Personnel services occupy one of the leading places in the management apparatus of state organizations and private firms.
The structure and staff of the personnel service enterprises (organizations) are developed on the basis of typical norms of time for staffing and accounting work.
Regulations which regulates the activities of the personnel service, is developed on the basis of model provision, which is approved by the highest authorities (relevant ministry or department).
The workplace of each employee of the personnel service should be organized in such a way that the mental and physical efforts of the specialist are directed to the performance of his functional duties without any obstacles. The optimal size of the premises of the personnel service in an enterprise with up to 2.5 thousand employees is approximately 150 square meters. meters.
In the office of an employee of the personnel service, there must be a desktop, an armchair, office equipment (computer, computer equipment, telephone), cabinets and shelves for storing documents.
In the structure of the personnel service (personnel department, personnel department), depending on the number of employees, different sectors, bureaus, groups (social security, youth work, innovators, etc.) can be created, or these functions are assigned to individual performers. The personnel service, along with the head and inspectors for personnel work, may include training engineers, lawyers, sociologists, psychologists, and physiologists.
The normative number of employees of the personnel service (H) can be determined by the formula:
Where 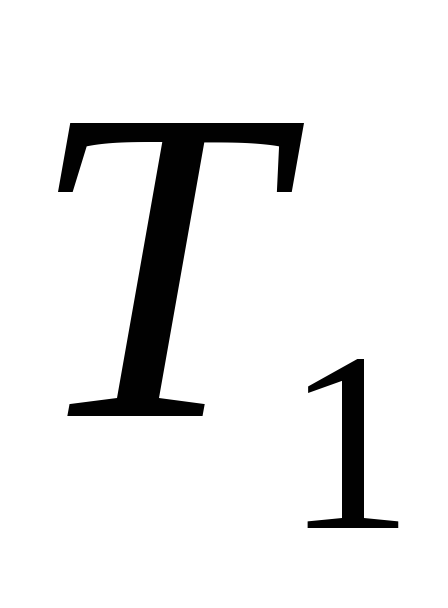 total labor intensity of work, which is calculated according to standard standards for a year (quarter), hours;
total labor intensity of work, which is calculated according to standard standards for a year (quarter), hours;
 coefficient that takes into account the time spent on performing work that is not listed in the normative part of standard norms (should not exceed 25% of the labor intensity of normalized work);
coefficient that takes into account the time spent on performing work that is not listed in the normative part of standard norms (should not exceed 25% of the labor intensity of normalized work);
 useful working time fund of one employee per year, hours.
useful working time fund of one employee per year, hours.
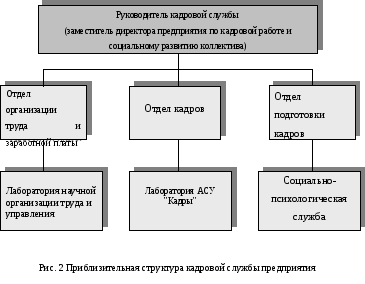
The approximate structure of the personnel service of the enterprise is shown in fig. 2.
In practice, it is often impossible to determine a permanent "unified" type of head of the personnel service. Its status depends both on the specifics of production and on the attitude of the owner (chief executive) to the role and importance of personnel work in the activities of the enterprise.
For example, in small and medium-sized enterprises, managers, as a rule, personally replace personnel departments, focusing on "everyday dialogue" with the staff. In large enterprises, on the contrary, there is a wide range of official positions that are occupied by representatives of personnel services: from the head of the department (department) of personnel to the deputy CEO enterprises (companies).
 The activities of personnel officers involved in the recruitment and accounting of personnel are regulated official instructions. Job descriptions are developed in accordance with the qualification directories of positions and are approved by the head of the enterprise or structural unit.
The activities of personnel officers involved in the recruitment and accounting of personnel are regulated official instructions. Job descriptions are developed in accordance with the qualification directories of positions and are approved by the head of the enterprise or structural unit.
In cases of large volumes of work, certain types of work may be assigned to personnel officers - processing resumes and conducting interviews, organizing psychological testing, getting acquainted with the history of the development of the enterprise, obtaining pensions, etc. When distributing work (functional duties) between performers, it is necessary take into account their qualifications, work experience in the specialty, personal and business qualities.
The implementation of the personnel policy provides for the interaction of the personnel service with other structural divisions of the enterprise. For example, operational personnel management at an enterprise is carried out by HR managers (representatives of the personnel department, personnel department) and line managers (shop foreman, shift supervisor, site manager). At the same time, the personnel manager is the main implementer of the personnel policy of the enterprise as a whole, and line managers are directly responsible for their subordinates, control the state of production, and draw up primary documentation for top management. The primary information of line managers is analyzed by personnel officers and makes it possible to draw generalized conclusions about the enterprise regarding the level of fulfillment of production standards, production volumes, labor discipline (the number of delays, absenteeism), the level of staff turnover, the level of professional and qualification compliance of employees with their positions, etc. .
The main functions of the representatives of the personnel service in the field of strategic and operational personnel management at the enterprise include:
Assistance to management in the implementation of personnel policy regarding hiring, relocation, dismissal, reduction of staff.
Active participation in the development of the organizational and management structure of the enterprise.
Assistance to line and functional managers in organizing educational work with staff in order to increase labor productivity, responsibility for the quality of work, ensure a normal socio-psychological climate in the team.
The implementation of these functions provides for the ongoing work of personnel services to improve the selection methodology, conduct interviews, competitive selection, determine the level of qualifications and professional suitability of candidates for vacant positions, conduct personnel certification, improve the professional level through training or internships for employees, develop forms and systems of material support , programs of social development of the team.
The implementation of effective activities of personnel services is impossible without constant cooperation with top management, the trade union committee, and other structural divisions of the enterprise, namely the financial and economic department, accounting, legal adviser, psychologist, social development service and others.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Employment agencies on their own carry out a preliminary selection of professionally trained employees, make up psychological characteristics for them, so that the personnel department of the organization knows enough about the applicants even before they meet in person, reserving the right to choose.
Recently, acquaintance with a candidate often begins in absentia - according to his resume. A resume is a self-characteristic that reflects, in addition to personal data, the purpose of the appeal, the desired position and conditions of the candidate; experience; Additional information: knowledge of languages, availability driving license, the ability to go on business trips, etc.
If the candidate is suitable according to the summary, he is assigned a meeting. After the interview, the applicant fills out a questionnaire, sometimes passes a professional test. If the applicant's professional and personal qualities match, a meeting with the immediate supervisor is scheduled for final decision the question of the possibility of accepting a candidate for a vacant position.
Formation of personnel service
Since the personnel department is designed to provide the human component of the company's work, which serves as an important guarantee of the effectiveness of the organization's activities, among its most significant tasks can be identified:
* help the company achieve its goals;
* effective use of skills and capabilities of employees;
* providing the company with highly qualified and interested employees;
* the desire for the most complete satisfaction of employees with their work, for their most complete self-expression;
* development and maintenance on high level the quality of life that makes working for that firm desirable;
* communication of personnel management with all employees;
* help in maintaining a good moral climate;
* traffic management for the mutual benefit of individuals, groups of enterprises, society.
There are two types of personnel management structures in an organization.
Staff structure - specialists of personnel management departments involved in the development of principles for working with the organization's personnel, specific programs and organization of personnel events (HR managers).
Linear structure - managers-practitioners who implement specific functions of working with personnel in the course of performing their own managerial functions (line managers).
In order to be able to implement various areas of personnel work at the level of specific departments, personnel management structures create a branched network that penetrates various levels of the organization.
However, for a newly created organization, all this “splendor” of a wide variety of structures and divisions is not yet available.
Therefore, when designing a personnel management structure, first of all, it is necessary to take into account:
1. The level at which it is supposed to implement personnel management:
* or it will become the subject of care and accounting at the highest corporate level and we can talk about corporate personnel management;
* either this will be made only an obligation for the middle level, and then we can talk about the organization of work with personnel, which will be implemented by the head of the personnel department together with line managers;
* either in the organization we will talk about the executive level of personnel management, which, as a rule, is expressed either in personnel work (documenting labor relations), or in solving individual problems (conflict resolution, recruitment), and then we can talk about the level of performers - employees of personnel departments (as a rule, the personnel department in the traditional view).
2. The staff of the personnel management service. Even in the largest corporations, no more than 150 people work directly in personnel management services. On average, there is one specialist for every 200 employees.
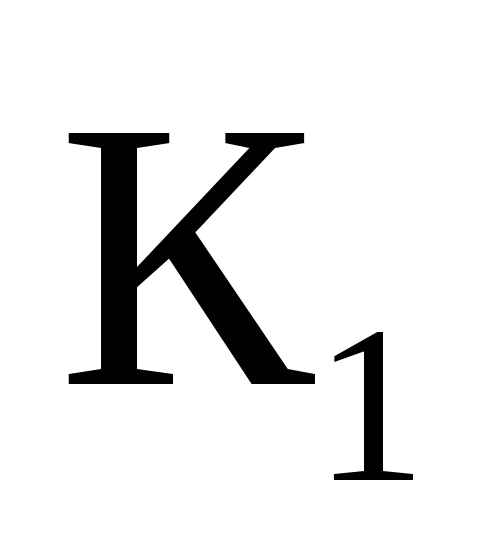
More precisely, the number of employees H required to perform recruitment and accounting work can be calculated using the following formula:
H \u003d T1 x K1: Fp
where T1 is the total labor intensity of work calculated according to standard norms for the year (quarter);
K1 - the number of personnel;
FP - wage fund.
It should be borne in mind that there are also national norms for calculating the ratio of the number of personnel officers and personnel. So, in Russia there are 50-100 people per employee of the personnel service, in Germany - 130-150, in France - 130, in the USA - 100, in Japan - 40 people.
3. The main tasks solved by the personnel management service. When characterizing the overall content of the activities of personnel management services, the following main tasks are distinguished:
* solving staff problems (recruitment, selection, orientation, evaluation, discipline) - 33%,
* compensation and benefits -- 28.5%,
* training, advanced training -- 1%,
* labor relations - 10%.
The structure of the personnel service
In small companies (up to 100 people), two personnel officers are enough; in medium-sized organizations (up to 500 people), it is advisable to create a personnel department of three or four personnel specialists, more large companies(over 1500 people) from seven to ten employees of the personnel service. The order of organization and functioning of the personnel body cannot be considered in isolation from its organizational structure and numerical strength. The latter are determined based on the content of the tasks of personnel work, the organizational and financial capabilities of the enterprise, and are regulated by the staffing table of the personnel service, which is approved by the director of the enterprise.
But, first of all, it is necessary to understand the content of the concepts of "organizational structure" and "strong strength".
The organizational structure of the personnel department means its main and auxiliary divisions (other internal structural units). As a rule, these divisions concentrate their work on independent areas of personnel work and closely interact with each other in the course of daily activities.
The numerical composition of the personnel department is characterized by the total number of employees of this unit, as well as quantitative ratio their main categories - managers, specialists and performers (both as part of the personnel department as a whole, and as part of its internal structural units). Woz- Under the internal structural unit (in the range of sources - the "basic structural unit") should be understood as a mini-division as part of the main structural unit (group, sector, etc.). The number of such mini-divisions usually does not exceed 2-5 specialist workers, one of whom also performs administrative functions in combination, being the immediate supervisor for the rest of the workers. The presence of mini-divisions in the structure of the personnel body is most typical for enterprises with a staff of 500 to 1000 people.
The head of the personnel department of the enterprise and manages its work is the head - as a rule, the head of the personnel department (NOC).
All employees of the personnel department, including the management staff (deputies and assistants of the head), specialists and performers, are subordinate officials in relation to the head, who, in turn, reports directly to the head of the enterprise (his first deputy or his deputy for personnel).
If the personnel department has several divisions, then each of them, in turn, is headed by a chief (except for mini-divisions). IN necessary cases the staff of the personnel department may include the positions of deputy chiefs (on general issues, in the most important areas of personnel work), as well as the positions of assistant chiefs. A winning managerial move is to combine the positions of heads of departments of the personnel department with the positions of deputy heads of the personnel department - thanks to this, funds are saved, and the material interest of workers occupying combined positions is enhanced.
As a rule, most often the personnel department is a structural unit within the personnel service.
The organizational structure of the personnel department is determined, first of all, by the number of employees of the enterprise, as well as the nature (volume and complexity) of the tasks of personnel work.
The main factors influencing the choice of the organizational structure of the personnel body of the enterprise are presented in the table. In view of the above, the organizational structure of the personnel department of an enterprise can be built in accordance with one of three typical options.
Human Resources Management
Human Resources is a service that manages personnel. Provides the enterprise with employees, recruits, selects and selects applicants, adapts, certifies and evaluates, motivates the personnel working at the enterprise, sometimes deals with issues of corporate culture. In general, everything related to personnel management issues.
It can be distinguished that personnel services are internal and external:
* The personnel service, as a personnel department at a large enterprise, existing in the state of this enterprise, as its department, is an internal personnel service (existing within the enterprise).
* Human Resources, as a separate service dealing with human resources outside of any particular enterprise, and working for money, performing the functions of the personnel department in several different enterprises, this is an external personnel service (involved from outside the enterprise).
But in any case, the personnel service exists to achieve the same goals, which can be divided into three points (each of these points in the personnel service is performed by different subsections, or different specialists):
1. Actually personnel management. The purpose of this subsection of the personnel service is to provide the enterprise with personnel in the quantities it needs and the quality it needs. As well as the assessment and motivation of staff.
2. Personnel records management or personnel department. The purpose of this subsection of the personnel service is to ensure the legally correct execution of all documentation relating to personnel, as well as all reporting to government agencies.
3. Corporate culture or hotel PR. The purpose of this subsection of the personnel service is to create, implement and maintain a positive corporate culture and image of the enterprise as an employer.
Office work in the personnel department
Personnel records management is a branch of activity that documents labor relations, fixes information about the availability and movement of personnel, as a result of which personnel procedures acquire documenting.
Almost any personnel document has a legal (commercial) value. With the help of personnel documents used as written evidence, the employer can prove his position in court. For example, in order to confirm tax benefits on income and property tax, an organization must submit a staffing table, payroll sheets, personnel orders, copies of work books, a time sheet and other documents.
In practice, tax inspectors allow that if the staffing table provides for the position of a lawyer or marketer, then the organization can no longer take into account the costs of paying for the services of third-party lawyers or marketers when taxing. However, arbitration practice confirms that in order to take into account expenses when calculating profit, it is sufficient that the services are provided as part of production or commercial activities, are aimed at generating income and are documented (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, detailed job descriptions, employment contracts and staff lists as written evidence in litigation establish the operational necessity of the organization's expenses for business trips and expenses for training and retraining of personnel.
Documenting labor relations, the vast majority of personnel documents contain very important information.
Therefore, the attitude to work with such documents should be extremely serious. The correctness of filling out personnel documents depends on the confirmation of certain legal facts on the basis of which certain employee rights arise. This may make it difficult for an employee to obtain early appointment labor pension, in particular for work with harmful and difficult working conditions, however, any mistake or inaccuracy in the name of the position may lead to the fact that the period of work in a "harmful" position will not be counted as a benefit and the employee will not have the right to an early retirement pension .
Particular attention should be paid to the procedure for maintaining work books, which, in accordance with Article 66 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, are the main documents for calculating the work and insurance experience of an employee.
In general, the provision of social, pension, and other guarantees provided by Russian legislation to employees may depend on documenting labor relations.
Laws, regulations, instructions and other documents containing labor law norms are necessary for professional work personnel specialist.
Therefore, the first step in creating a personnel service is the formation of a sufficient base of regulatory documents.
Documents that should be at hand every day with a personnel officer can be divided into two independent groups:
The first group includes legislative and by-laws containing labor law norms and labor protection norms. These documents are mandatory. The second group includes methodological documents on managerial work and personnel records management. They are advisory in nature. The documents contain recommendations on how best to draw up personnel papers, how it is more convenient to organize work with them. At the same time, the personnel officer has the right to independently decide whether to adhere to these recommendations or act in accordance with corporate standards.
In the block "Documents on labor law and labor protection" five normative legal acts can be noted:
The first is the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This is the basic law that should guide the work of a personnel specialist in any organization. The norms of the Labor Code regulate the procedure for hiring and dismissal of employees, the organization of their working time and rest time, the conditions for payment wages providing employees with various benefits and compensations.
The second is the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of July 27, 2006 No. 149-FZ "On Information, Information Technologies and Information Protection". Based on this law, all the work of the personnel service with the personal data of employees is built. For example, the question of how will be processed and where will be stored the information received from the employee when he enters the job is being decided.
The third is Law of the Russian Federation of July 29, 2004 No. 98-FZ "On Trade Secrets". It establishes a list of information that may constitute a trade secret of the organization, a list of employees who have access to it, a procedure for familiarizing with secret data, and responsibility for the dissemination of confidential information.
The fourth is the Law of the Russian Federation of July 17, 1999 No. 181-FZ "On the Fundamentals of Labor Protection in the Russian Federation". The provisions of this document allow you to competently build a system of labor protection in the organization. And this is very important. Because healthy and safe conditions work is one of the main conditions that the employer guarantees by concluding an employment contract with employees. If a violation of the rules of labor protection and safety is revealed, the labor inspector brings the guilty officials to administrative responsibility.
Fifth - Law of the Russian Federation of August 8, 2001 No. 134-FZ "On the protection of the rights legal entities And individual entrepreneurs when conducting state control (supervision)". The law gives an idea of the rights and obligations of the employer when conducting various inspection checks in the organization. For example, the law refers to the documents that the employer has the right to demand from the inspector when he appears in the organization, the right of the representative of the company personally be present during the inspection, on how the organization can appeal the unsatisfactory results of the inspection.
Another group of regulations required in the work of the personnel service includes methodological materials on the organization of managerial work and on working with personnel documents.
Firstly, it is GOST R 6.30-2003 "Unified Documentation Systems.
Unified system of organizational and administrative documentation. Requirements for paperwork". This state standard defines a list of details that must be present on a document issued by an organization, the order in which they are located, and requirements for letterheads.
For example, the standard dictates the rules for the location of the State Emblem, the emblem of the organization and its trademark. Sets in which case the abbreviated name of the organization is written in the title of the document, and in which it is not, and what elements it consists of registration number order.
The standard applies to all organizational and administrative documents of the company: resolutions, orders, orders, protocols, acts, letters. All of the above documents are handled by personnel officers.
Secondly, this is the List of standard management documents generated in the activities of organizations, indicating the periods of storage, approved by the Federal Archives on October 6, 2000. This normative act provides an exhaustive list of internal documents, depending on the legal significance, regulates the procedure and terms of their storage. How long should be kept, for example, the staffing table, the regulation on bonuses, the time sheet, job descriptions and other documents, the personnel worker will learn from this departmental document.
Thirdly, these are unified forms of primary accounting documentation on the accounting of labor and its payment. Forms of orders for hiring, dismissal, transfer, assignment on a business trip, promotion, as well as forms of personal cards of employees and some other documents are included in the album approved by the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1.
Moreover, the maintenance of these unified forms, in accordance with clause 2 of the said resolution, is mandatory for all organizations operating in the territory of the Russian Federation, regardless of the form of ownership.
Fourthly, this is the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225. "On work books" and the Decree of the Ministry of Labor of Russia of October 10, 2003 No. 69 "On approval of the Instructions for filling out work books." These documents will be needed by the personnel officer when working with work books of employees. The recommendations contained in these documents will help the HR officer correctly, without errors, fill out the employee's work book, if necessary, make appropriate changes to it or issue a duplicate instead of a damaged or lost document.
Fifth, these are intersectoral aggregated time standards for recruitment and accounting of personnel and intersectoral aggregated time standards for work on documentary support of management, approved by the Decree of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of November 25, 1994 No. 72. These documents can also be included in the list necessary tools personnel officer. With their help, you can calculate the number of employees of the personnel service, as well as determine the amount of time required for each of them to perform their job duties. It is necessary to follow the recommendations contained in the regulatory and methodological documents, although they are not mandatory. The fact is that in most cases they simplify the work with documents. In addition, the labor inspectorate attaches great importance to these instructions and, if they are not followed, can fine the organization.
It is important to know which documents are mandatory for the company, which become such only under certain conditions, and which papers can be omitted, as they are advisory in nature. This will allow you to be well prepared for the meeting with labor inspectors.
When creating documents, HR specialists need to be guided in their activities by the following:
1. Type of internal documents, the procedure for their development, approval, etc. the one that is convenient for this organization is used;
2. The type of external documents must obey general rules giving these documents legal force;
3. Documents should be stored in the organization, taking into account the requirements of the archival service.
Tasks of the personnel service
1. Planning and accounting of personnel. One of the main tasks of personnel services is the development of a plan for the organization's needs for personnel. Below we will dwell on the problems of personnel planning in more detail. The tasks of personnel services also include accounting for those who have come to work, up to retirement, accounting for official movements, vacations, illnesses, certification results, etc.
2. Search for personnel. With the expansion of the personnel of the organization, personnel services search for specialists to fill vacancies. For the search to be effective, a good knowledge of the labor market is necessary. A timely and effective solution to the problem of personnel search is the creation of a reserve for the most "critical" positions and jobs.
3. Personnel selection. In order for vacancies at the enterprise to be filled by employees who really meet the requirements set by the enterprise, special work is needed to select personnel: conducting interviews, testing, assessing personnel for professional and personal qualities. If there are several applicants for one workplace, it is necessary to select the most suitable among them. In some cases, the problem can be solved by selecting a candidate for a vacant position from a pre-formed personnel reserve.
4. Determination of salary and benefits. The productive work of the personnel at the enterprise largely depends on the policy pursued by the management of the enterprise to motivate and stimulate employees. Of great importance is the formation of a wage structure that allows taking into account the real contribution of the employee to manufacturing process, to ensure the effective functioning of the enterprise. Specially established monetary bonuses and benefits for good quality work contributes to the orientation of employees to achieve the goals of the enterprise.
5. Professional adaptation. Among the tasks facing the personnel service of the enterprise, not the last place is occupied by the promotion of a favorable working environment, a comfortable workplace, a benevolent psychological climate in the team. Successful adaptation (and hence high labor productivity in the future) of newly hired employees to new working conditions and the team largely depends on the quality of work in this important area of the enterprise's personnel service.
6. Training and promotion of personnel. In connection with the tightening of competition, the increase in the requirements for the quality of products and services, with the increase in the complexity of the nature of the work, the complexity of the technologies for the production of products or services, the requirements for the level of vocational training workers.
Therefore, at every enterprise striving to produce competitive products or services, constant attention should be paid to improving the skills of employees, their training and retraining, and the training of new specialists.
7. Certification of personnel. Certification is the main tool for assessing the professional level of a specialist, his compliance with the requirements set by the management of the enterprise.
To conduct certification, it is necessary to develop or use special methods. The composition of such methods should include the development of criteria, scales for assessing the compliance of an employee with a workplace, the effectiveness of his work, and determining the level of qualification. The result of the certification should be an analysis of the assessment of employees, summarizing the results and preparing recommendations on the appropriateness of personnel changes in accordance with the personnel policy of the enterprise.
8. Permutation of personnel based on the results of certification. Recommendations prepared based on the results of the certification of employees of the enterprise, as a rule, contain proposals for promotion, reduction, transfer, and dismissal of employees. They may also contain proposals for additional incentives for employees, the advisability of their professional retraining, etc.
Based on the presented attestation commission proposals, the personnel department of the enterprise prepares a structure for the movement of employees within the enterprise, and also prepares proposals for management on the advisability of dismissing employees who do not meet the requirements for them.
9. Training of leading personnel. One of the most important tasks facing the personnel service of the enterprise is to carry out work to ensure the efficiency of the work of the management staff by strengthening it with professional management personnel. Naturally, decisions to strengthen the management staff with managerial personnel are made by the management of the enterprise, however, the preparation of timely proposals is carried out by the personnel service and the security service of the enterprise.
In order to solve this problem in a timely and efficient manner, the enterprise must have a system for training a reserve of managerial personnel, including from a contingent of young specialists, which to a large extent ensures continuity in the enterprise management system.
10. Social protection of personnel. The subject of constant attention of the management of the enterprise should be the social conditions created for its employees, since labor productivity and their attitude to work are largely determined by social conditions.
The personnel department of an enterprise should monitor the working and living conditions of employees and their families, have a clear idea of the average level of social conditions, of the social conditions created for employees by competing enterprises. The personnel service should prepare recommendations for improving the working and living conditions of workers, for the development of social infrastructure. The personnel service, as far as possible, should contribute to providing employees and their families with normal living conditions, solving problems related to health, rest, and food.
11. Legal and disciplinary aspects. The responsibilities of the personnel service of the enterprise include the development of forms and the conclusion of employment contracts, contracts with newly hired employees or the transfer of all employees of the enterprise to new contractual conditions, if the decision on this is made by the management of the enterprise.
If necessary, proposals are prepared on disciplinary measures in relation to individual employees.
The Human Resources Department also develops job descriptions, consideration of labor disputes and conflicts, applications and complaints of employees.
Earlier, we discussed the main subsystems of the personnel management system, designed to solve the problems facing personnel services. Now we will discuss in more detail some aspects of the activities of personnel services that require a sufficiently high professional level of their employees.
The Role of Human Resources
IN Soviet period there were personnel departments in almost all organizations, but their functions differed markedly from what departments with the same name did in countries with market economies, three factors public life of that period, this specificity was determined by the centralized management of the national economy, the politicization of the economy and the totalitarian ideology. Personnel departments were entrusted only with the functions of hiring and dismissing employees, as well as organizing their training, advanced training and retraining. Often the last of the functions were performed by the departments of training (technical training).
At present, personnel departments are still neither a methodological nor a coordinating center for personnel work. They are structurally disconnected from the departments of organization of labor and wages, the department of training, social and other departments of the enterprise that perform the functions of personnel management. There is no unified system of work with personnel at enterprises, the abilities and inclinations of employees are not studied, there is no system for their professional and job advancement in accordance with their business and personal qualities.
With the weakening of the centralized system of economic management and the development of market relations, enterprises began to face fundamentally new tasks related to human resource management.
Namely:
The tasks of determining the current and future needs for personnel;
Study and analysis of the labor market;
Issues of labor incentives and personnel policy, expressed in the process and form of hiring;
Development of individual career plans.
Solving these tasks requires completely different skills than those that were sufficient for documentation and reporting. For effective personnel management and ensuring normal conditions his work, it is necessary to be able to do socio-psychological diagnostics, analysis and regulation of group and personal relationships, relations between the leader and subordinates, manage industrial and social conflicts and stresses, plan the needs of staff and their business careers, manage labor motivation.
In the transition to the market, the solution of these problems comes to the fore, and every enterprise is interested in their solution. Today, personnel officers are not always able to offer the heads of organizations effective solutions to problems related to personnel management.
In this regard, the question arises: how to change, reorganize the personnel service of the enterprise, what functions should it perform, what skills and knowledge do employees of this service need?
Among the many modern organizations, multinational corporations have accumulated perhaps the richest experience in personnel management. Their human resource departments deal with a wide range of issues and play a key role in the development of the organization. Therefore, it is necessary to turn to the experience of countries with market economies and see what the modern concepts of personnel management in an enterprise are. A generalized analysis of the work of human resource management departments of transnational corporations allows us to build a certain model of personnel management.
The first stage of the model in the formation of staff is the development and implementation of personnel policy, including planning, hiring, selection, placement of employees who can perform future work. To do this, you need to start with an analysis of the position (work).
To do this, HR must:
* know how to collect data for job analysis and how to compose questionnaire forms;
* be able to describe this position (work);
* process results, specifically use processing methods;
* draw up work specification cards, where it is necessary to indicate the required skills, abilities and experience.
The next step is professional selection. To perform this function, personnel officers must themselves be aware of existing methods selection of candidates and give correct recommendations for their use by line managers.
The second stage in the work of personnel management is the development effective system motivation, i.e. streamlining payment within the enterprise and other types of motivation (career planning, participation in management, etc.) to perform work. At the same time, the manager responsible for personnel management must be familiar with modern concepts of motivation, according to which a person has many needs: not only material, but also such as recognition, belonging to a certain group, self-realization, etc., which are strong incentives to work, but, however, cannot be satisfied only through money. However, at present; time in Russia, money is the most important motivator. Therefore, the personnel service should take an active part in the development of the remuneration system at the enterprise.
The next step is performance evaluation, which is important function in personnel management. Logically, this part of the work is based on the results of the working analysis, where the content of the work and the requirements for personnel are determined. The company can use to evaluate performance various methods, but which ones - it is necessary to decide together with employees of personnel services.
In case of poor performance, it is necessary to find the cause and determine what changes in the personnel management system should be made: change the requirements for recruitment, conduct additional training and consultations, use new incentives, etc., i.e. carefully look at the entire personnel management model .
Studies of foreign practice show that personnel management services occupy an important place in the organization's management system. This is largely due to the highly professional staff of these services. So, out of every 10 employees, 6-7 are specialists, psychologists, economists, specialists in the field of labor relations, etc. Most of them are graduates of business schools (for personnel management), as well as major universities and pedagogical universities.
The growing importance of the personnel management service was reflected in the official status of their leaders. As of 1992, 43% of the chiefs of personnel departments of American firms held the positions of vice presidents, and 32% were on the boards of directors. In the early 1970s the corresponding indicators were at the level of 27%. In Japan, the post of vice president of the company is occupied by 51% of heads of personnel services, and in Italy - 20%.
All of the above shows how much the functions of personnel services should change in the context of economic reform, when there is a departure from hierarchical management, a rigid system of administrative influence, practically unlimited power to market relations, property relations based on economic methods.
It seems that new personnel management services should be created on the basis of traditional services: the personnel department, the department of labor organization and wages, social welfare and other departments. This service should be headed by a vice president (or deputy director), who reports directly to the first head of the organization - President, CEO, etc. (in smaller organizations, a department head can perform a similar function, however, he must retain direct reporting to the head of the organization).
The VP of Human Resources' position in the internal hierarchy reflects his dual role in running the organization. On the one hand, he is the head of a certain functional service - personnel, on the other - a member of the leadership of the entire organization. As a functional manager, this vice-president will ensure that, from the point of view of the organization (its president), the operation of personnel management systems is satisfactory - recruitment, training and development, assessment and work motivation, work on their improvement and manage employees of his unit.
As a member of the top management of the organization, he will share with other managers the responsibility for managing the entire organization, will take part in the discussion of the most important development issues for the enterprise, determine the strategy (for example, the decision to start the development of new regions and how this process will be carried out - by opening a sales office, creating joint venture, branch, etc., what will be the production strategy of the company, what capital investments will be required for this, etc.).
Of course, when discussing the issues of managing the entire organization and developing a business strategy, the head of the personnel department will be able to act, first of all, as a specialist in the field of people management, as a kind of internal consultant for other managers. However, in addition to competence in his professional field, he must understand the general laws of the organization's development, know the market, competitors, products manufactured by the company and the services provided to it, must have strategic thinking, i.e. be a specialist in managing your enterprise as a whole.
Otherwise, his advice, even in the field of human resource management, will not be professional enough, and his authority with senior management and in the organization as a whole will not correspond to his position. And, on the contrary, it will be much easier for the head of the personnel service, who is competent in terms of managing the organization, to implement purely functional projects due to his weight in the organization.
The latter is true for all employees of the service, who often complain about insufficient attention to them and unwillingness to cooperate on the part of other managers, primarily line managers. The source of such underestimation is often their own incompetence in key issues of the organization's activities, which makes them inferior in the eyes of colleagues.
Thus, in addition to the main management functions, the head of the personnel service can provide additional ones:
1. Coordination. He acts as a coordinator and area of personnel management and should be part of the top management of the enterprise.
2. Work with personnel. Selection, recruitment, training, performance evaluation, development of reward systems, career planning. In addition, organization and leadership special programs(health and safety, retirement, etc.).
The implementation of an expanded list of functions will allow the heads of personnel departments to more clearly plan the personnel potential of the enterprise and take a direct part in its formation and development. Thus, in order to implement a program to increase human resources, the head of the personnel service can and must improve his managerial potential himself.
The composition of the personnel service
The personnel department (human resources department), where, in addition to specialists in the field of labor relations, other specialists should be represented - psychologists, lawyers, sociologists. With absence regular places for such specialists, positions are combined through specialized (in this area) training of existing specialists of the personnel department. Russian practice does not have legislative basis to determine the staffing of the personnel department. You can focus on foreign experience, where, as a rule, 2-3 full-time personnel workers are allocated per 100 people working.
The construction of the personnel department should be carried out according to the following basic principles:
* Optimization of the structure of the department.
In addition to the usual (traditional) divisions, such as the recruitment sector, the personnel records management sector, the training of the personnel reserve, etc., it is advisable to include modern and important structures that process personnel information, career development employees, selection of top managers, marketing and personnel economics, etc.
* Specialization of personnel workers of the department.
Each employee of the department, having annual and quarterly plans for his work, specializes in a specific type of his activity (recruitment, training, motivation or rotation, etc.) with mandatory internships in the divisions of his company. The purpose of such internships is a deeper understanding of the specifics of the work of each department of the company, of course, with a deeper reflection of this specifics in further personnel decisions.
* Analytical work of the department.
Issues of processing personnel information, assessing its completeness and reliability, the regularity of its presentation to the most different levels management are a necessary condition for the effectiveness of the department. In the collection and processing of personnel information, it is necessary to possible application contemporary information technologies, as well as the use of sociometric measurements, sociological surveys, public opinion analysis.
Other professional personnel departments, such as a training center, a personnel assessment group, a bulletin (magazine) editorial office, etc. modern conditions market competition, implementation innovative technologies special meaning have the creation and operation of corporate training centers (universities, colleges) with an appropriate organizational and educational and methodological structure.
Usually, successful companies have specialists in personnel work with the personnel of the company's supreme management body (board of directors, supervisory board, etc.). Most often, this role is played by advisers (assistants) to the general director on personnel matters, who have their own scope of work, their own tasks, and corresponding expense items.
In order to build a personnel vertical, it is advisable to establish the institution of authorized personnel for personnel work from the heads of the company's divisions for the constant interaction of the personnel Service with line divisions. As a rule, such representatives of departments are determined by their heads and approved by the general director. The personnel service regularly informs these authorized persons about the personnel actions taken at this stage, includes them in the practical personnel work of departments in cases where the personal participation of their leaders is not required.
External Human Resources Services (recruitment agencies, consulting firms, training organizations), with which the company's human resources department constantly interacts. The main task of such interaction is to determine the quality of work of such firms and organizations (on the basis of tenders, competitions), to use them in their work to reduce the cost of personnel costs (instead of full-time employees).
Organizationally, such interaction may look like the work of one of the employees of the HR Service, who is obliged to monitor the level of work of such structures, conclude contracts in case of interaction and decide other aspects of possible joint work.
Necessary information structure of personnel work:
Provision of instructive and administrative documents.
* Personnel policy (strategic personnel plan) for the current year (or with a perspective of 2-3 years), including an estimate of personnel costs. This document is prepared by the Human Resources Department, coordinated with all divisions, approved by the top management of the company, and the CEO controls the progress of its implementation. This is the main personnel document of the company.
* Regulations on the personnel work of the company. The document defines the procedure for building personnel work, the place and role of the company's divisions and professional personnel services in personnel management, the procedure for reporting and control.
* Regulations on the personnel department (human resources department), other personnel departments.
* The status of an employee of the company, the code of professional conduct of an employee. These are documents that, in addition to the provisions of the Labor Code, determine for each employee of the company his basic rights, opportunities, behavior, training, interaction with colleagues, customers, competitors.
* Documents that determine the implementation of specific personnel decisions: the schedule of the meeting of the board of directors on personnel issues, the timing of certification, the training plan, personnel rotation, reserve training, etc.
* Personnel technologies. These are documents that determine the procedure for fulfilling and monitoring the achievement of the goal for specific personnel positions: hiring new employees, evaluating the results of work, motivation, rotation, employee training, corporate holidays and rituals, etc.
The procedure for analyzing and processing personnel information
Weekly analysis is advisable (the format of personnel reporting at a weekly operational meeting with the first head), quarterly (assessment of the current personnel situation with an analysis of dismissals, punishments, training and development of employees, work with personnel of specific heads of departments), annual (strategic analysis with an assessment of the progress of personnel company programs, trends, problems and solutions in the field of personnel).
Thus, the assessment of the infrastructure of personnel work is carried out according to the following criteria:
* the presence of the required number of highly qualified specialists in the personnel Service and their specialization;
* provision of these workers with resources, necessary documents and regularly received information;
* the presence of an algorithm for the interaction of HR departments with departments and services of the company, including assistance to line managers.
Regulations on personnel service
Regulation - a legal act that determines the procedure for the formation, rights, obligations and organization of the work of an enterprise or structural unit, i.e. the provision is a document regulating all types of activities of each structural unit and the entire institution (organization) as a whole. Since the 90s state, private, municipal organizations, public associations to fix (and subsequent registration) the rules of formation, management, activities of the entire organization more often use such a document as a charter. However, the situation remains the most important document to consolidate the tasks and functions of individual structural divisions. The role of the position is to create the interaction of all structural units, to eliminate duplication in their work.
It is known that the structure, functions, tasks of a structural unit (service, department, department) are fixed by a number of internal organizational documents developed for these purposes: regulations, regulations, instructions, internal labor regulations (staff regulations), structure and staffing, staffing, orders on the distribution of duties.
Among the listed documents, the most important, from the point of view of the regulatory establishment of the legal status and scope of activities, are the provisions and job descriptions. They are included in the category of long-term regulations and are intended to regulate all parties and activities of structural units (or officials). The system (complex) of provisions on the structural divisions of the organization ensures their interaction, determines the competence, fixes the functions.
The personnel service, as a rule, is created as an independent structural unit. Traditionally, a structural unit is considered independent, which reports to the head of the organization (enterprise) or his deputy. In small organizations with a staff of about 300 people. the functions of the personnel service are usually carried out by a specially dedicated employee (inspector, manager). With a small number of staff, it is possible to perform the functions of the personnel service by an accountant, secretary, directly by the head, that is, their combination with other duties.
Of all the organizational forms considered, the development of a provision is mandatory in cases where the personnel service is created as a structural unit.
The development of regulatory and organizational documents is a rather complex and responsible task. At the same time, compliance with generally accepted legal norms, established requirements for structure, text and design is of paramount importance. There are several sources that can help solve these problems.
The fundamental documents in the development of provisions are the current legislation and modern state regulatory and methodological documents, for example, GOST R 6.30-97. USD USORD. Basic requirements for paperwork. Another source is model provisions, but it should be remembered that they cannot replace individual ones, since they usually contain a typical set of personnel service functions. In the specific conditions of the activity of an organization, there may be important differences in the structure, and in the rights, and in the duties of the service.
Individual provisions are developed, first of all, to consolidate certain tasks and functions of the personnel service based on the characteristics of documenting labor relations, the specifics of the organization's activities, and the composition of employees. When developing a provision, in addition to those listed, they usually also use documents that determine the activities and structure of a particular organization, primarily the charter and memorandum of association. These documents establish the basic provisions of management: the internal organizational structure, the distribution of functions and responsibilities of managers.
The requirements for the execution of the provision coincide with the usual rules for the preparation of organizational and administrative documents, since this document is unified. The provision in the header should contain the same details that are placed on the forms used to prepare the internal documents of the organization: the name of the organization, the name of the document, the date and place of its preparation. The title to the text (as in other management documents) is consistent in the case with the title of the document. For example: Regulations (about what?) About the personnel department. To the right of the text is a stamp of approval. Its design must comply with the requirements of GOST R 6.30-97. USD. USORD.
The regulation on the personnel service fixes the status of the service, its place in the management system, internal organization, tasks and functions, rights and obligations performed in the course of its activities. The composition of the sections of the provision corresponds to the purpose of the document: “ General provisions”, “Main tasks”, “Functions”, “Management”, “Rights and obligations”, “Structure”, “Relationships. Connections". The text of each section is set out in separate paragraphs, which are numbered in Arabic numerals.
Its head develops the regulation on the service, he also signs this document. Approves the position of the head of the organization.
The “General Provisions” section begins with a paragraph that establishes the exact name of the personnel service (management, department, etc.), its place in the organizational structure, the degree of independence, the position of the head to whom it reports, the procedure for determining the number and staff of the service. This section establishes the procedure for determining the number of employees of the personnel department, its staffing table.
A separate paragraph provides a list of the main legal, directive, normative and instructive documents by which the service is guided in its work. It is customary to list first the current state legal and regulatory documents, then sectoral, then internal organizational and administrative documents of the organization itself.
The Human Resources Department in its activities is guided by the current legislative acts of the Russian Federation on labor, regulatory and regulatory and methodological acts of the Government of the Russian Federation, the Basic Provisions of the State Documentation Support System for Management (GSDM), state standards, the developments of the Federal Archive, Instructions on the procedure for maintaining work books, the charter and other organizational documents of the organization, orders and instructions of its head , instructions for documenting personnel activities, internal labor regulations and this regulation.
...Similar Documents
Modern personnel service and the organization of its work on the example of Stroitel LLC. Structure, functions and employees of the personnel service. Documentation of personnel activities. Formation of a pension. Work with outgoing and incoming documents. Storage of documents.
thesis, added 03/02/2009
The concept and essence of personnel management. Principles and purpose of the work of the personnel management department at the enterprise. Analysis of work efficiency, development of ways and directions for improving the activities of the personnel department in the Monetka retail chain.
term paper, added 09/12/2010
Goals and objectives of the personnel service of the enterprise. Analysis of the management system at the enterprise JSC "KORMZ". Analysis of the number and structure of the organization's personnel. Study of the work of the personnel service of the OJSC enterprise, development of measures for its improvement.
term paper, added 09/23/2011
The essence of personnel policy: structure, methodology and functions. Personnel policy as a system element government controlled. Current state and development of the personnel potential of the state civil service of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
term paper, added 11/03/2014
Principles of personnel policy in the public service system, features of international experience. The mechanism of organization, social and legal institutions of personnel policy in public service Russian Federation. Modern concept, optimization problems.
term paper, added 01/20/2012
Evaluation of personnel policy at a modern enterprise as a tool to ensure its competitiveness and development. Application of a competent personnel policy for effective personnel management. Analysis of job descriptions of HR employees.
practice report, added on 01/09/2014
The process of formation of personnel policy and its types, external and internal factors influencing its improvement. The organizational structure of the personnel management service, its tasks. Development of personnel policy, the leading concept of personnel management.
test, added 10/26/2013
Motivation of personnel as a function of personnel service. Analysis of the organization of personnel work on the implementation of the personnel motivation system at the enterprise. Personnel work in the formation and implementation of the system of motivation in the organization, ways to improve it.
term paper, added 09/26/2012
Place, role, functions and principles of organization of the state civil service. Analysis of the main areas of personnel work of the Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Novosibirsk Region.
thesis, added 08/29/2012
Personnel policy as a system of people management. The content of the personnel policy in the regional divisions. Building personnel work, staffing, qualifications and motivation of civil servants in the office of the governor and the government of the Nizhny Novgorod region.
The main goal of the personnel service is to fulfill the tasks of managing personnel and ensuring normal working conditions for it. The most important tasks are:
socio-psychological diagnostics;
analysis and regulation of group and personal relationships, management relationships;
management of industrial and social conflicts and stresses;
employment management;
evaluation and selection of candidates for vacant positions;
analysis of human resources and staffing needs;
personnel marketing;
business career planning and control;
professional and socio-psychological adaptation of employees;
management of labor motivation;
legal issues of labor relations;
psychophysiology, ergonomics and aesthetics of labor.
Currently, the listed tasks are paramount, each organization is interested in their solution.
Personnel management in modern economic conditions is of particular importance, because it allows you to implement and generalize a whole range of issues of human adaptation to external conditions taking into account the personal factor in building the organization's personnel management system.
The essence of the organization's personnel management today is the increasing role of the employee's personality, knowledge of his motivational attitudes, the ability to form and direct them in accordance with the tasks facing the organization.
In our time, there is a departure from hierarchical management, a rigid system of administrative influence, and practically unlimited executive power to market interactions, property relations based on economic methods. Therefore, one of the new approaches to the priority of values in the organization is the focus on employees, and outside the organization - focus on consumers of products. Under the new conditions, hierarchy fades into the background, giving way to culture and the market.
Modern personnel management services, as a rule, are created on the basis of traditional services: the personnel department, the labor organization and wages department, the labor protection and safety department, etc. The main task of the new services is to implement personnel policy and coordinate labor organizations. In this regard, new services are beginning to expand the range of their functions and are moving from purely personnel issues to the development of systems for stimulating labor activity, managing professional advancement, preventing conflicts, studying the labor market, etc.
The structure of the personnel management service is largely determined by the nature and size of organizations, as well as the characteristics of products. In small and medium-sized production organizations, many personnel management functions are performed mainly by line managers; in large, structural divisions are formed to implement functions.
Depending on the size of organizations, the composition of units will change. In small organizations, one unit can perform the functions of several subsystems, in large organizations, the functions of each subsystem, as a rule, are performed by a separate unit.
The experience of domestic and foreign organizations allows us to form the main goal of the personnel management system: providing labor resources, organizing their effective use, professional and social development. In accordance with these goals, the organization's personnel management system is being formed.
You have read the introduction! If you are interested in the book, you can buy full version book and keep reading.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
Search for ways to improve the work of personnel services in the Republic of Belarus through the analysis of the personnel policy of the enterprise LLC "Belkrus" and the implementation of the main tasks and functions of the personnel service. The role of the personnel service in the management of the organization.
term paper, added 10/12/2010
Organization of the personnel service, the structure of the regulation on the personnel department. Key Responsibilities of the Head of Human Resources. Powers, structure and functions of the department. Ways to improve the work of personnel services in modern conditions.
term paper, added 06/25/2014
Goals, objectives, functions and structure of the personnel service of the enterprise. Features of compiling the organizational and economic characteristics of the enterprise. Analysis of the professional and qualification composition of the personnel service of OAO "Shebekinsky Machine-Building Plant".
term paper, added 03/02/2010
The place of the personnel workflow subgroup in the management structure. Characterization and storage of personnel organizational, administrative, accounting documents at the enterprise. Documentation of labor relations. The structure and functions of the personnel service.
thesis, added 09/23/2016
The essence and significance of the personnel policy of the enterprise. Organizational and economic characteristics of LLC "Atrium". Analysis of the use of labor resources and elements of the personnel policy of the organization. Proposals to improve the effectiveness of staff training.
thesis, added 05/28/2014
Essence, functions, role and significance, the main directions of development of the personnel service in the organization. Organizational and economic characteristics, analysis of the availability and use of the personnel of the enterprise under study. Improvement of the personnel policy of the enterprise.
thesis, added 08/16/2012
Organizational structure of the enterprise, staffing. The main functions of the divisions. The process of working with personnel, recruitment. Areas of activity of a security company on the example of "AN-Security S-Z" LLC. Formation of principles of personnel work.
practice report, added on 06/04/2015
Introduction
1. Personnel service of the enterprise
1.1 The concept and tasks of the personnel service
1.2 The structure of the personnel service
2. The place of the personnel management service in the structure of the organization
Conclusion
List of sources used
INTRODUCTION
Personnel management as a theoretical and applied branch of management science and practice began to take shape at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries. Special units dealing with issues related to personnel began to emerge in the 20-30s of the last century. Since then, the functions of these services have been intensively developed from ancillary technical work to the solution of almost all key issues related to the organization's personnel management.
Currently, personnel management services perform a number of functions that used to belong to economic, production, technical and other departments. Such a concentration of functions in one structural unit makes it possible to implement an effective toolkit for managing the organization's human resources. Today, the attention of personnel management services is mainly paid to improving labor relations, selecting candidates for vacant positions, developing and implementing training programs and social development programs, as well as motivating and stimulating labor activity. Decision-making on the above issues is carried out not only by the head of the personnel service, but also by other line managers of the organization.
Thus, today the work of personnel management services is increasingly dominated by not accounting, but analytical and organizational aspects of activity. At the same time, a sharp increase in the professional level of employees of personnel services was noted. Today they include specialists in the field of psychology and sociology, labor relations, specialists in the development and organization of curricula, as well as managers.
Recently, a number of new professions and specialties have appeared in intra-organizational management, such as specialists in the selection and hiring of personnel (recruiters), specialists who interview applicants for vacant positions (interviewers), specialists in curriculum development, trainers (teachers) , career development, career guidance and organizational planning consultants.
It should be noted that at present, many Western organizations in the field of HR issues use the services of outsourcing companies, which are recruiting agencies, training centers, consulting firms, etc. Outsourcing companies in the personnel sector include, for example, developers of automated management systems for PM services, organizations specializing in building a system of payments and compensation (benefits). Also on this moment there is a specialization of recruiting companies and the separation of the function of selecting management personnel, as well as specialists high class. The most significant in terms of the scale of personnel services is the sphere of vocational training and advanced training, it accounts for 20 to 40% of the costs of organizations.
The purpose of this work is to give the concept of personnel service, to consider the structure of personnel service.
task term paper is to study the place of the personnel management service in the structure of the organization.
1. HR SERVICE OF THE ENTERPRISE
1.1 The concept and tasks of the personnel service
The personnel service of an enterprise is a set of specialized structural units in the field of enterprise management, together with the officials (managers, specialists, performers) employed in them, who are called upon to manage personnel within the framework of the chosen personnel policy.
The main purpose of the personnel service is not only to be guided in the implementation of personnel policy by the interests of the enterprise, but also to act in accordance with labor legislation, the implementation of social programs adopted both at the federal and at the territorial level.
The functions, structure and tasks of the personnel service are closely related to the nature of the development of the economy, the understanding by the management of the enterprise (organization) of the role of personnel in fulfilling the goals and objectives of production (organization).
In the context of the economy's orientation towards the use of extensive methods, the personnel service was most often represented by a small personnel department, the personnel training department (technical training), and the welfare service.
The functions of the personnel department at domestic enterprises were reduced mainly to the hiring and dismissal of the workforce, and record keeping. This reduced the personnel department to a secondary structural unit, in fact, fulfilling only the instructions of the enterprise management and the orders of the heads of structural divisions regarding the recruitment of labor from outside.
In the same time various types personnel work, other divisions of the plant management were occupied: the department of labor and wages (calculation of the number, organization, rationing and remuneration), the planning department (planning the number, planning the costs of labor force), the party committee (reserve for promotion, selection of leadership personnel, educational work in a team), trade union organization (organization of everyday life, recreation, cultural pastime), safety department, chief technologist service (formation of an operational division of labor that determines the training of workers and their placement, content of labor), department of technical education (training), etc.
The great disunity of all these highly specialized structural divisions reduced the efficiency of work with personnel, did not allow for a comprehensive solution of the problems of formation and, moreover, the effective use of personnel. great job, especially related to the selection, placement and use of personnel, was performed by line managers (shop managers, foremen), often without the necessary knowledge or time, since their main task was to ensure timely and high-quality performance of production tasks. Their communication with the personnel department, the personnel training department was more of an operational nature and resembled a "duty service" system - the operational execution by the personnel department of orders for a specific production for recruiting personnel from outside.
The personnel service was not endowed with the functions of planning, organizing, coordinating, stimulating, controlling, did not participate in the development of personnel policy, limiting itself to current work with frames. In fact, the majority of domestic enterprises did not have the personnel service itself as a set of interrelated structural units involved in personnel management. Appearance in last years the position of deputy general director for personnel did not save the situation, since, as a rule, only the personnel department, the personnel training department and the assistant director of household were subordinate to him. Outside the field of his activity were other departments of the enterprise, engaged in the performance of the functions assigned to them in accordance with their own understanding of the tasks of personnel management. Big shortcomings took place in the technical and information support of the personnel of the enterprise (organization) Technical capabilities embedded in information system ACS "Personnel" (ARM "Personnel"), turned out to be unclaimed due to the narrowness of the tasks facing the personnel management of the enterprise.
With the change in tasks and guidelines in personnel management, the tasks of the personnel service, its functions and structure have also changed.
We are talking about the formation at the enterprise of a multifunctional personnel service as a single whole, about the organization (coordination) of all the work of structural units in the production management system, to some extent engaged in working with people, under a single leadership. Only in this case is it possible to comprehensively solve not only the issues of staffing production, but also the main task of the personnel service in the new economic conditions - to combine the goals of production development with the needs of workers realizing these goals, to balance the development strategy of the enterprise (organization, firm) and those employed in it frames.
As already noted, personnel management is not only a function of the personnel service. In one direction or another, within the framework of their competence, other subjects of management are also directly involved - line managers of production units, together with specialists subordinate to them.
"In the upper echelons of management (management) issues of a strategic nature are resolved: personnel policy, strategy and tactics for its implementation are formed, tasks for the development of methodological and regulatory materials (documents), control over their implementation and general leadership all HR departments.
At the level of individual productions in the association, work on personnel management is mainly of an operational nature. The division of personnel management functions between the administration and the heads of individual production structures should be quite clear, excluding parallelism in work, which increases responsibility for the results.
The functions of personnel management at the shop level are performed by line managers of the shop (shop manager, foremen, foremen), as well as specialists of shop management structures (economists, organizing engineers, rate-setters), shop public organizations (primarily the trade union). Line managers are involved in the recruitment, and foremen, together with specialists, provide conditions for highly productive work and the use of an employee according to his abilities.
The personnel service in modern conditions should be the organizer and coordinator of all work with personnel at the enterprise. It is designed to perform the function of monitoring the implementation of personnel policy in structural divisions, to oversee wages, medical care for employees, the socio-psychological climate in the team, and social protection of employees.
The effectiveness of the work of the personnel service in the enterprise depends on:
Its structuring and concretization of the functions of each structural unit;
- interconnected work of structural divisions within the service itself;
Organic connection of the work of the personnel service with the work of the technical and economic service of the enterprise;
Staffing services.
In modern conditions, the most priority areas of work of personnel management services are the solution of the following tasks:
ensuring that the level of qualifications meets the requirements of a modern economy, where basic skills and knowledge require continuous updating;
controlling rising labor costs;
determining the policy of multinational corporations in the field of combining the hiring of cheap labor from foreign countries and the population of their own countries;
expanding the norms governing labor and organizational relations, from compliance with labor laws to moral and ethical standards (for example, in the field of discrimination, healthy lifestyles, etc.);
development of methods to support employees working on a virtual basis using telecommunications at home and not visiting the office.
In modern organizations, the functions of the PM service can be conditionally divided into two types:
labor relations management;
documentary registration of labor relations.
Labor relations management includes the following functions:
personnel planning;
providing the organization with personnel;
personel assessment;
professional training and development of personnel;
organization of the system of remuneration and social development;
coordination of work on quality management of working conditions and compliance with safety regulations.
In total, these functions correspond to the functions of the personnel management system described above.
Registration of labor relations includes the following functions:
preparation of personnel orders;
maintaining forms of mandatory primary accounting documentation for the accounting of labor and its payment;
registration and accounting of work books;
conducting personal affairs;
employee counseling;
preparation and adjustment of vacation schedules;
execution of documents related to various payments, allowances and benefits;
and some other features.
It should be noted that the structure of the personnel service in a particular organization should be determined by its functions and tasks, and not vice versa.
The nature of the functions performed and the tasks to be solved also predetermine the requirements for the personnel service, in particular the need for research and development (for example, surveys to identify factors, causes, consequences in relation to labor relations), establishing contacts with territorial labor authorities, with the employment service and vocational guidance, universities and technical schools (colleges), with private structures specializing in the selection of personnel, due to the need to study the situation on the labor market, recruitment, their training and advanced training, etc.
1.2 The structure of the personnel service
When organizing the personnel service, structuring its composition, it is necessary to proceed from the following assumptions.
The list of works related to ensuring effective personnel management has a relatively standard view for all businesses. This means that their implementation is a necessary and sufficient condition for the implementation of management tasks and functions.
The fundamental structure of the personnel service in modern conditions does not have a generally recognized form. One of its variants is shown in Figure 2.1. It is oriented towards standard set work and the implementation of a strategic approach to personnel policy in conjunction with the development of the enterprise (organization).
The specific structure of the personnel service, the distribution of personnel work between structural divisions, and within the structural division between performers, can vary in a wide range, since it depends on many points. Among them, it should be noted, first of all, the size of the enterprise (the number of personnel employed in it), the volume of managerial work of each type, the understanding of the tasks of personnel management by management: despite the effectiveness of an integrated approach to personnel management, in some enterprises, nevertheless, the focus is, for example, selection of personnel, for others - career planning, for others - evaluation of results and remuneration. The style and methods of directing the administration of subordinates also influence, etc.
When designing the structure of the personnel management service and organizing its work, it is assumed that the existence of any structural unit is justified only under certain conditions (with a certain number of personnel, the amount of managerial work of this type). In other conditions given function can be entrusted (transferred) to another structural unit or even to an individual as part of any structural unit.
First of all, the volume of work should be sufficient to load at least two or three people so that a separate group (bureau) can be singled out within the department.
A study of the domestic practice of organizing personnel management shows that work with personnel at enterprises is built according to a scheme that is very different from that shown in Figure 2.1. Organizationally, work with personnel continues to be dispersed across many functional divisions of the plant management. Moreover, there may not be an independent personnel service with a single administrative and methodological leadership at all.
At the same time, positive trends are emerging, in particular, the transformation of personnel departments into personnel management departments, however, so far with a slight transformation of functions, which, of course, does not significantly affect the effectiveness of work with personnel. Other enterprises go much further and subordinate to the personnel manager not only such traditional management structures as the personnel department, the personnel department (or the department of technical training), but also the sociological departments (if any), the department of labor and wages (having previously transferred planning the main labor indicators in the economic department), the department (laboratory) of NOT, etc.
The expansion of the independence of enterprises, the change of forms of ownership, the process of disaggregation of enterprises and the creation of independent small enterprises on the basis of structural divisions significantly change the existing personnel work at the enterprise. Often, the disaggregation of enterprises is followed by a reorganization of the plant management, including the personnel department: many of its functions are transferred to small enterprises, where this work is carried out by one or two people. There is also the preservation of a centralized personnel service, whose services are in the selection of personnel, their training and retraining, evaluation, etc. on a contractual basis are used by small businesses.
After determining the functional structure of the personnel service, its constituent units (departments, bureaus), the issue of the list of tasks of each structural unit, its functions, the number of employees and the proper structure of the employees employed in them is resolved, official duties each of them, as well as on the relationship of departments with each other within the framework of the personnel service and with other departments of the enterprise in terms of incoming and outgoing information, and in relation to the methodological support of personnel work, the implementation of the function of control and supervision over its implementation.
2. THE PLACE OF THE PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT SERVICE IN THE STRUCTURE OF THE ORGANIZATION
Structure management organization or organizational structure- one of the key concepts of management development. It is closely related to the strategic goals, functions, management process and distribution of powers among those working in the organization. Within the framework of the structure, the entire management process takes place: the movement of information flows, the adoption of management decisions, in which all personnel participate. The structure is necessary so that all processes occurring in the organization are carried out in a timely manner and with high quality.
Scientists, management theorists define the structure as "a set of management links located in strict subordination and providing the relationship between the control and managed systems" (N.I. Kabushkin) or as an ordered "set of its constituent elements, in one way or another connected with each other" (V.G. Vesnin). In addition to an ordered system of "sustainably interconnected elements that ensure the functioning and development of the organization as a whole, as well as forms of division and cooperation of managerial work, within which the management process is carried out according to the relevant functions aimed at solving the set tasks and achieving the goals" (Z.P Rumyantsev), from the angle of personnel management, we see the structure of the organization as a system of optimal distribution of functional duties, rights and responsibilities between its constituent bodies and people working in them.
The key concepts of management structures in this perspective are elements, connections (relationships), levels and powers. The elements of the management structure can be both individual employees and services performing functional duties and operations. The relationships between the elements of the management structure are supported by links, which are divided into vertical and horizontal (linear and functional).
For decades, domestic enterprises have been dominated by a technocratic approach to management, when production plans, budgets, structures, administrative orders. Personnel policy was the prerogative of state bodies and ideological mechanisms. The heads of enterprises did not have sufficient authority to subordinate personnel work to the interests of production. Monopoly in the sphere of labor led to a narrowing of labor motivation and low productivity.
The traditional model of organization management in the command-administrative system was focused on the actions of higher authorities and assumed:
· stable functioning and "eternal" existence of the enterprise;
Rigid construction of internal structures and performance of prescribed functions;
production of planned products;
· Guaranteed sales with relatively difficult to obtain additional resources.
Traditional system personnel management, based on the above provisions of the organization's management, mainly carried out accounting functions and was not responsible for the efficient use of labor and personnel development.
At centralized system management, the wage fund was part of the national income budgeted annually as a separate line. In the hands of the state were all the levers for managing wages: the tariff system, differentiated by sectors of the economy; rules for the payment of bonuses, various additional payments and allowances for special working conditions; staffing limit in enterprises. Strict control was established over the expenditure of the planned wage fund. In case of deviation from the government model regulation on wages, for violation of the terms of payment of wages, overspending Money the head of the enterprise was personally responsible.
In this mechanism of state regulation, a special role was assigned to the interconnection of payroll payments with the fulfillment of state planned targets. The previous labor legislation and the mechanism for resolving labor disputes at enterprises provided workers with a certain level of social protection.
The internal structure of organizations was characterized by the presence of numerous technical and design divisions, developed supply divisions, large divisions of the social and domestic spheres, and inconspicuous financial and economic services.
However, the complete "nationalization" of the reproduction of labor resources by the end of the 70s became a brake on the development of productive forces. The centralized organization of wages with elements of its leveling has ceased to fulfill its stimulating role.
Meanwhile, researchers and practitioners show that traditional management tools are becoming less and less effective. This is due to the fact that industrial and commercial activities are becoming more and more complicated, and enterprises, for their survival and development, must look for ways to adapt to changes in the environment. The identified shortcomings of the linear-functional structure of enterprise management (when the principle of unity of command and functional division of labor is observed) include:
1) discrepancy between powers and responsibilities, rights and obligations, control and execution;
2) the difficulty or impossibility of a complete and reliable assessment of the actions of the functional service or official from public positions;
3) restrictions in the implementation of the principle of unity of command, putting the principle itself into question;
4) the predominance of current, operational issues that are urgent and easier to form over promising and strategic ones due to excessive concentration of powers at the top level of management.
So, the current difficulties of modern enterprises are largely related to inefficient management: a high concentration of decision-making power remains with the management, there is no long-term strategy for personnel, an aggressive management policy towards workers and trade unions remains.
Enterprises where all proposals, usually solved in functional departments, must be transferred to a higher level, i.e. it is not uncommon to have a decision only through the central office. In fact, many issues are decided by the head himself according to the principle of subordination "director - functional departments" and "functional departments - enterprise management"; the disunity of the structural divisions of the administrative apparatus, caused by the fact that their work is aimed at performing a certain function, does not achieve a common goal with certain final results.
The disadvantages of management in the traditional structure are related to the fact that existing organizations mainly have vertical links, while horizontal links between structures are difficult and officially “not spelled out”. To solve this problem, a block approach is used to design the organizational structure of management in organizations, taking into account not only vertical, but also horizontal links. The block center of horizontal communications is endowed with a set of coordinating tasks and functions, which, along with the organization of production or trade, can perform tasks to improve the management of production or trade and, together with the information and computing service, constitute the block center of horizontal communications, which is directly subordinate to the director of the enterprise . In our opinion, this approach creates additional work for the head of the organization, as it expands the scope of control and thereby complicates its activities.
In the early 1990s, centralized regulation of labor remuneration was practically abolished, enterprises independently began to solve the issues of organizing wages, the number of personnel, organizing and rationing labor. Direct state regulation was limited to the establishment of a minimum wage and the determination of wage rates for workers in the public sector. Giving enterprises the right to independently establish systems and wage rates was a justified decision, since in a market economy they became fully responsible for their financial and economic situation, including for the social protection of their employees. Many business leaders are only taking the first steps towards reforming wages based on the principles of the price of the labor force that is formed in the labor market. To develop this process, new legislation was required - the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, adapted to a market economy (the old Labor Code of the Russian Federation no longer reflected the changes that had taken place in the social and labor sphere). But so far, some industries have not developed labor standards that take into account the new market realities.
Since the objectives of privatization were unclear, changes in the organizational and legal form of enterprises had little effect on the internal organizational structure of management: the general meeting of shareholders more often confirmed the transfer of managerial functions to former managers under the name of the executive directorate or board of directors.
So, until now, in many organizations, personnel departments are structurally separated from departments of the organization of labor and wages, departments of labor protection and safety, legal services and other departments that perform the functions of personnel management, which is reflected in the typical management structure (Scheme. 2.2) .
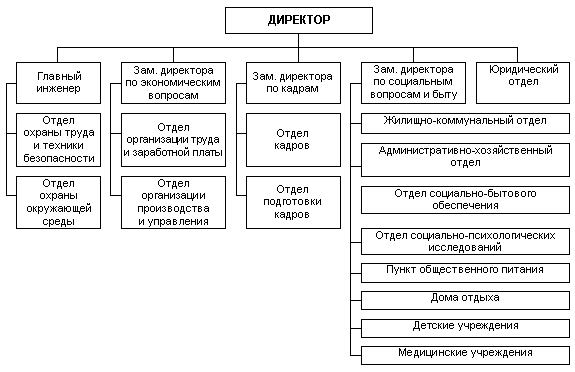
Scheme 2.2. The current organizational structure of the personnel management system in the organization
Each division solves independently or jointly with other divisions the tasks of personnel management. At the same time, a number of tasks in such organizations are not taken into account at all. Among them, for example, the analysis of human resources and staffing needs. Thus, human resources departments are not the coordinating center of personnel work in the organization. Therefore, they do not meet the requirements of the personnel policy, their activities are mainly limited to solving the issues of hiring and dismissing employees, drawing up personnel documentation. The structure of personnel departments, their qualitative composition does not correspond to the tasks of implementing an active personnel policy.
The traditional model of personnel management in a market economy, which cannot cope with the tasks of competition in all its manifestations, including the struggle for the quality and professionalism of the workforce, is undergoing a dramatic change today. The system of motivation and incentives for employees becomes much more complicated, the time frame for hiring is reduced (short-term contracts, bankruptcy of enterprises, seasonal work), material incentives for employees are strictly linked to the profits received. The prevailing point of view is that the decisive prerequisite for competitiveness is human potential. In this regard, it is necessary to create new management structures, the main features of which are:
1) focus on a highly skilled and proactive workforce integrated into the production system;
2) the continuity of the process of enrichment of knowledge and qualifications;
3) flexibility of labor organization;
4) delegation of responsibility from top to bottom;
5) partnerships between the participants in the production;
6) a new organizational culture focused on employees.
The specific place and role of departments - carriers of personnel management functions - in common system management of the organization are determined by the place and role of each specialized division for personnel management and the organizational status of its immediate supervisor (this organizational status is confirmed by a set of powers and responsibilities determined by the position of the first head of the organization in relation to the personnel service).
CONCLUSION
Starting from 1995, against the backdrop of a rise in the cost of resources and a sharp reduction in the possibility of raising prices for manufactured or sold products, the overload of the operational activities of the top management of the enterprise remains. Changes in the internal organizational structure are largely chaotic, when many units are created for non-economic reasons (for example, in order to retain a certain leader, they increase his formal status); at the same time, the reduction of design services continues. The logic of such transformations has come up against the high inertia of the existing models of enterprise management: the negative impact of layoffs is increasing, the planning function is forgotten, the influence of a well-coordinated team on increasing labor productivity, etc. In the new economic conditions, when enterprises must be consumer-oriented, qualitative paradigm changes are needed. personnel management systems, the creation of an integrated personnel management system, which are dictated by the following circumstances:
1. A more careful selection of workers is needed, taking into account the characterological and physical features, increasing the load on each employee, the optimal distribution of employees by workplace. Reducing the number of personnel is the most important lever for increasing the efficiency of production in a transitional economy.
2. Decrease in the number of employees, which should be compensated by a greater intensity of labor, and, consequently, by a higher qualification of workers. In this regard, the responsibility of the personnel department or the personnel management department increases in choosing the directions for the qualification growth of employees, in improving the forms of training and stimulating their work.
3. Implementation of the restructuring of the personnel service, which entails an increase in the role of all levels of management in personnel management and necessitates a radical restructuring of the activities of all departments and the creation of a multifunctional personnel service.
In the new conditions, the personnel management system, oriented towards the strategy of cooperation and the development of contractual relations, deserves attention, when the main emphasis in management needs to be shifted to the unique competitive advantages of personnel and the internal company culture created by a focus on human resources. This approach is based on the restructuring of enterprises.
LIST OF USED SOURCES
1. Grachev M.V. Superframes. Personnel management in an international corporation. - M.: "Delo", 1993. S. 191-193.
2. Dessler G. Personnel management / G. Dessler. - trans.9th English ed. D.P. Konkova; Ed. I.M. Stepnova. - M., 2004. - 799s.
3. Egorshin A.P. personnel management /: textbook for student universities on special “Personnel management” and “organization management”. - N. Novgorod, 2005. - 713 p.
4. Mordovin S.K. Personnel Management. Modern Russian practice: textbook for example “Management” / S.K. Mordovin. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2005. - 302 p.
5. Spivak V.A. organizational behavior and personnel management / V.A. Spivak. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2000.







