
The figure below shows the gear transmission of the Ugra NMB-1 walk-behind tractor, consisting of cylindrical and bevel gears. The engine is rigidly attached to the gearbox, which in turn is rigidly connected to the bevel gear. The design of the NMB-1 walk-behind tractor does not have chain and belt drives, which, according to its developers, are an unreliable link in transmissions due to the tendency to break, damage and belt slippage.

Motoblock Ugra NMB-1 with gear transmission

The design of the transmission of the motor-block Ugra NMB-1

The scheme of the gearbox of the Ugra NMB-1 motoblock: 1 - Clutch fork, 2 - Retaining ring, 3 - Adjusting ring, 4 - Bearing, 5 - Retaining ring, 6 - Adjusting ring, 7 - Retaining ring, 8 - Cuff, 9 - Retaining ring, 10 - Bearing, 11 - First gear and reversing, 12 - Gear of the second and third gears, 13 - Adjusting ring, 14 - Bearing, 15 - Driven gear shaft, 16 - Driving gear shaft.

Scheme angular gear walk-behind tractor Ugra NMB-1 (N): 1 - Retaining ring, 2 - Adjusting ring, 3 - Bevel gear, 4 - Adjusting rings, 5 - Bearing, 6 - Intermediate gear shaft, 7 - Upper housing, 8 - Output shaft, 9 - Adjusting rings, 10 - Bearing, 11 - Bevel gear, 12 - Retaining ring, 13 - Boot cup, 14 - Boot, 15 - Cuff, 16 - Adjusting rings, 17 - Lower case, 18 - Adjusting gasket, 19 - Bearing , 21 - Cover, 22 - Gear, 23 - Gear, 24 - Shaft.
The torque from the crankshaft is transmitted to the drive shaft 16 (Gearbox Diagram) of the gearbox and is removed from the bevel gear of the driven shaft 15 by the vertical shaft 6 of the angular gearbox (Angular Gear Diagram), which transmits rotation to the hexagonal shaft 8 of the drive wheels. To avoid violation correct operation transmission, it is not recommended to disassemble the walk-behind tractor transmission, which can lead to a misalignment of the gears.
The gearbox by its design is mechanical two-way with 3 gears forward and 1st reverse. The transmission has two power take-off shafts (A) and (B).
Worm and gear transmissions. consisting of two gearboxes - the upper gear and the lower worm gear - are usually used on light walk-behind tractors. Crankshaft engine is vertical. Sometimes machines with a gear-worm transmission are equipped with a centrifugal automatic clutch. A similar device of a walk-behind tractor provides an increased compactness of the unit.
Belt-gear, belt-chain and belt-gear-chain transmissions are quite common in light and medium walk-behind tractors. The engine rotates the shaft of a gear or chain gearbox using a belt drive, which is also a clutch. Gear-chain transmissions are often implemented in one crankcase.
For a belt drive, to change the speed of the walk-behind tractor and take off power, the pulleys can have an additional stream. The advantages of such a transmission include a simpler disassembly and assembly of a walk-behind tractor than in the case of a gear transmission.
The figure below shows the V-belt transmission of the GreenField walk-behind tractor model MB-6.5 (with a belt-gear transmission), which, along with torque transmission and speed reduction, also performs the functions of a clutch and a gearbox (shifting speeds).

Belt drive of the GreenField MB-6.5 walk-behind tractor
The linkage function is implemented using tension roller and a control mechanism consisting of a rod and a system of levers that allow you to change the position of the roller that tightens or loosens the belt and, accordingly, turns on or off the transmission of torque from the engine to the gearbox. Gear shifting is carried out with the help of two-strand pulleys. By rearranging the belt from one stream to another, they get a different speed of the walk-behind tractor.
A similar scheme has been implemented in domestic walk-behind tractor Salute 5, shown in the figure below. The V-belt transmission transmits rotation to the gear reducer of the walk-behind tractor.

V-belt drive motoblock Salyut 5
As a rule, motoblock transmissions have PTO shafts. providing the transmission of torque to the working bodies of the machine. By their type and location in the transmission, power take-off shafts can be independent, located before the clutch and rotating regardless of its state (disengaged or engaged), or dependent, located after the clutch, and synchronous to a certain gear. In one walk-behind tractor there can be several power take-off shafts - different in type and speed of rotation.
The clutch, which is part of the transmission, performs several functions. Transfer of torque from the engine crankshaft to the gearbox (gearbox) shaft, disconnection of the gearbox and engine during gear shifting, ensuring smooth starting of the walk-behind tractor and stopping it without turning off the engine.
Structurally, the clutch can be performed in different ways. As V-belt transmission(see above), tensioning or loosening the belt with the clutch lever leads to the transfer or termination of the transmission of torque from the engine to the gearbox. Or in the form of a single-disk or multi-disk friction dry or wet (oil) clutch, which is more reliable and is used in most models of walk-behind tractors. Some machines use a much rarer conical clutch.
On the Ugra motoblock already considered by Kadvi LLC, a clutch is installed, which is the most traditional in its design - a friction multi-plate clutch with a pressure spring operating in an oil bath. The device of a walk-behind tractor with such a clutch should provide for the presence of a crankcase for the clutch, where gear oil is poured.

Ugra NMB-1 walk-behind tractor clutch scheme: 1 - Motor shaft, 2 - Leading half-coupling, 3 - Driven half-coupling assembly with release bearing, 4 - Belleville spring, 5 - Drive disks, 6 - Driven disks, 7 - Spring thrust ring.

Clutch lever: 1 - Axle, 2 - Fork, 3 - Clutch half, 4 - Lever, 5 - Clutch cable, 6 - Bolt, 7 - Nut, 8 - Washer, 9 - Spring washer, 10 - Sleeve.
The clutch consists of a driving half-coupling 2 (motoblock clutch scheme), a driven half-coupling 3, a belleville spring 4, leading 5 and driven 6 discs, a thrust ring 7. It works as follows. When the clutch lever is released, the Belleville spring compresses the driven and driving discs assembled in the package alternately. Due to the friction between the discs, torque is transferred from the engine to the gearbox. When the clutch lever is depressed, the force is transmitted via a cable to the clutch release lever 4 (Clutch lever). In this case, the clutch fork 2 through the driven half-coupling and release bearings compresses the spring, separating the driven discs from the leading ones and stopping the transmission of torque.
Differential
To improve maneuvering and implementation smooth turns, in the design of some walk-behind tractors (mainly heavy ones), a differential is provided. The purpose of the latter is to ensure the rotation of the left and right wheels at different speeds. Differentials can be with or without wheel locking. Instead of a differential, mechanisms can be used to turn off one wheel while driving.
Chassis
The chassis of the walk-behind tractor is a frame on which the main components and wheels are fixed. Sometimes the frame is missing, and its role is played by the transmission, to which the engine and wheels are attached.
In most walk-behind tractors, the distance between the wheels can be changed, this makes it possible to set the track of different widths. Two main types of wheels are used - conventional pneumatic and weighted metal wheels with wide lugs. Weights can be welded to the wheels or bolted to them. Many designs of metal wheels provide for the fastening of loads of various weights. This allows, if necessary, to increase the weight of the walk-behind tractor to values that provide required grip ground wheels.
Metal wheels can be with a solid rim or made in the form of two or three narrow hoops interconnected by lugs. The former have the disadvantage that earth accumulates between the lugs, preventing good grip ground wheels.
Governing bodies
The controls are a set of mechanisms that provide a change in the direction of movement and speed of the walk-behind tractor. These include: steering wheel, levers and gearshift rods, clutch control levers, supply of "gas", emergency stop of the engine, etc. Since the design of motoblocks, with very rare exceptions, does not provide for a seat for the operator, the motoblock device must provide with one hand.
Some controls ( air damper carburetor, switching on the power take-off shaft, etc.) are located on the corresponding units and assemblies.
Usually on the left steering rod there is a clutch control lever and an emergency engine stop lever, on the right - the “gas” handle, the wheel drive lever and the brake (if any). The design of the steering column of walk-behind tractors provides, as a rule, for adjusting the position of the handles in the horizontal and vertical planes. The figure shows the controls of the SunGarden MF360 walk-behind tractor.

Motoblock SunGarden MF360

Walk-behind tractor controls

Walk-behind tractor controls
When using the content of this site, you need to put active links to this site, visible to users and search robots.
Motoblock device
The device of motoblocks is almost the same, regardless of the brand of motoblock. Motoblock, consists of such units as: engine, chassis, transmission and controls. Below is a diagram of the MTZ-05 walk-behind tractor

Motoblock device (MTZ-05): 1. Magneto 2. Silencer 3. Air cleaner 4. Carburetor 5.22 Rod and control lever throttle valve 6. Gas tank 7.13 Rod and differential lock lever 8. Lever for engaging the power take-off shaft 9.11 Rod and gear shift lever 10. Steering column 12. Gear shift lever 14. Clutch lever 15. Cable 16. trailer shackle 17. Hitch 18. Control column 19. Fuel pump 20. Lever 21. Nut for fixing the vertical installation of the steering column.
Motoblock engine device
As a rule, a classic internal combustion engine is installed on walk-behind tractors. On most walk-behind tractors, a four-stroke gasoline engine is installed, on more heavy models, install diesel engines. There are motoblocks, as a rule, light, low power, where two-stroke engines are installed.

The device of a four-stroke gasoline engine: 1. Forged crankshaft 2. Fuel filters 3. Air filter 4. Electronic ignition 5. Cylinder 6. Valves 7. Support ball bearing.
Petrol single cylinder four stroke engine, consists of the following main constituent parts and systems: crank mechanism, gas distribution mechanism, fuel supply systems, control systems, lubrication systems, air supply and exhaust gas systems, starting systems, ignition systems and cooling systems. This information, will be useful when repairing the engine.
The transmission is designed to transfer the rotational movement from the engine to the wheels and change the direction and speed of movement. The transmission consists of the following components: gearbox, differential, as well as gearboxes and clutches (in some models).
The purpose of the differential is to ensure the rotation of the right and left wheels at different speeds to improve maneuverability.
According to their type, transmission elements (gearboxes and transmissions) can be belt, gear and chain.
Motoblock gearbox device
The gearbox is designed to change the gear ratio and transfer rotation from the gearbox pulley to the wheels. Below is a diagram of the gearbox.

Reducer device: 1. Shaft 2. Bearing cap 3. Gear case 4. Intermediate shaft 5. 6. Sprocket block 7. Intermediate shaft 8. Chain 9. Sprocket block 10. Intermediate shaft 11. Chain 12. Oil drain plug 13. Shift knob 15. Input shaft 16. Input sprocket 17. Chain 18. Nut 19. Chain 20. Chain 21. Deep groove ball bearing.
Gear box device
The gearbox is used to switch speeds, which can be up to 6 forward and up to 2 back.

Gearbox device (UGRA NMB-1N1) 1. Clutch fork 2. Locking ring 3. Adjusting ring 4. Bearing 5. Locking ring 6. Adjusting ring 7. Locking ring 8. Cuff 9. Locking ring. 10 - Bearing, 11 - First speed and reverse gear 12. Second and third speed gear 13. Adjusting ring 14. Bearing 15. Driven gear shaft 16. Driving gear shaft.
The chassis is a frame on which the wheels and the main components of the walk-behind tractor are fixed.
The controls of the walk-behind tractor include gearshift rods, steering column, clutch levers, throttle control, etc.
Homemade 2-speed gearbox for a walk-behind tractor or mini tractor
In order to immediately avoid questions like “why?” and “why?”9 I will explain the scope. Such a gearbox can be installed (mostly) on a home-made or, if desired, on a factory walk-behind tractor or minitractor or their trailer equipment. Especially if you want to change the direction of rotation before and after this checkpoint. It can be used as a gearbox for shifting down and up gears or as a reverse gear (with certain modifications). Operating principle 2x speed gearbox:
And for switching between high / low gears with a change in the rotation of the shafts, and without changing the rotation of the shafts when using a chain drive instead of gears.
B reverse gear.
I think it’s clear where the chain and where the gear transmission is.
The purpose of the topic: To convey to those interested in the principle of action, the possibilities of application, possible + and -, well, and bring up the creation of my home-made checkpoint for discussion
Well, I immediately submit for discussion the creation of my checkpoint. I will use it on a home-made walk-behind tractor, firstly to change rotation, and secondly to switch between upshifts and downshifts. After a 4-speed gearbox, according to the plan, I had to have a chain gearbox with gear ratio 2.6. But after a series of calculations, it became clear that the speed with this gearbox would be very low (in 1st gear 1500 rpm 900 m/h and in 4th gear at 3500 rpm 5.8 km/h) and pulling force decent. This is certainly good, but if you need to go somewhere for something easy (let's say 5 kilometers from home), then you simply get bored and burn decent fuel. If you remove the intermediate gearbox, then max. the speed increases to 15 km / h, but the traction decreases and, moreover, plowing or milling becomes impossible for a number of reasons. Then the idea of creating a similar gearbox was born that would help maintain traction and at the same time help drive faster. The number of gears increases to 8 forward (4 upshifts and 4 downshifts) instead of 4 and up to 2 reverse gears instead of 1st.
The idea is painfully simple. Those who have ever dismantled the ant's gearbox will immediately understand what's what, but for the rest I will sign everything in the process.
So, let's begin. Let's start as usual with input shaft. It will have to be sharpened by yourself. It has not yet been machined and I cannot show the input shaft assembly, I plan to do this one of these days and will post it as soon as I do it. Here is the drawing:
No. 1 - The landing site of the bearing, unfortunately, there is no number on mine, but its dimensions are 20x52x15. This is the "rear9 bearing secondary shaft Gearbox motorcycle Ural. You can also use 20x52x20 but in this case you should increase seats by 5mm. In the gearbox there will be 2 such bearings (one each on the primary and on the secondary shaft), both will be on the same side.
No. 2 landing gear of the 1st (reduced) gear. As a gear, a gear was taken from the IZH gearbox (like with IZH). I don't know what show she's from. She has 19 teeth, the outer diameter of the teeth is 52.3 mm and she looks like this:
the gear is cut along the red line. The gear should turn with the shaft. It can also be cut to the teeth on the other side and simply welded to the shaft. But I plan to make the input shaft completely collapsible (I don’t know how yet, I’ll turn the shaft there it will be visible) with the possibility of replacing all the elements of the shaft and I won’t cut it.
No. 3 On the right, on the edge, right next to seat No. 4, the drive gear of the 2nd (high) gear will sit. Between these gears, I will have something welded to the shaft that will hook both gears and make them spin with the shaft. There will be one of these gears:
Together, where they converge on the shaft, they differ slightly in width. For the one that is slightly smaller in width, I will make the washer 2mm thick. These will be the driving and driven gears of the 2nd gear and, if desired, they can be swapped on the shafts. Obi with a Ural motorcycle gearbox (I don’t know exactly from which gears I had it disassembled, you have to search the Internet and look at the gearbox device). The smaller gear has 26 teeth and a tooth diameter of 70.6mm. The large one has 29 teeth and a tooth diameter of 78.7mm. I indicate the diameters because this gear has a clone in the gearbox of the Ural motorcycle. It fits the count. teeth but has a slightly larger diameter. If you put this clone instead of this gear, then between the gears in 1st gear there will be big gap and the teeth can break under load. So even if you do not confuse these gears, there will still be a gap between the gears of the 1st gear, but it will be only 0.75mm, I think this is not critical.
No. 4 A bearing with dimensions of 25x52x15 will sit here and a removable place for the gland to slide will sit right next to it. This place can be taken from the checkpoint of the Ural motorcycle (by the way, the bearing is also there, they also sit nearby). It is located on the input shaft on the clutch side. I used a slightly different place to slide the gland. It looks like this:
Strictly speaking, this is not for the gland at all. This is the place to slip roller bearing from the crankshaft of an ant engine. It is slightly different in width and has a slightly larger diameter, but it will fit perfectly under the gland. I will have oil seals with dimensions 49.4x33.4x8.5
In the place indicated by the arrow, modify the shaft for yourself, depending on how and with what type of transmission you plan to apply rotation to the shaft.
So the primary shaft is over. Let's move on to the secondary.
The secondary shaft is taken ready; this is the secondary shaft with the gearbox of the Ural motorcycle. It looks like this (it's already shortened):
and here is a drawing of its dimensions
No. 1 bearing seat 20x52x15 or 20x52x20 (if desired) An oil seal will stand next to this bearing. This part of the shaft will turn for me cardan transmission. I use a place for sliding the stuffing box from a cardan drive.
No. 2 is the installation location of the driven gear of the 1st gear (it seems that at the Ural checkpoint this is also the gear of the 1st gear). The gear has 36 teeth and a tooth diameter of 94.9mm. It looks like this:
The gear rotates freely on the shaft, there is a brass bushing inside to reduce wear, because in the Ural gearbox, the shaft rotation speed in 4th gear relative to the rotation speed of this gear is very large. The gear has splines that are part of the gearshift mechanism.
No. 3, the rest of the gear shift mechanism sits here. The switching mechanism consists of 2 parts. The photo shows that the shaft has large slots, this little thing sits on these slots (I don’t remember its name):
As you can see in the photo, there are large slots inside as well as on the shaft. This part is mounted on the shaft and rotates with it. On outside there are also grooves where a ring is inserted that has slots inside and moves along this thing with a fork. The fork at one time moves the ring with the help of a groove on the outside of the ring.
Further, behind this mechanism, the driven gear of the 2nd gear is installed (one of those that was laid out earlier, any) which, like the gear of the 1st gear, has splines. The gears are splined to each other. Both freely rotate on the shaft. Assembly mechanism:
The fork moves the ring in one direction and with the help of the ring and splines on the gear, the ring and that thing, the large gear comes into engagement with the middle part (I don’t remember how the hell it is with that thing) which in turn spins along with the shaft. Thus, the gear begins to turn the shaft and the 2nd gear gear rotates freely on the shaft. When the ring is moved to the other side, the 2nd gear begins to rotate with the shaft, and the 1st gear rotates freely on the shaft.
Gearshift Mechanism Assembly:
I think everything is clear with the switching mechanism.
No. 4 place for bearing 25x52x15. The shaft has a diameter of 26mm and the place for the bearing needs to be somehow grinded off by 0.9mm. But I’m not sure whether it will be possible to do this on a stonka, whether the shaft will crumble and whether the cutter will mow me. Well, I'll think of something anyway.
And finally, a drawing of the bearing seats:
The bearing seats are made 17mm, which is 2mm more than the bearings themselves. I will adjust this size after turning the seats themselves. The seats for the oil seals are also made 15mm while the oil seals are 8.5mm. This is done so that it can already be adjusted in place where exactly the gland will go in the place for sliding. After that, these places will also be adjusted.
I plan to make the crankcase from sheet metal 4mm thick, as it should be under mulso.
Well, that's all for now. I will make drawings of the crankcase parts after I have machined the input shaft and seats and put it here.
I have made two mini tractors, so there is no experience. both with two checkpoints. In life, in my operating conditions, really at the first checkpoint, I use the first two gears. But I don’t have transport hauls, if you use the mini as a transporter, then the third and fourth gear may be needed. But only on asphalt, on an unpaved road, without springs and with a rocking chair in front, you won’t go fast .. That’s why I’m thinking of making a mini . with gearbox. instead of the first checkpoint.
Well, yes, this would be ideal. 2 checkpoints is too much. even if they are 4-speed, then 16 gears are obtained. you have to switch.
Max wrote.
without springs and with a rocking chair in front, you won’t go fast.
Therefore, I am going to make a cart on shock absorbers. I wanted to do something on the MB, but I didn’t. time will tell, if needed, it will not take long to redo it.
Well. Today I machined the main shaft. Although due to my inexperience and the rather lax state of the machine, I spent 4 hours with the shaft, but the darkening turned out to be pretty good.
I machined the shaft seats with a diameter of 20.1mm according to the drawing. As planned, the bearings did not fit. After cutting off unnecessary parts of the workpiece, I clamped the shaft into the machine and fitted the seats directly on the bearings with a wide file. On the left side, the size is 19.98mm, the bearing comes in with light taps on the shaft with a hammer and sits tightly. WITH right side 25.05mm, you have to tap a little more comfortably, but not too much. I think if you put on and remove the bearing a couple of times, everything will rub in and it will be the norm.
Seats that will be cooked to the crankcase hastily machined. The beginning of the bearings by hand with a little effort enters them. Then just attach. I think I got into right size, if I finish it with an engraving. Tomorrow I will ban unnecessary bearings in them and cut them to size right on the bearings.
Attention, only TODAY!
One of the most important elements of the walk-behind tractor is the drive. If you need to purchase a gearbox for a walk-behind tractor, then you should know that the service life of the entire unit will depend on its reliability. The gearbox for a walk-behind tractor, (made by oneself), is designed to convert and transmit the torque that it receives from mechanical gears and makes agricultural machinery work.
How to make a gearbox for a walk-behind tractor with your own hands
There are several differences between the worm and chain gearboxes for a walk-behind tractor important characteristics: gear ratio, efficiency, number of shafts and gears, angular speeds and power.
What are the gearboxes for a walk-behind tractor
Non-collapsible gearboxes are usually installed on cheap walk-behind tractors. The design of such a unit is not particularly reliable. It also has a short lifespan. In addition, it is impossible to carry out repairs or disassembly-assembly. In the manufacture of such units, low-quality metal and non-sleeved parts are used. In order to understand why it is impossible to use the gearbox for a long time, you need to familiarize yourself with its diagram.
It is customary to install collapsible gearboxes on expensive walk-behind tractors. Thanks to this, it is possible to disassemble the walk-behind tractor gearbox and carry out Maintenance. They repair the gearbox of the walk-behind tractor to increase its service life, if high-quality spare parts are used when replacing faulty elements.

IN without fail it is necessary to regularly diagnose the gearbox in order to repair the necessary unit in time. Regular lubrication of the gearbox should also be carried out, which will allow the unit to be used much longer.
Most often, a gearbox for a walk-behind tractor is used so that a high angular velocity is converted into a low one. On input shaft noted high speed, and the output shaft has low speed.
To avoid unexpected breakdowns, it is necessary to carry out regular maintenance, which will allow you to work successfully on an agricultural machine. If the change in angular velocity occurs in steps, the gearbox is called a gearbox, but if the change occurs steplessly, it is called a variator.
Homemade angular gearbox for walk-behind tractor
You can make a walk-behind tractor yourself. To do this, it will be necessary to calculate the rated power (Pn); Pn \u003d Pe (hp) xFS, as a result of which the correct type of angle is determined for the bevel gear. Torque and RPM are also calculated.

You also need to determine the operating conditions of a home-made gearbox for a walk-behind tractor, which includes: radial and axial load shaft ends, minimum and maximum temperatures, environmental conditions, intermittent or non-intermittent operating cycle, type of lubricant.
After defining technical parameters, you can start assembling the angular gearbox.
To do this, it is necessary for the angle gearbox to select a housing.
For example, you can use the factory one, from the Ural or Dnepr motorcycle. Then, based on the diameter of the gearbox housing, we make the gear shaft bearing housing from steel. Here we use the appropriate size drill and caliper. Then, in accordance with the intended dimensions, we select the gear shaft bearings (2 pcs).

On reverse side reducer we install a steel flange. It will have a steel washer and a flanged bearing inside. Using several screws, we fasten the steel flange to the generator housing. Before that, we select the driven gear shaft, steel key and drive gear. All nodes are connected to the transmission mechanism and the shaft of the rotary generator. The V-belt pulley is located on the transmission mechanism and is attached to the driven gear shaft with a nut and spring washer.
To assemble a homemade angle gearbox, you will need the following tools: a caliper and a ruler, a straight and Phillips screwdriver, metal drills, files and metal files, wire cutters and pliers, rubber gaskets, a vice and a hammer.
Angle gearbox for walk-behind tractor
The angle gearbox is widely used in motorcycle technology: in automotive industry, modified cultivators, industry. When installing an angular reduction gear on walk-behind tractors, with heavy loads achieve more effective work.

This type of gearbox is usually used to connect the engine to a transmission designed for a chain. The angular gearbox for a walk-behind tractor is made from existing samples, similar ones are installed on Dnepr or Ural motorcycles. Then you will need to modify the gearbox.
The main elements of the angular gearbox
The components of the bevel gear are: generator housing, flange bearing, rotary shaft, steel washer, steel flange, bevel drive gear, bevel gear housing, steel key, gear shaft bearings (2 pcs), driven gear shaft, bearing steel housing pinion shaft, pulley mount, V-belt pulley, flange mount.
Motoblocks with a gear reducer and a reduction gear for a motoblock
A reduction gear for a walk-behind tractor, in common people a creeper, is installed on a modern diesel and gasoline walk-behind tractors air cooled. Thanks to this, the user can use the walk-behind tractor on especially heavy soils for plowing and digging potatoes. The reduction gear helps with wheel slip when there is not enough own power.

Motoblocks with gear reducer
To understand what a gear reducer is, consider the structure of the transmission. It transmits torque from the engine to the wheels, and changes the speed and direction of the walk-behind tractor. The transmission consists of a gearbox, differential, gearbox and clutch. Transmission units are gear, chain, belt, or a combination of one or the other.
Gear transmission consists of bevel and cylindrical gears (gear reducer). It is used on some models of machines and heavy walk-behind tractors. The figure shows the gear transmission of the Ugra NMB-1 walk-behind tractor, which uses a gear reducer.
Reverse gear for walk-behind tractor
In the reverse gear, reversing is carried out according to the following scheme: between the opposite bevel gears, which sit freely on the drive shaft, there is a clutch.

She is in extreme positions clings to the splines on these gears. Therefore, when the clutch engages, the direction of rotation of the gear changes. The gears must be of the helical type. The clutch drive mechanism is a traditional fork or cam.

Related Posts:
 How to make a homemade walk-behind tractor with a ZID engine, video and photo instructions
How to make a homemade walk-behind tractor with a ZID engine, video and photo instructions  We make a homemade walk-behind tractor with an engine from a scooter, photos and drawings
We make a homemade walk-behind tractor with an engine from a scooter, photos and drawings  We make a homemade electric walk-behind tractor
We make a homemade electric walk-behind tractor  Wheels for a walk-behind tractor, how to choose and how to do it yourself
Wheels for a walk-behind tractor, how to choose and how to do it yourself