In this article, we will talk about various types suspensions used on cars, we will talk about them design features, pros and cons of operation in each case. Suspension design is to remove four of the six possible "degrees of freedom" and leave the remaining two - the rotation of the wheel, for movement and its vertical movement for our comfort on bumps.
In practice, this is impossible, and is primarily due to the lack of absolutely rigid materials. It is very difficult to completely eliminate the possibility of rotation about the transverse and longitudinal axis. Constructors independent suspensions in practice it has been found that it is better to allow camber to change, but make it equal and opposite to body roll, as this keeps the wheels upright when cornering. Of all the types of suspension used in the 20th century in car designs, only six basic solutions have now gained popularity and practicality.
These are multi-link, double levers, MacPherson, trailing arm, trailing arms connected by a transverse beam, torsion beam. Of these elements, only the last three (trailing arms connected by a transverse beam, trailing arms and torsion beams) are used only for the rear suspensions of front-wheel drive vehicles, and the rest can be used both in front and behind, for any of the wheels of the car.
Unlike the others, "trailing arms connected by a transverse beam" and "torsion beam" are not entirely suitable for independent suspension, they are also called "semi-dependent" (the vertical movement of one of the wheels affects the movement of the opposite).
Of the rarely used suspensions, without a doubt, the oldest is the axle beam, on each side of which a wheel is installed. Now they are used as a suspension of cars on spar frames (in other words, they write in the catalogs that this is a "rigid axle" or "dependent suspension"). Such suspensions are used not for comfort, but so that they serve for a long time when operating a car on rough terrain (or outright off-road).
MacPherson suspension
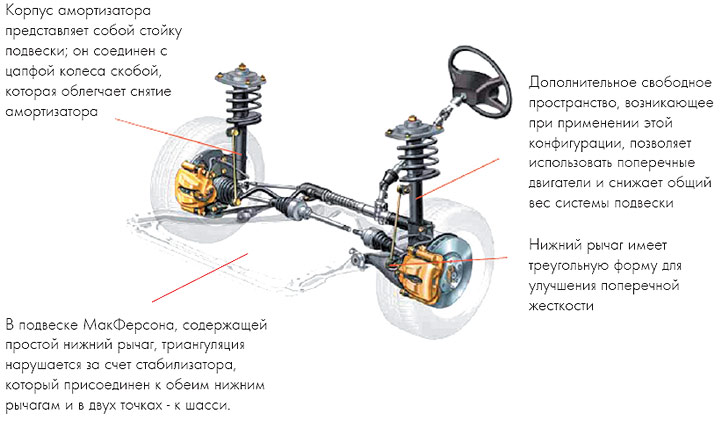
More spatial and structurally efficient design than double wishbone suspension (in other words, it became possible to install transverse motors more power and new boxes for cars with small dimensions). The system transfers loads to the body frame through three separate and conveniently located points (the upper pivoting "turret" of the strut itself and two points of attachment of the levers). This makes it possible to place the engine without interference top supports racks.
The suspension is obtained by connecting the lower part of the telescopic shock absorber strut to the steering knuckle of the wheel hub. The lower part of the rack is located transversely to the protruding part of the lower arm or a pair of individual arms.
The MacPherson strut provides a high roll center - usually desirable - and because the strut is long, there is little change in camber during vertical travel or body roll.
MacPhererson has two drawbacks.
1. The roll center can move a large distance from its static position during a turn, which can lead to handling problems.
2. Steering the wheels attached to the struts causes the struts to turn, which increases the effort applied to the steering and requires the use of a low friction top rotator. The MacPeherson type suspension is used on VAZ vehicles with front-wheel drive from eights to the present.
Behind this system rarely used, in the front it is used in the vast majority, even brands such as Jaguar have switched to it.
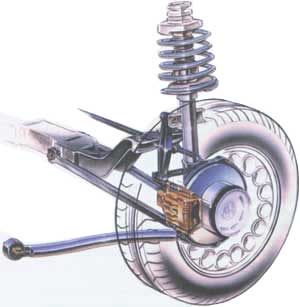
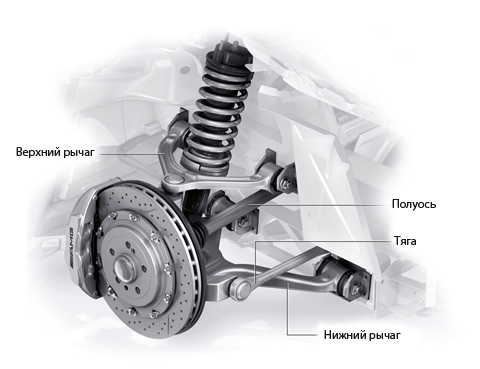
Rear suspension - MacPherson strut with multi-link mechanism. The strut holds the wheel vertically, the large trailing arm provides longitudinal fixation, and the two transverse arms fix the lateral movement of the wheel and ensure wheel alignment.
Usually MacPherson strut suspension uses coil springs mounted around the shock strut, but this is not the only way. In the past, for example, Fiat used MacPherson struts for the rear suspension, which elastic element one wide leaf spring mounted from below was used.
It has been found that setting the springs slightly offset from the damper reduces the "stiffness" problem when the vertical forces acting on the wheel are small. "Rigidity" - the tendency of the strut to not move until a threshold force is exceeded and then start moving unexpectedly - can lead to an unpleasant feeling of stiff suspension on flat roads. 
Front suspension. with widely spaced lower control arms and steering in the normal position, well hidden for safety behind the transversely mounted engine.
Widely spaced double wishbone front suspension with extended knuckle arm. Coil spring and telescopic damper installed separately (gives additional features in setting).
The suspension consists of two bifurcated arms located one above the other, the bifurcated sides of which are attached to the body, and the opposite ends are hinged to the upper and lower parts of the pivot pin. Hub front wheel can rotate around two hinges when rotated.
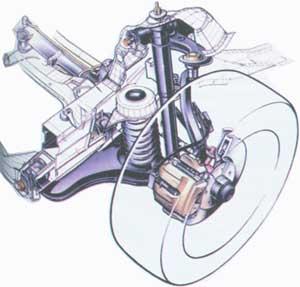
Usually only one of the levers may be bifurcated, the other may be a simple lever. If the arms are the same length, then when the body rolls in a corner, the camber angle is the same as the roll angle and stability can be severely affected. Therefore, levers usually do various lengths, upper arm Briefly speaking. This causes a slight change in camber during vertical wheel movements, but with body roll in corners, the change in camber can actually be eliminated, at least on the heavily loaded outer wheel relative to the center of the turn.
Suspension geometry double levers can be changed not only by changing the length of the levers, but also by the angle of inclination of the levers relative to the horizontal plane, when viewed from the front stationary car. The axles about which the arms rotate and which pass through the arm mounts to the body may be slightly inclined relative to the horizontal plane, and sometimes the arm mounts may also be moved forward or backward in order to create vertical forces (against nodding and yaw) acting on body under braking and acceleration, or "tweak" the geometry to obtain the preferred camber change during a critical manoeuvre.
For an accurate understanding of how the suspension will behave in certain situations and what length of levers is needed, computers and computer-aided design programs help. One of the advantages of this suspension is better cornering stability and control (we are talking about the front suspension) than the MacPherson strut, but it requires more "man hours" and costs for development and testing, which makes the car more expensive. That's why this species suspensions are used on D-class and higher cars and expensive "image" cars.
At the rear, such a suspension is now rarely used: either a shock absorber and a spring come in one set (MacPherson), or additional levers are used (multi-link system).

Low arm with widely spaced attachment points, a much smaller upper arm, the axis of which is high angle with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, swan neck of the pivot arm, for higher placement of the upper arm, compact spring around the upper section of the shock absorber, anti-roll bar roll stability, connected to the lower part of the shock absorber, articulated links, and ventilated disc brake with hinged links attached to its ends. This design leaves room for front wheel drive and is the most typical suspension on double levers.
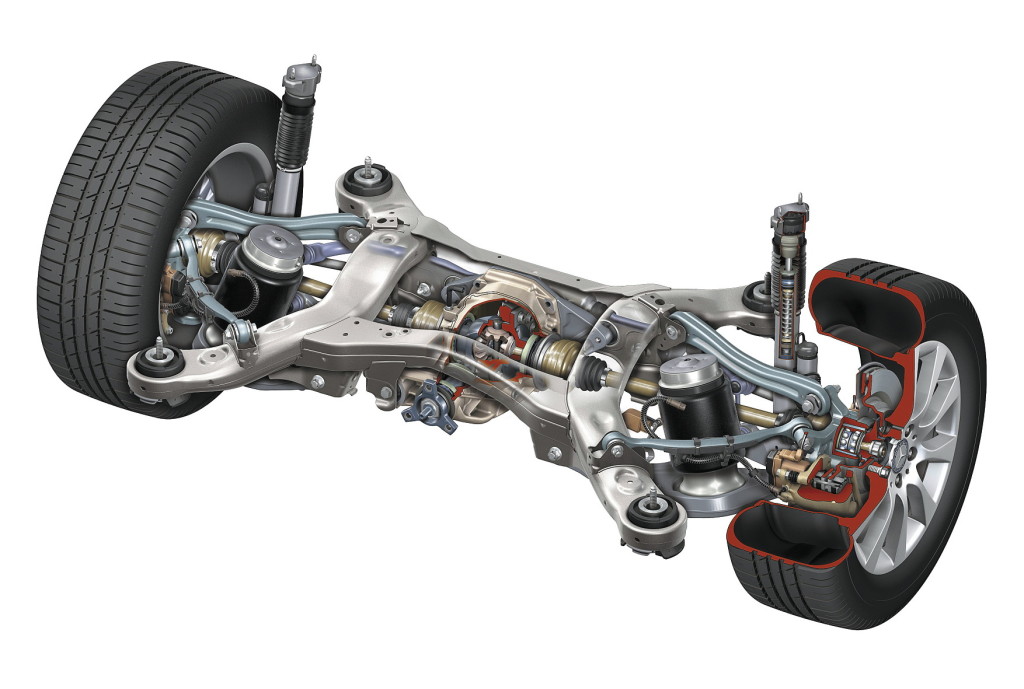
Multi-link suspension
similar to double wishbone independent suspension, with each arm cut into two separate links, sometimes with a fifth link added. Now it is used for the rear suspension of "executive" class cars and some "C" class cars.
Each link and link controls a specific aspect of the wheel's behavior, such as changing its camber or lateral movement. Links can be designed to work together and yet not interfere with each other, or they can be shaped to make room for the designer's need for body interior or other design features.
The design process is very complex, it can only be carried out with the help of a computer. Multi-link suspension is very expensive to manufacture and maintain, but it is the most "comfortable" for all passengers. A large number of links, silent blocks and hinges perfectly absorb shocks during a sharp collision with obstacles. All elements are mounted on the subframe through powerful silent blocks, which greatly increases the sound insulation of the car from the wheels. Nevertheless, driving over rough terrain (over bumps and potholes) for this suspension is undesirable, because. can easily disable it, and maintenance of this type of suspension is relatively expensive.
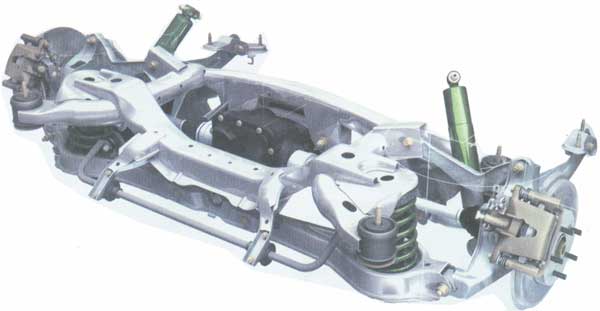
Rear independent multi-link suspension Jaguar X-Type
trailing arms
The easiest way to create an independent suspension is to attach a wheel to the end of a trailing arm that is pivotally attached to a beam attached across the car body, effectively a trailing arm suspension design.
This beam often takes the form of a transverse tube which acts as a subframe and absorbs all lateral forces. Construction on trailing arms x ensures that the wheels are parallel to the longitudinal line of the car all the time, apart from some bending of the levers and deformation of the connecting bushes. The wheels lean at a camber angle identical to body roll when cornering.
Some chassis designers welcome the resulting slight reduction in traction. rear tires, because it becomes possible to reduce excessive understeer, although this leads to a decrease in total strength cornering grip.
The bushings with which the levers are attached to the beam smooth out the shock and vibration transmitted from the wheel to the body, previously this type of suspension was used on B-class cars, which gave additional volume for the trunk and passenger seats. Now this suspension is rarely used, instead it is used torsion beam.
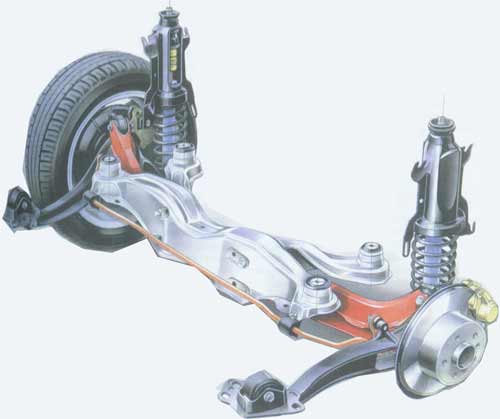
Rear suspension with trailing arms, vertical shock absorber spring struts.
One of the most widely used rear suspensions in small to medium sized front wheel drive vehicles, it first appeared in the mid 70s.
It consists of two trailing arms connected to a cross beam, part of the length of which is made in the form of a small letter H, which is pivotally attached to the body from above, and the wheels are attached from below. The crossbeam itself is hollow inside and can easily twist, allowing the arms to move up and down independently, while the remaining rigidity is sufficient to keep the arms at a constant distance.

The torsion beam is good in terms of space efficiency, even on small cars can be designed big trunk and a body for the convenience of passengers rear seats. It is also cheap to manufacture and maintain, and is easily installed on a vehicle on assembly lines.
One of the biggest drawbacks: the low comfort of rear seat passengers due to the additional vibrations transmitted to the body from the wheel and the inability to make "decent" sound insulation, which negatively affects comfort when driving long distances.
The suspension is applied on front wheel drive vehicles VAZ from 2108 to Priors.
Trailing arms connected by a transverse beam is one of the evolutionary directions of designers aimed at reducing the cost of car production (just like a torsion beam).
As with the torsion beam, this suspension allows you to make a large body for passengers and trunk, it is inexpensive to manufacture and maintain, and it is easy to install on a car.
Cons: hard to make comfortable ride for rear seat passengers on rough roads. And the vibration transmitted from the wheel through this suspension to the body, which adversely affects sound insulation.

rear ford suspension Fiesta
Of the rarely used suspensions, without a doubt, the oldest is the axle beam, on each side of which a wheel is installed. (rigid axle or dependent suspension)
To improve handling, reduce body roll in corners and improve ride comfort, a transverse torque rod (Panhard rod) is often installed with the axle beam.

The main task of this suspension is to withstand heavy off-road and heavy loads, it is also used to transport goods and is already mounted together with leaf springs. Cars on which this suspension is installed, as a rule, do not have high-speed qualities and comfort, but they have cross-country ability.
Often found on cars with a spar frame, as rear suspension, used on VAZ 2101 2102 2103 2104 2105 2106 2107 cars.
On all-terrain vehicles, it is usually installed front and rear.
- this is a complex of mechanisms due to which there is an elastic connection among the wheels and axles of the car, reducing the weight on the bearing parts, as well as adjusting the position of the body while driving.
Suspension is the transitional component between the car chassis and the road surface. The main task of engineers is to make sure that the suspension has a low weight and provides the necessary safety of the car while driving.
Double wishbone suspension
This type the chassis is a diagram of two levers, the connection of which is made using a steering knuckle. Usually, lower arm installed by means of silent blocks on the subframe, and the top one is installed in the same way, but already on. Such a scheme minimizes the buildup and travel of the wheels, as well as a small angular step during up and down vibrations. The shape of this design makes it possible for any axle to separately feel bumps and be vertical relative to the road, without transmitting vibrations to the opposite axle.
Multi-link suspension
The scheme of this suspension is a bit similar to the above and uses all of its best qualities. Such types of suspensions are more complex and expensive in structure, but they are distinguished by great plasticity and excellent coordination of the machine. A wide range of parts (silent blocks and ball bearings) dampen bumps better than others domestic roads. All parts are attached to the subframe. And impressive silent blocks between the parts and the subframe increase noise isolation. Multi-link independent suspension is used most often on S-class cars. It stabilizes the contact of the wheels with the most different types pavement and accurately regulates the car in minutes of direction change.
Advantages of multi-link suspension
- The independent activity of each wheel is free from the others;
- Light weight;
- Sovereign transverse and longitudinal adjustments;
- Excellent turning ability;
- Ideal option for all-wheel drive models auto.
The negative point is the complexity of the mechanism, and, of course, the high cost.
McPherson suspension
However, despite the improvement, dependent suspensions differ in one point: when accelerating, the car seems to “squat”, but when braking, the “nose” drops, i.e. balance is lost. In order to eliminate the imbalance, auxiliary elements of the direction are used.

Rear dependent suspension
The traditional example of this scheme is the rear suspension, in which the elastic elements are helical springs in the form of a cylinder. In addition, in order to increase the percentage of stable control, reduce the tilt of the body during maneuvers, and also improve the smoothness of the ride, the suspension is equipped with a transverse torque rod.
The downside is the impressive weight of the beam rear axle. And if the bridge is leading, then its mass is even greater, which becomes a serious deterioration in the smoothness of the course and leads to the appearance of oscillations.
Semi-independent rear suspension
This chassis with the participation of two trailing arms, in the center united by a longitudinal beam. This variety can be used exclusively in the back cars, but almost all of them are front-wheel drive.
The advantages of the design are ease of installation, small dimensions and low weight, and most importantly, the most optimal location of the wheels at an equidistant distance is ensured.
There is only one drawback: this design is unquestionably suitable for a passive rear axle.
The suspension of a car consists of many nodes that connect the body of the car and the wheels. It includes shock absorbers, springs, stabilizers, different levers, hinges and has a very important role in the behavior of the car on the road.
If the suspension turns out to be stiff, then you will feel every pothole on the road. But a rigid suspension will be "on hand" for motorists in sports cars, thanks to very good, as well as precise handling at high and low speeds. Soft suspension more suitable for a representative car, which is alien to sharp movements and stunning turns.
In this article we will talk about the suspension device for a MacPherson car and torsion bar suspension.
MacPherson Suspension Device
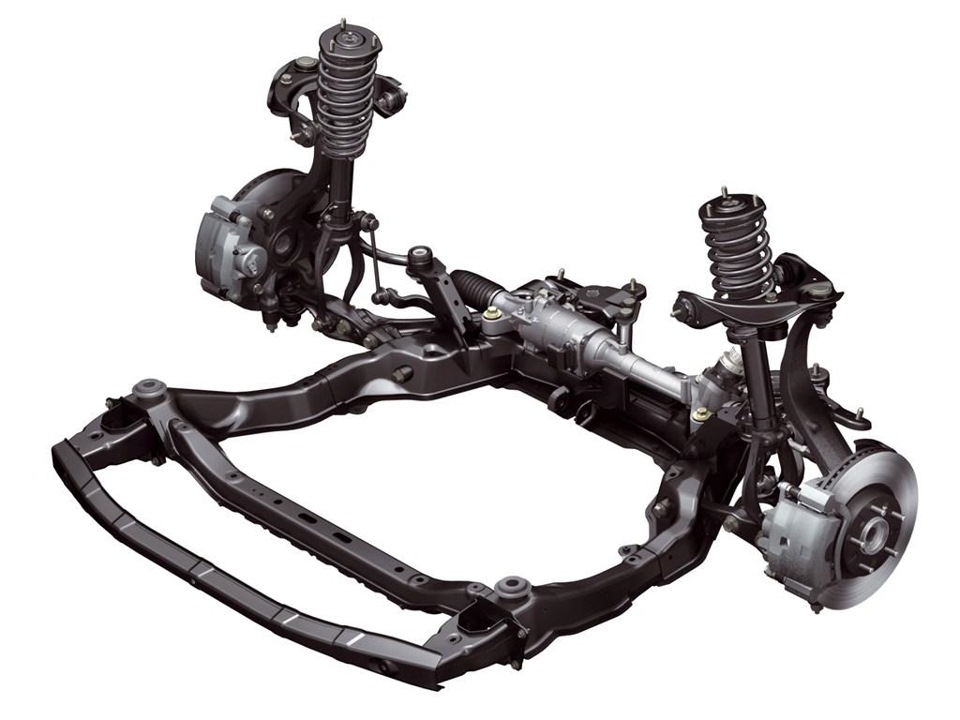
Suspension MacPherson (McPherson) - one of the most common types of car suspension (in English - MacPherson suspension). In this article, we will learn what a MacPherson strut suspension is, its main pros and cons, and also consider the scheme and design of this suspension.
The main structural element of the suspension is the suspension strut, which is why it also received the name "swinging candle". "Candle suspension" is mainly used for the front wheels. Version for rear wheels in English-speaking countries, the "Chapman suspension" is named after the Lotus engineer who developed it.
The use of the MacPherson strut made it possible to place the engine and gearbox transversely in the engine compartment and led to its widest use in modern front-wheel drive automotive industry.
The MacPherson strut consists of:
- stretcher
- wishbone
- rounded fist
- shock absorber
- anti-roll bar
Most MacPherson modifications include such structural elements: anti-roll bar, suspension strut, steering knuckle, wishbone and subframe. It is also possible to use a torsion bar as an elastic element.
The main bearing element of the suspension is the subframe.
Its fastening to the car body is carried out using silent blocks. The use of rubber-metal bearings reduces noise and vibration transmission to the body. The subframe acts as the basis for mounting the steering mechanism, supports wishbone and anti-roll bar.
On both sides with rubber bushings to the subframecross arms attached
right and left wheels. The levers are double fastened, which gives the structure rigidity in the longitudinal direction. To the other end of the transverse arm through ball joint swivel is attached.
Rounded fist
by means of a swivel attached to the steering rod, ensuring the rotation of the wheel. The upper part of the steering knuckle is fixed to suspension strut, and the lower one is connected to the transverse arm. It also contains stopping support and bearing assembly.
suspension strut
includes a spring and a shock absorber coaxially located withcompression buffer
. The upper part of the rack is attached to the wing mudguard with a rubber bushing, the lower part is connected to knuckle. Some auto manufacturers separate the spring and shock absorber into two structural elements.
Torsion suspension device
Torsion suspension- it's metal torsion shafts, working in torsion, one end of which is attached to the chassis, and the other is attached to a special perpendicularly standing lever connected to the axle. The torsion bar suspension is made of heat-treated steel, which allows it to withstand significant torsional loads. The basic principle of the torsion bar suspension is bending work.
The torsion beam can be located longitudinally and transversely. The longitudinal arrangement of the torsion bar suspension is mainly used on large and heavy trucks. On passenger cars, as a rule, a transverse arrangement is used. torsion bar suspensions, usually on rear wheel drive. In both cases, the torsion bar suspension provides a smooth ride, regulates roll when turning, provides the optimal damping of wheel and body vibrations, and reduces vibrations of the steered wheels.
On some vehicles, torsion bar suspension is used for automatic leveling, using a motor that pulls the beams together for extra rigidity, depending on speed and condition. pavement. The height-adjustable suspension can be used when changing wheels, when the vehicle is raised with three wheels and the fourth one is raised without the help of a jack.

The main advantage of torsion bar suspensions is durability, ease of height adjustment and compactness in width. vehicle.
It takes up much less space than spring suspensions. The torsion bar suspension is very easy to operate and maintain.
If the torsion bar suspension is loose, then you can adjust the position using a regular wrench. It is enough to get under the bottom of the car and tighten the necessary bolts. However, the main thing is not to overdo it in order to avoid excessive rigidity of the course when driving. Torsion bar suspensions are much easier to adjust than spring suspensions. Car manufacturers change the torsion beam to adjust the driving position depending on the weight of the engine.
The prototype of a modern torsion bar suspension can be called a device that was used in the Volkswagen Beetle in the 30s of the last century. This device was modernized by the Czechoslovakian professor Ledvinka to the design that we know today and installed in the Tatra in the mid-30s. And in 1938, Ferdinand Porsche copied the design of the Ledwinka torsion bar suspension and implemented it in mass production KDF Wagen.
Torsion bar suspension has been widely used in military equipment During the Second World War. After the war, automobile torsion bar suspension was used mainly on European cars(including cars) such as Citroen, Renault and Volkswagen. Over time, passenger car manufacturers have abandoned the use of torsion bar suspensions on passenger cars. cars due to the complexity of manufacturing torsion bars.
It's no secret that the suspension is one of the most important parts in a car that affects such important parameters like handling, ride and stability of the car as a whole. Today we will try to figure out what types of suspensions exist and for which cars they are best suited.
Theory
To begin with, we need to understand what exactly the suspension design affects? Initially, the suspension is responsible for the behavior of the wheel during compression and rebound. The ideal case is when the trajectory of the wheel always remains perpendicular to the road - it is in this case that the contact patch of the tire with the surface remains as large as possible. However, this is not always the case, as a rule, in the process of compressing the suspension, the camber angle of the wheels changes, and in the case of cornering, the wheel angle changes in a place with a body tilt. As you understand, in this case, this leads to a decrease in the contact patch of the tire with the surface. Thus, it is the structure of the car's suspension that directly affects the grip properties of tires.
The whole suspension modern cars can be divided into three groups of elements:
- guide elements - levers;
- elastic elements - springs and stabilizers;
- damping elements - shock absorbers.
All these elements ultimately affect the smoothness of the car, as well as its efficiency. Also, do not forget about the effect the suspension has on the level of vehicle roll. For this parameter in the suspension, not springs and shock absorbers are responsible, but levers. The center of the transverse roll, that is, the point around which the car body begins to roll, depends on their location.
One of the most important suspension parameters is the camber and toe:
- collapse- this is the deviation of the wheel plane from the perpendicular, which, in fact, is the roadway. If the upper part of the wheel is littered outward, then the camber angle is positive, if inward, it is negative.
- Convergence- this is the angle between the direction of movement and the plane of rotation of the wheel itself.
Based on these facts, we can conclude that designing a suspension is by no means the most trivial task. Engineers need a lot of time to find the right balance between strong rolls, handling and comfort. Now let's move on from theory to practice and look at the main types of suspension used today.
Practice
On this moment seven types can be distinguished various types pendants. For a better understanding, we will look at each type separately.
dependent suspension. This type of car suspension is one of the oldest, but nevertheless, it is successfully used to this day. Distinctive feature of this type of suspension - a rigid connection of the axles of the wheels by means of a bridge or an ordinary beam.
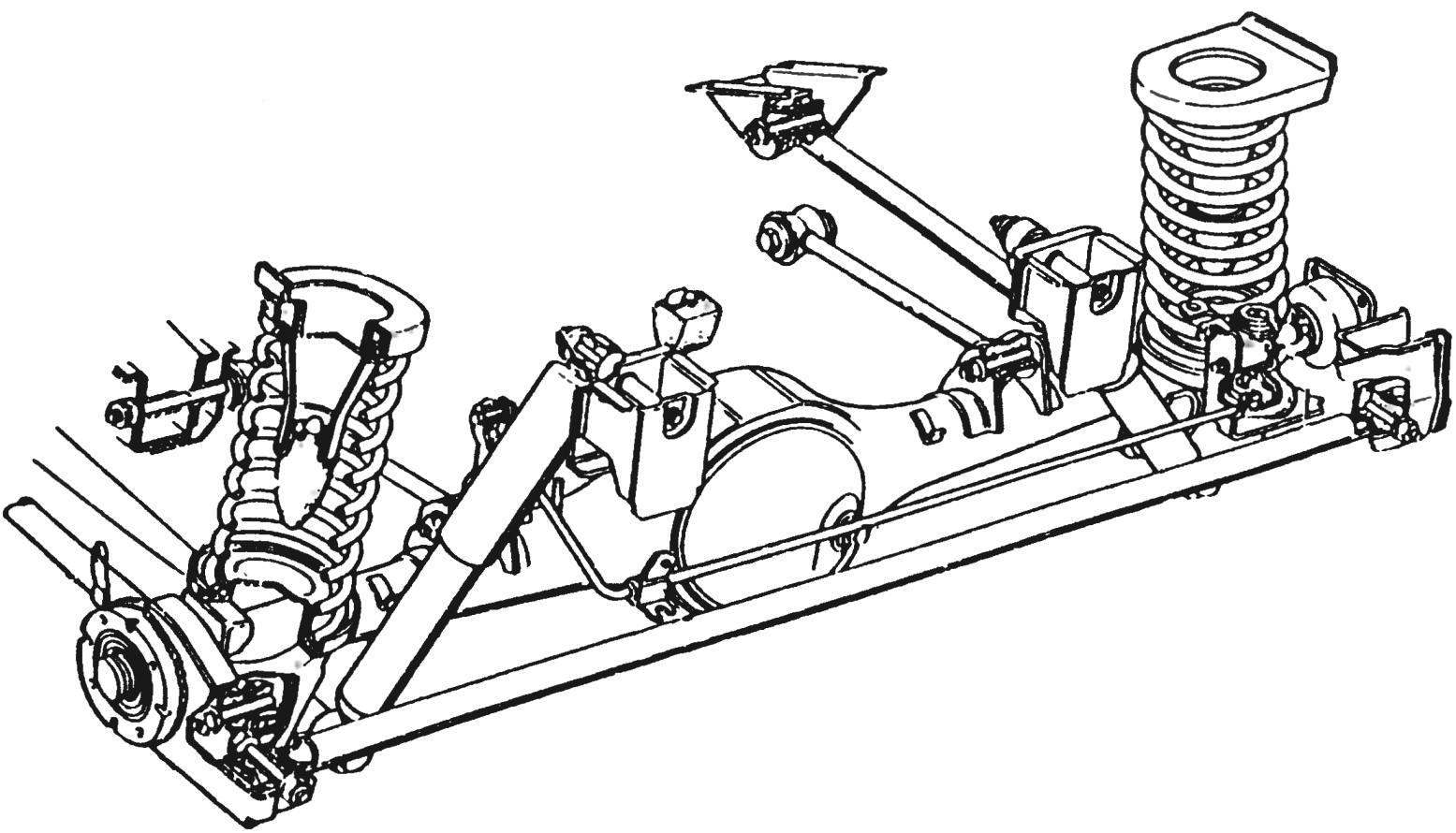
Initially, springs were used as elastic guide elements of the dependent suspension, but in modern counterparts a special cross member is used, which is held on the sides by trailing arms. Today, most often this type of suspension can be found on SUVs and inexpensive front-wheel drive cars.
Many people think that this suspension has no advantages over modern analogues, but this is not entirely true. The dependent suspension is very simple, has an extremely low weight and does not need camber adjustment. But there is also one significant disadvantage– instability of behavior on uneven surfaces, which can lead to skidding.
Semi-independent suspension (torsion-lever). This type of suspension has much in common with the previous version. But unlike the dependent suspension, the cross member between the wheels is not on the same axis of the wheels, but is shifted closer to the lever supports. In addition, the crossbar itself this case not only counteracts lateral forces, but also plays the role of an anti-roll bar. It is very easy to distinguish this suspension by the type of cross section, which usually has a U-shape.
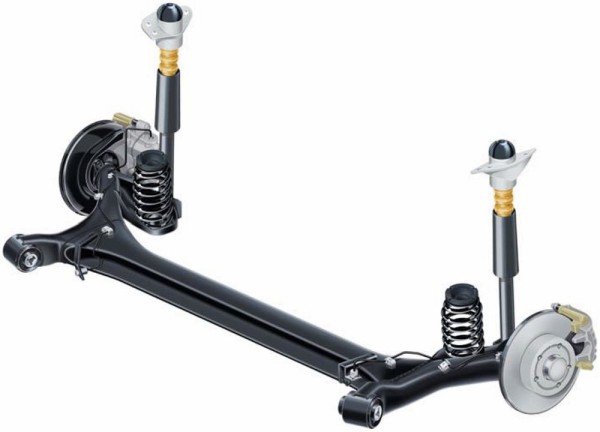

As in the case of dependent suspension, this type does not change the camber angle on a relatively flat surface. But as soon as the road gets worse or a turn is necessary, the cross member twists, thereby preventing the wheels from tilting.
At the moment, this type of suspension is the most popular and is used in many compact cars. Simplicity of design, stability on a straight road and solid cornering stability made it mega popular. The only significant drawback of this type is the need for more space for its placement under the bottom.
Trailing arm suspension. This type of suspension is the simplest representative of the so-called independent suspensions. Each of the wheels rests on its own lever, which, moreover, must counteract the longitudinal and lateral forces. You yourself understand how strong the lever must be in such a suspension.

During the operation of this type of suspension, there are a number of both positive and negative points. For example, the wheels in such a suspension rotate strictly in the longitudinal plane, which is excellent on a perfectly flat surface. But on the other hand, on uneven surfaces and during turns, the wheels roll along with the body, which reduces the grip of the tires.
It would seem, why such a clumsy type of suspension? The answer is tritely simple - this type of suspension takes up very little space on the bottom of the car, in addition, its design is very simple.
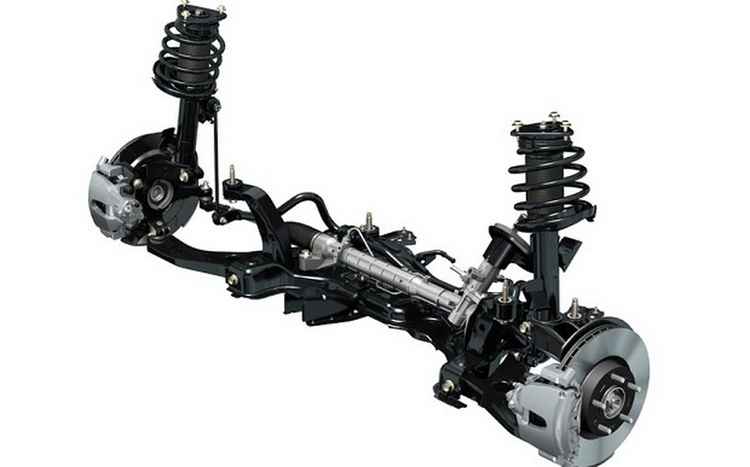
Double wishbone suspension. This type of suspension was developed in the 1930s of the last century, but despite this, it is still used in most sports cars. The wheel is attached to the body or subframe with two levers. In addition, usually the upper arm is always made a little shorter, which, at the moment of compression of the suspension, fills the upper part of the wheel inward. This, in turn, provides better grip of the wheel to the surface during cornering.

But this flexibility also has a downside. For example, during braking, the wheels also compress, resulting in poor contact. In addition, the suspension structure itself requires high altitude installation, for this reason it is mainly used only on the front axle.
MacPherson. This type of suspension is the most popular today. MacPherson design is very simple and compact, which allows you to give more space engine compartment. The design of this type of suspension consists of a lower transverse arm and a shock absorber strut, which plays the role of an upper guide element. This leads to the fact that this type of suspension has lost the ability to change the camber with a stable track. But when developing the next car on the MacPherson suspension, it is possible to initially set the camber. For example, by pushing the lower arm outward, you can get better grip in corners. And by moving the lever inward, you can ensure track stability, but worsen cornering behavior.

The main disadvantage of this type of suspension is the increased load on the shock absorber strut, as well as on the place of its attachment.
Suspension on "oblique" levers. This type of suspension is practically not used today, but nevertheless, there are still enough cars on our roads that were produced in the 1990s, when this type of suspension was super popular.
The structure of the suspension is very simple, as in the case of the trailing arm suspension, this type also uses two, but oblique levers. At the stage of development of the car, engineers had to choose the angle of inclination and the length of the lever in order to provide the desired kinematic properties of the suspension of the future car.

Most often, this type of suspension could be found on rear axle in cars concern BMW. Bavarian engineers immediately noted one very important property this suspension - in case hard braking, the body is pressed to the ground as much as possible, which makes the behavior of the car more predictable. In addition, by changing various parameters (which are described just above), you can influence the handling of a car, making it prone, for example, to oversteer.
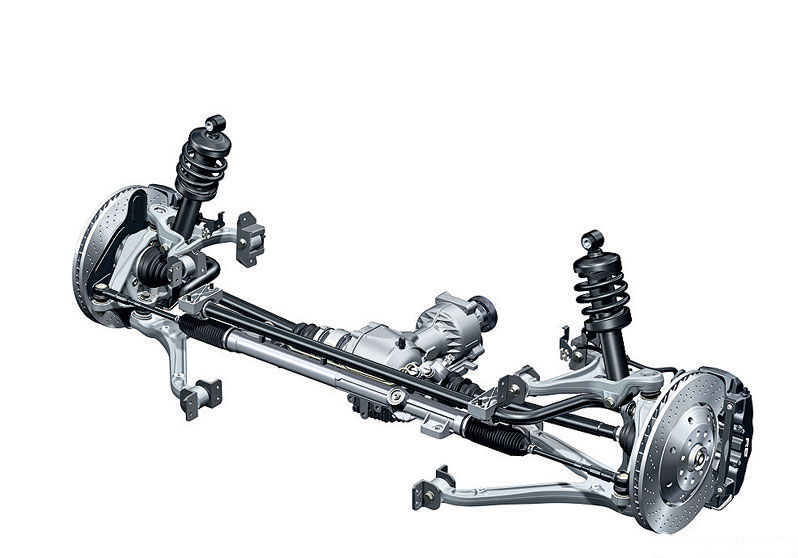
Multi-link suspension. This type of suspension was designed to combine the advantages of a double wishbone and a suspension with oblique levers. In other words, a multi-link is a double wishbone suspension, into which trailing arms are integrated, which should pull the wheel at the moment of compression. Usually this type of suspension is used on the rear axle. If the car is front-wheel drive, then it is adjusted to neutralize understeer, and if it is rear-wheel drive, then this type of suspension counteracts oversteer.

The main disadvantages of this type of suspension can be considered the high cost of construction and its complexity. For this reason, most often it can be found only in expensive cars.
Outcome
It is extremely difficult to sum up and say which of the suspensions is the best. All the described designs have the right to exist and are used by manufacturers to solve a certain range of problems.
- , 19 Oct 2015
The suspension is one of the most important components of a vehicle. It is to this node that the attention of the mass of engineers and designers is riveted. Types car suspensions are different, depending on the cost of the car, the drive and, of course, the segment that occupies the model. More on this later in the article.

Suspension system or car suspension - a set of mechanisms, components and parts that play the role of a connecting link between the road and the car body. The suspension performs the following functions:

- Physically connects solid bridges or wheels with the carrier system of the car - the frame or body.
- It supplies the carrier system with the moments and forces that arise in the process of interaction of the wheels with the roadway.
- Provides the desired nature of the movement of the wheels relative to the frame or body, as well as the required smoothness.
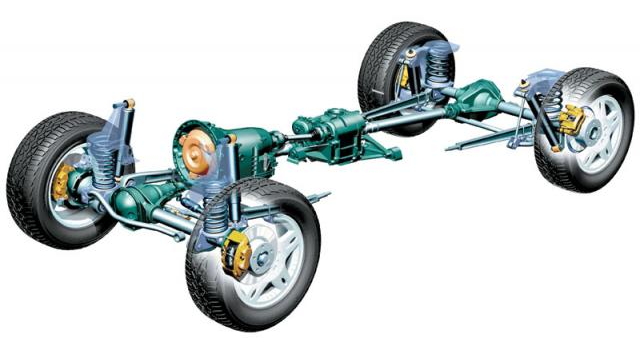
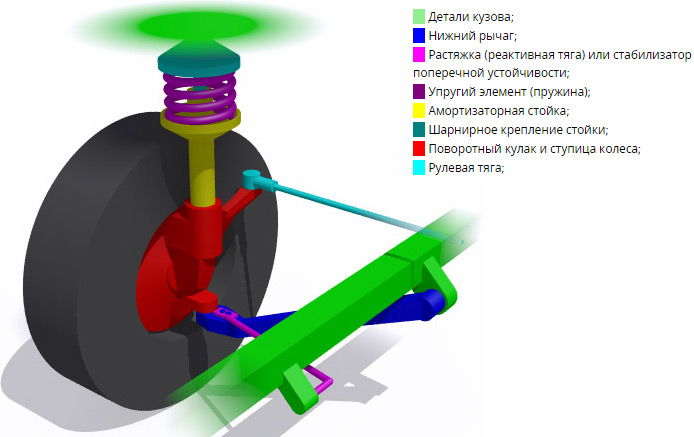
The main suspension components are:
- Resilience components.
- Force direction distribution components.
- Roll stabilization components.
- Extinguishing component.
- Fasteners.
There are many types of pendants. Some were used earlier, others are still used today, so we will consider those types that are in modern automotive industry received the most distribution.
MCPherson suspension, device, advantages and disadvantages
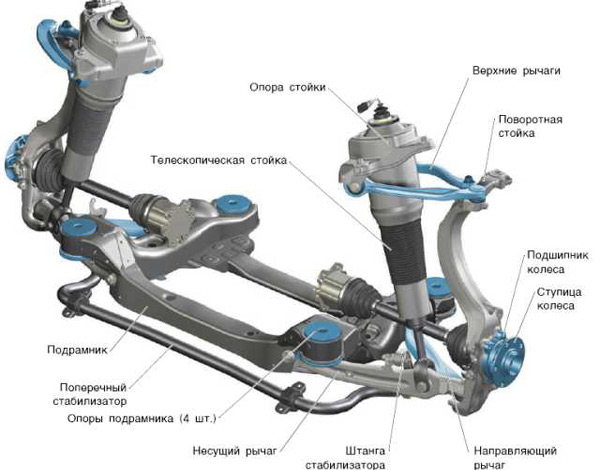
This suspension variation was developed by engineer Earl MacPherson in 1960. Named after the inventor. Its main components:

- Lever arm.
- Anti-roll bar.
- Block (consists of a spring element and a telescopic shock absorber).
Another name for a telescopic shock absorber is a "swinging plug" because it is attached to the body by means of a hinge and is able to swing when the wheel moves up and down.

This type of suspension has its drawbacks - a significant transformation of the camber angle, but it is very popular due to its simplicity of design, reliability and affordable price.

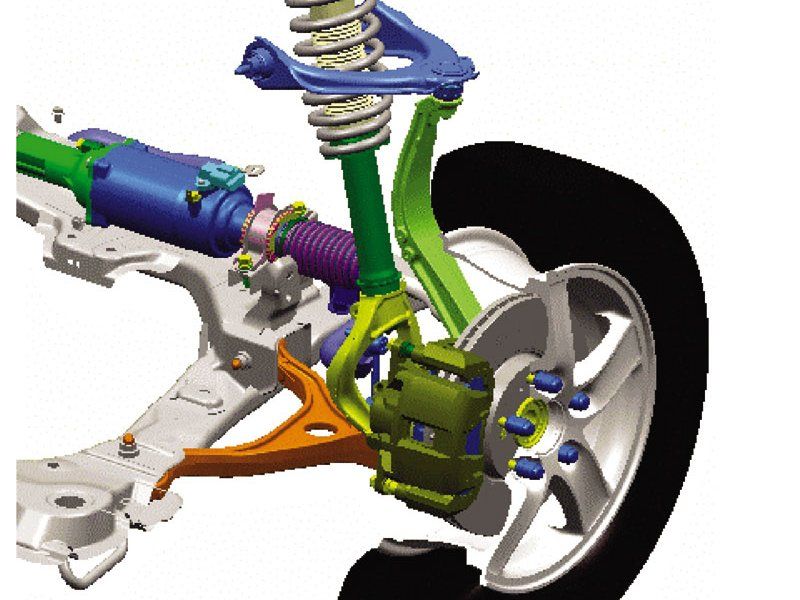
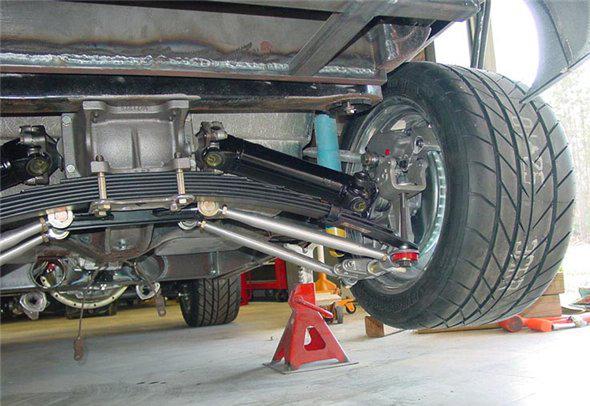
Double wishbone suspension, device, advantages and disadvantages
![]()
One of the most advanced designs. It is a suspension with two levers of different lengths (short upper and long lower), which guarantees the car minimal tire wear and excellent lateral stability on the roadway (transverse wheel movements are generally insignificant).
Consequently, each wheel perceives bumps and pits independently of the others - this makes it possible to maintain normal grip of the tire with the roadway and the greatest vertical relationship to the road.
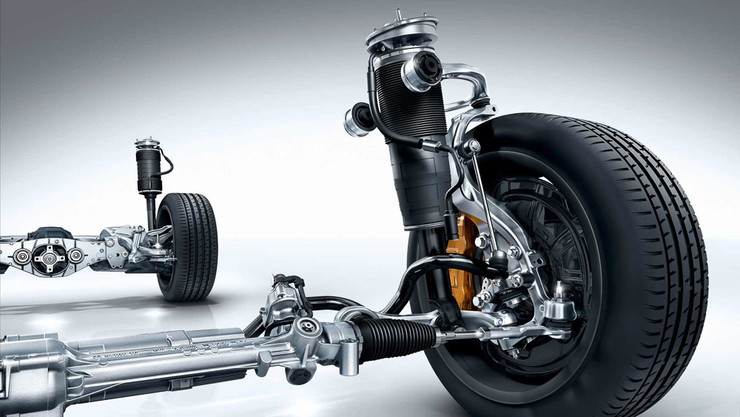
Multi-link suspension, device, advantages and disadvantages

This variation of the suspension is a bit like a two-lever system, but it is much more perfect and more complex. It is not surprising that all the advantages of the previous type were transferred to it. This is a set of hinges, silent blocks and levers mounted on a special subframe. Most of the "silent" and ball bearings provide not only excellent smoothness, but also perfectly dampen shocks during a sharp collision with any obstacle. In addition, they reduce the noise in the car from the wheels.

This arrangement allows the maximum better grip tires with any type of road surface, perfect handling and smoothness. Benefits of multi-link suspension:
- Optimum wheel turning.
- Small unsprung masses.
- Separate longitudinal and transverse adjustments.
- Independence of each wheel from the rest.
- Good potential in all-wheel drive.

The only, but significant drawback of the "multi-link" is the high cost. It should be noted that previously this type of suspension was used only on executive cars. Nowadays, even golf-class cars are equipped with it.
The suspension is adaptive, the device, the pros and cons of the suspension

Adaptive suspensions are fundamentally different from other variations. When creating such a scheme, the hydropneumatic suspension was taken as the basis, which was implemented on cars mercedes benz and Citroen. However, then it was quite heavy, primitive and took up a lot of space. Today, designers have got rid of all such disadvantages, and the only drawback of the adaptive suspension is based on its complexity.

Benefits of adaptive suspension:
- Automatic adaptation to any road surface.
- Adaptation for a specific driver.
- Forced damping.
- Excellent stability.
- High security.
- Wave buildup on high speeds and minimal body roll.

Different concerns apply their own adaptive suspension schemes, but their common features are the same. Any adaptive design includes the following components:
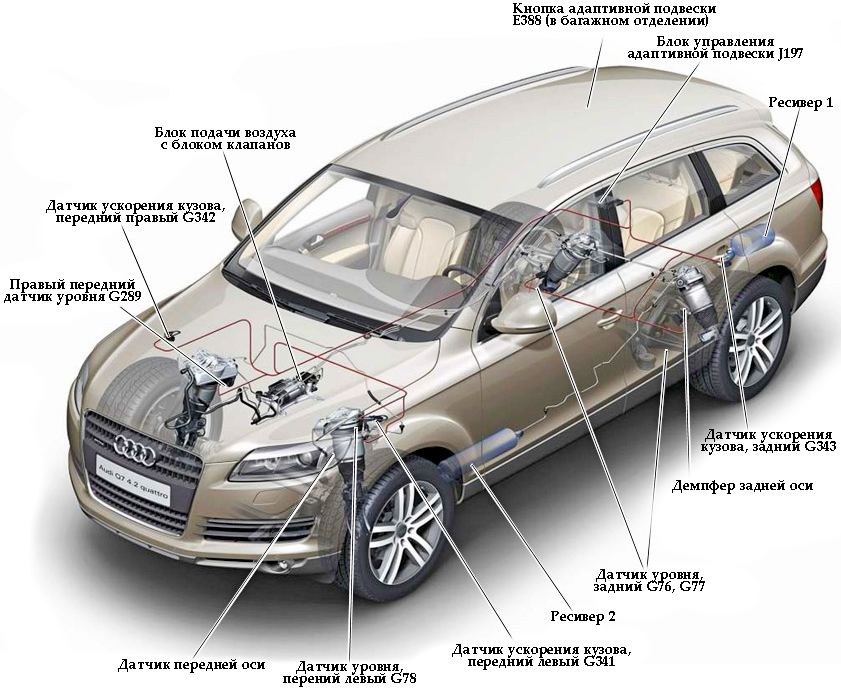
- Electronic sensors - clearance, rough roads and so on.
- Running section control unit.
- Active shock absorbers.
- Anti-roll bars (adjustable).

The control unit analyzes the information received from the sensors, and then sends commands to the shock absorbers and stabilizer. All this happens almost instantly.

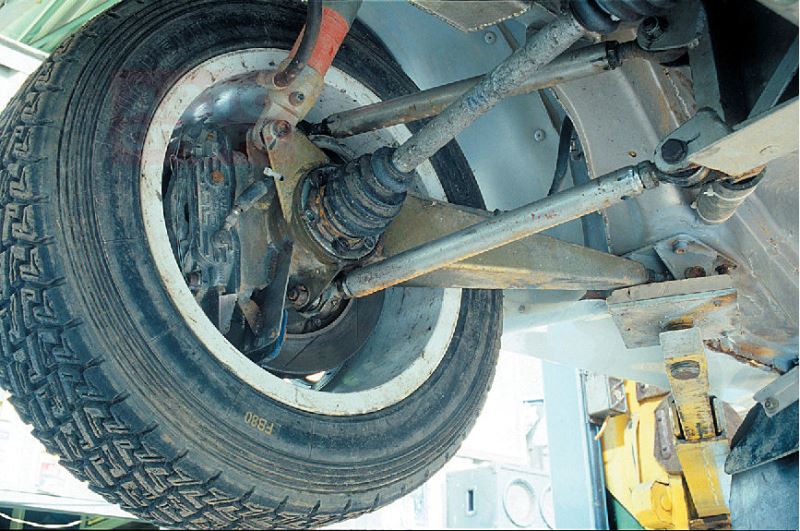
"De Dion" suspension, pros and cons

This pendant is also named after the inventor (like MCPherson), who was the Frenchman Albert De Dion. The purpose of this type of suspension is to minimize the load (by separating the main gear housing) on the rear axle of the car. If earlier it was attached directly to the bridge beam, now the crankcase is fixed on the body itself.

This makes it possible to transmit torque by means of semi-axes, which are fixed on the CV joints. However, it was not possible to get rid of the main shortcomings of all dependent variations of this suspension. For example, it is virtually impossible to slow down “without pecking”, and in the case of abrupt start the car simply "crouches" on rear wheels. Despite attempts to eliminate these shortcomings through the installation of additional components (guides), the unbalanced behavior of the machine remains the main problem.

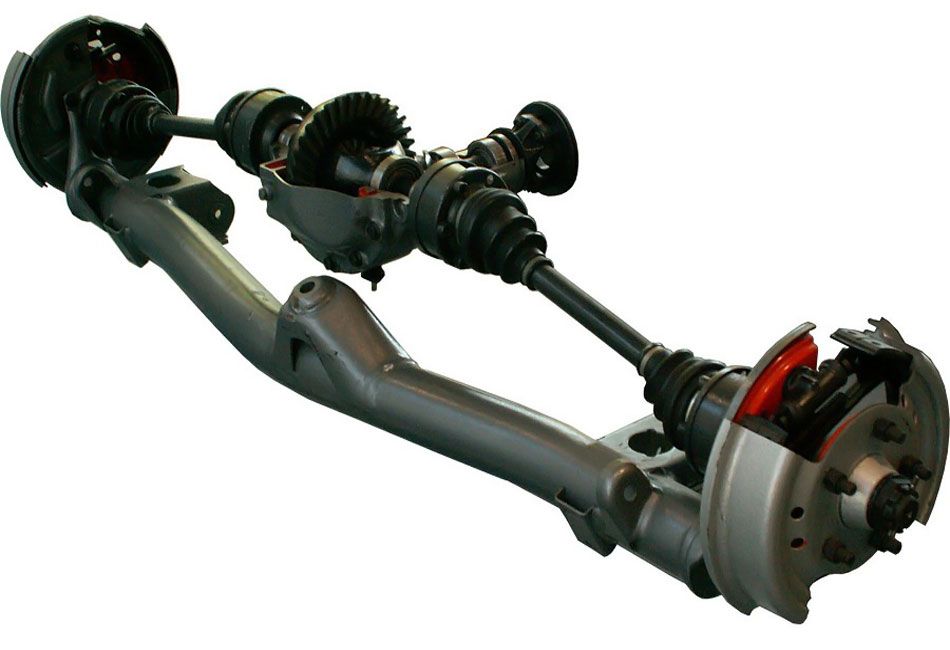
Rear dependent suspension, classic suspension
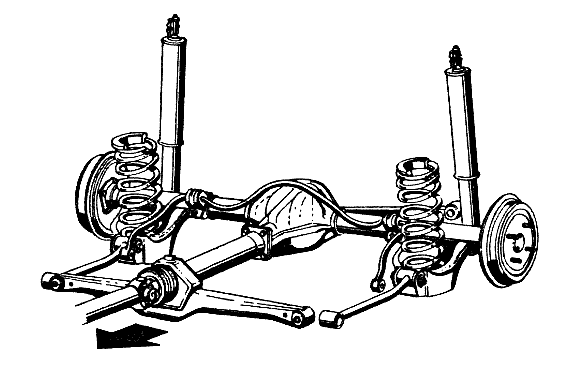
This type is a characteristic feature of the "classic" Zhiguli. A feature of this design is cylindrical helical springs, which play the role of elastic components. On these two springs, the rear axle beam “hangs”, which is fixed to the body by means of four trailing arms.
This set is complemented by reactive transverse bar, the purpose of which is to improve handling performance and dampen body roll.

Ride and comfort leave much to be desired, as a result of the heavy weight of the unsprung masses and the rear axle itself. This is especially true when the rear axle turns out to be the leading one, since the crankcase is attached to the beam main gear, reducer and other elements.
Semi-independent rear suspension, device, advantages and disadvantages
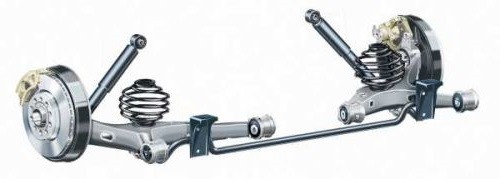
This scheme has received widespread and is used in the design of many modern four-wheel drive vehicles. It consists of two trailing arms attached in the center to the crossbar. This type of suspension has many advantages:

- Light weight.
- Small sizes.
- The best wheel kinematics.
- Ease of repair and maintenance.
- Significant reduction in unsprung masses.
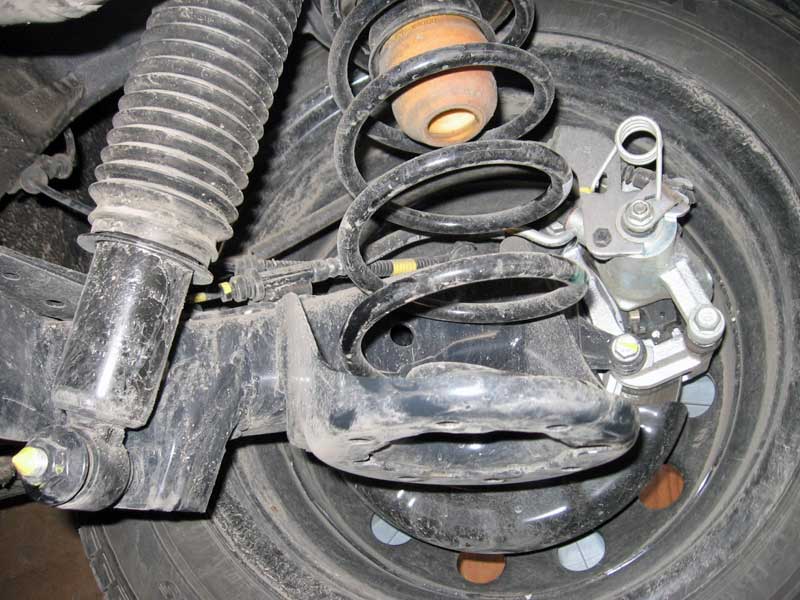

The disadvantage of this design is the inability to use it on rear-wheel drive vehicles.
SUV and pickup suspension, device, advantages and disadvantages

IN different models jeep designers are coming different ways. It depends on the purpose and weight of the SUV. There are three suspension options available:
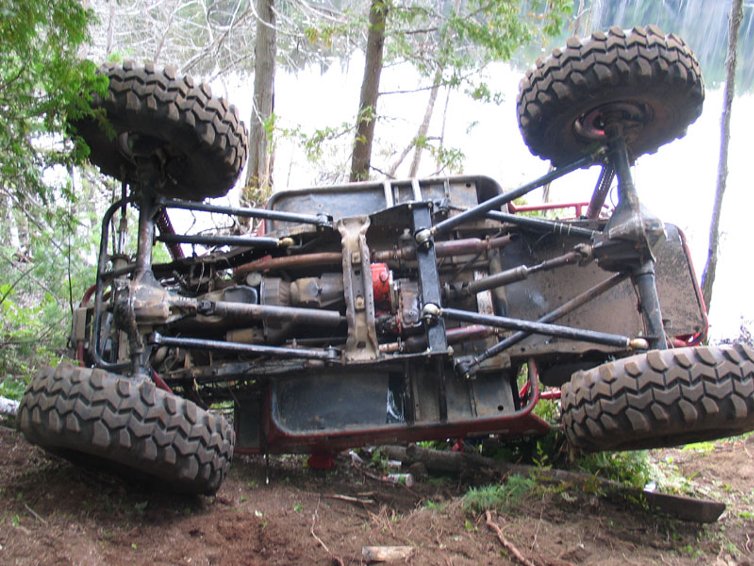

- Fully dependent suspension.
- Completely independent option.
- Front independent and dependent rear circuits.

The rear axle, as a rule, is equipped with spring or spring suspension in combination with solid rigid axles. Springs are used to create heavy jeeps and pickups, as they are unpretentious, reliable and able to withstand heavy loads. In addition, such a scheme is quite cheap, as a result of which some budget cars are equipped with springs.
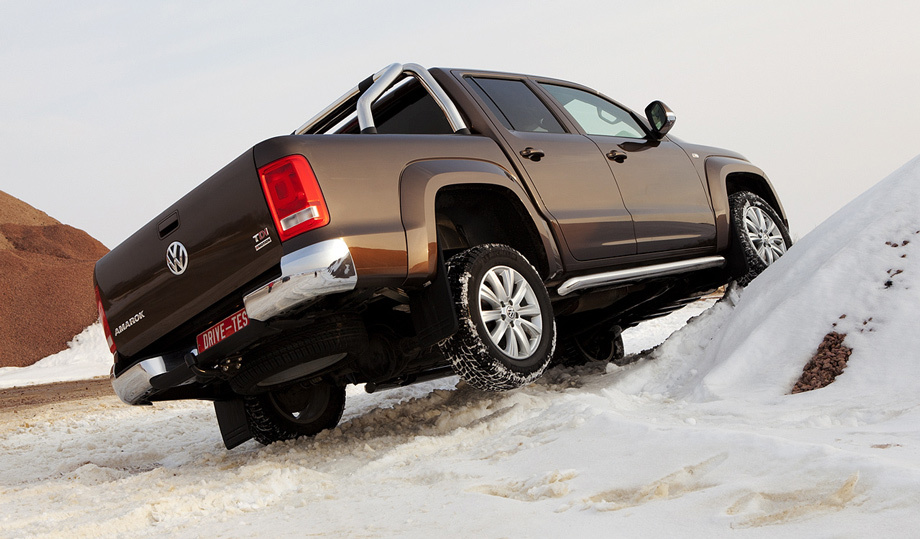

The spring circuit has a long stroke and softness. It is more focused on comfort and is mounted on light jeeps.

In the front axle, as a rule, dependent spring or torsion schemes are used. Some jeeps are equipped with rigid solid bridges, but such a solution is rarely seen in our time.

Truck suspensions, device, advantages and disadvantages
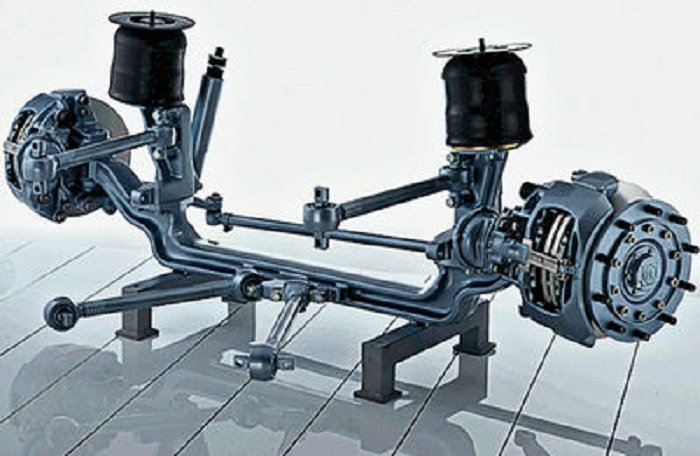
Trucks usually use a dependent design with shock absorbers hydraulic type and longitudinal or transverse springs. Due to its simplicity, this suspension is widely used in production to date.

Longitudinal springs are fixed in the body brackets. The bridge is also suspended from the brackets. Shock absorbers are attached to the rear axle beam. The main role in this design is given to the springs that support the bridge, connect the body to the wheel and act as guiding components.








