What is Euro-3? Car compliance with this standard
Question: Dear Alexander Mikhailovich? What parameters determine whether a car belongs to Euro-3 standards? Where can I read or watch them?
Answer: I am a philologist by education. The EURO-3 standard is something related to exhaust gases. There is some place where they take such certificates. In general, when a car is released at the factory, it already has equipment in accordance with certain exhaust parameters. However, given your ignorance of what it is, I would not advise you to buy a car abroad. They inflate. And there are no benefits for students.
Question: We are resettling for permanent residence in Russia under the Program for Assistance in the Voluntary Resettlement of Compatriots (Decree of the President of the Russian Federation No. 637 of 06/22/2006). According to the discount, we can take one car with us, it corresponds to the Euro 3 class. I would like to clarify: we have an elongated Sprinter cargo-passenger 9 seats, are there any restrictions on the number of seats and total weight vehicles imported under this program.
Answer: The decision does not say anything about the type of car. I believe that you can import the car you specified.
Euro 3 - environmental standard governing the content harmful substances in the exhaust gases of vehicles with diesel and gasoline engines. It was introduced in the European Union in 1999 and replaced by the Euro 4 standard in 2005. All vehicles, produced or imported to Russia since January 1, 2008, must meet the requirements of the Euro III standard. In Kazakhstan since January 1, 2009.
Modification of the design of a car that meets the requirements of Euro II, under Euro standard III usually results in a change to the exhaust system and engine management system. Also, the engine power of the car is usually reduced.
Central Research Automobile and Automotive Institute(NAMI) and Rostekhregulirovanie developed a table. on the basis of which it is necessary to determine whether the machine complies with the environmental class "Euro 3" or not. The table was developed by order of the Ministry of Industry and Energy and the Federal Customs Service.
The table shows in which countries and when the Euro 3 norm was introduced by law.
Starting from the current year of manufacture, cars are automatically considered certified and no certificates or documents are required for them.
For used cars, in accordance with the table, a Euro 3 Standard Certificate is required. Without this certificate, customs officers are not entitled to issue a PTS.
List of documents for issuing a EURO 3 certificate:
1. Statutory documents (for individuals- copy of the passport)
2. Vehicle data (make, WIN, body number, engine number, etc.)
3. A document confirming compliance with EURO 3 or higher (TUV type certificates and other foreign TCP or expert opinion.) For old cars - a document on re-equipment.
Table with information on the compliance of cars with environmental emission classes, depending on their year of manufacture and country of origin
*Note: European Union includes: Austria, Belgium, UK, Hungary, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Ireland, Spain, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Finland, France, Czech Republic, Sweden and Estonia.
On the introduction of environmental class 3 (Euro-3)
The Federal Customs Service informs interested citizens, as well as participants in foreign economic activity, that in accordance with clause 14 of the Government Decree Russian Federation dated October 12, 2005 No. 609 “On approval of the special technical regulation “On requirements for emissions automotive technology, put into circulation in the territory of the Russian Federation, harmful (polluting) substances" from January 1, 2008, in relation to automotive equipment put into circulation in the territory of the Russian Federation, environmental class 3 (Euro-3) is introduced.
Ensuring compliance with this requirement provides for the determination by the customs authorities of the Russian Federation of the environmental class of the vehicle, based on the information contained in the certificates of conformity, "Vehicle type approvals" and "Conclusions on the conformity of the vehicle with the requirements." The specified information is formed by the Federal Agency for technical regulation and metrology (Rostekhregulirovaniye), are updated monthly and officially sent to the Federal Customs Service of Russia and the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia.
For citizens who want to carry out customs clearance of the car in the optimal time, you need to know an identification number(VIN), make and year of manufacture of the purchased vehicle. Based on the knowledge of these criteria, any citizen can independently determine the environmental class of a car for himself by resorting to the official website. federal agency on technical regulation and metrology (www.gost.ru/wps/portal). If the environmental class of the checked vehicle corresponds to Euro-3 and higher, then when it customs clearance additional supporting documents are not required.
If it was not possible to determine the environmental class of the car, then in this case the citizen should contact the certification bodies that carry out work to confirm compliance with the requirements of a special technical regulation. With their addresses in each federal district can be found on the official WEB-server of the Federal Customs Service of Russia in the section "Information for participants in foreign economic activity" (www.customs.ru/ved_info/baza).
The Russian customs service, which is the state regulatory body, warns that if the environmental class of the vehicle (Euro-2 and below) does not comply with the requirements of the technical regulation or if its environmental class is not confirmed (not lower than Euro-3), the vehicle passport will not be issued by the customs authorities.
Customs clearance vehicles customs bodies of the Russian Federation is carried out and will continue to be carried out in strict accordance with the current customs legislation.
Press Service of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation
http://puchkov.net
Promised two years waiting
Under the chiming clock and the clink of glasses, not only came to Russia New Year, but also the long-awaited standard Euro 3. According to technical regulations"On the requirements for automobile and aviation gasoline, diesel and marine fuel, fuel for jet engines and heating oil", the transition to Euro-3 should have taken place since 2009. Now Russia should have already used the Euro-4 standards and prepared for the introduction of Euro-5, but the plans, as often happens, significantly diverged from reality and timing had to be pushed back 2 years.What is Euro-3?
Euro-3 standard (according to Russian classification- class 3) establishes stringent requirements for the content of sulfur and aromatic hydrocarbons in motor gasoline. The mass fraction of sulfur in Euro-3 gasoline cannot exceed 150 mg/kg (in Euro 2- up to 500 mg/kg). The content of aromatic hydrocarbons is limited - no more than 42% (Euro-2 - as it turns out), while the content of the most harmful aromatic hydrocarbon - benzene - cannot exceed 1% (Euro-2 - up to 5%). Sulfur compounds and aromatic combustion products harm human health and destroy car engines. In addition, strict standards for the content of alcohols are established for class 3 fuels: methanol - no more than 5%, ethanol - no more than 10%. This restriction also applies to bioalcohols obtained from plant materials.Of course, Euro-3 gasoline cannot contain octane-boosting additives based on lead, iron or manganese, which are harmful to human health and create carbon deposits on candles and engine parts. However, these additives are not allowed by Euro-2 standards.
Euro-3 requirements for diesel fuel are similar. The mass fraction of sulfur is not more than 350 mg/kg (Euro-2 allows 500 mg/kg), the content of polycyclic aromatics is not more than 11% (Euro-2 does not regulate this norm).
Moscow fights for clean air
Moscow has the greatest need for environmentally friendly fuel, where about 3.9 million vehicles are registered. According to the Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology of the Russian Federation, 100% of Moscow residents are exposed to "high and very high air pollution." The share of vehicles in the capital accounts for about 87% of pollutant emissions. Not surprisingly, the Moscow authorities impose special requirements on the environmental performance of the fuel sold at filling stations. Despite the fact that the use of Euro-3 fuel in Russia became mandatory only from January 1, 2011, Moscow refused to use gasoline that does not meet Euro-3 requirements back in 2007. The Department of Nature Management and Environmental Protection of Moscow noted that this made it possible to stabilize the ecological situation in the city, but it will be possible to achieve changes for the better only with the transition to Euro-4. It was planned to introduce Euro-4 in 2011, but the initiative of the Moscow authorities to further increase fuel requirements is held back due to lack of quality gasoline- not all refineries supplying the capital with oil products are ready to switch to Euro-4 yet.Total year
If the government does not decide to reschedule the introduction of environmental standards on motor fuel, then in a year Russia will switch to Euro 4. The requirements for the mass fraction of sulfur in Euro-4 gasoline are very strict - no more than 50 mg / kg, aromatic content - no more than 35%. Diesel fuel manufactured in accordance with Euro-4 standards cannot contain more than 50 mg/kg of sulfur.Most likely, Russian refineries will have time to prepare for 2011. For example, many LUKOIL plants are already capable of producing Euro-4 gasoline, and those lagging behind are quickly catching up. In particular, before new year holidays The Nizhny Novgorod refinery of LUKOIL announced the production of the first batch of Euro-4 gasoline. This became possible after the launch of a catalytic cracking complex at the enterprise. In the first quarter of 2011, the Nizhny Novgorod Refinery plans to launch an alkylation unit, the use of which will make it possible to produce gasoline that fully complies with Euro-5.
There is no limit to perfection
The introduction of the standard in Russia is scheduled for 2015. The transition to this standard will require a very serious modernization of refineries, especially in the field of gasoline production. The standards for sulfur content in gasoline and diesel fuel are extremely strict - no more than 10 mg / kg, which is 50 times less than allowed by the Euro-2 standard! The exhaust from such fuel is much less toxic, which is very important, especially for large cities.Europe, meanwhile, does not stand still and is preparing a standard Euro 6.
EURO 3 diesel fuel is not good enough for a metropolis
Euro-3 - environmental standard regulating the content of toxic substances in the exhaust gases of vehicles with diesel and gasoline engines. In 1999, the standard was introduced in the European Union, replaced by the Euro 4 standard in 2005.
Euro-3 in Russia: all vehicles manufactured in the Russian Federation or imported into the Russian Federation, starting from 01/01/2008, must comply with the requirements of the Euro-3 environmental standard.
What is the Euro 3 standard?
Euro-3 gasoline has a sulfur concentration limit of 150 mg/kg (whereas in Euro-2 fuel it is up to 500 mg/kg). The volume fraction of aromatic hydrocarbons in Euro 3 gasoline does not exceed 42%, olefin components - 18%. In class 3 gasoline, the mass fraction of oxygen should not exceed 2.7%, oxygenates (in particular, the volume fraction of ethers) should not exceed 15%. class 3 contains a mass fraction of sulfur not more than 350 mg/kg.
In Russia, the timing of the transition to Euro 3 fuel has been repeatedly postponed due to the fact that Russian oil companies did not have time to modernize their plants in time. For example, Euro 2 fuel was originally expected to end in 2009, but the deadline has been pushed back to 2011. And only in September 2011 was announced new term Russia's transition to Euro 3 - from January 1, 2013.
And with the New Year's chimes of 2013, the standard came to us Euro 3, which has been waiting since 2009. And although Russia, according to plans, already seems to have to follow the requirements of Euro-4 and prepare for the introduction of Euro-5, the reality turned out to be more severe, so the deadlines had to be postponed by 2 years.
Euro 3 fights for clean air
Exhaust plume from diesel fuel EURO 3 classMost environmentally friendly fuel needed big cities. For example, about 3.9 million vehicles are registered in Moscow, which account for about 87% of all toxic gas emissions in the capital. Therefore, the Moscow authorities refused to use fuel that did not meet Euro-3 requirements back in 2007. This somewhat stopped the deterioration of the environmental situation in the capital, but a clear improvement can only be expected with the transition to Euro-4.
Euro-3 fuel characteristics
According to GOST standards, it contains no more than 350 mg/kg sulfur. Also, indicators such as the content of carbon monoxide, nitric oxide, hydrocarbons, which provide carcinogenicity, also pass the norm. The level of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere is 30-40% less than in the case of Euro-2 diesel fuel.
| Cetane number, not less than | 51 |
| - for class 1 | 49 |
| Cetane index, not less than | 46 |
| Density at 15 °С, kg/m? | 820-845 |
| Density at 15 °С, kg/m?, for class 1 | 800-845 |
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, % (by mass), no more | 11 |
| Sulfur content, mg/kg, max, for fuel: | 350 |
| Flash point in a closed crucible, °C, above | 55 |
| Coking capacity of 10% distillation residue, % (by mass), not more than | 0,30 |
| Ash content, % (by mass), no more | 0,01 |
| Water content, mg/kg, no more | 200 |
| General pollution, mg/kg, no more | 24 |
| Corrosion of a copper plate (3 hours at 50 °C), scale units | Class 1 |
| Oxidative stability: total amount of sediment, g/m?, no more | 25 |
| Lubricity: corrected wear scar diameter at 60 °C, micron, max | 460 |
| Kinematic viscosity at 40 °С, mm?/s | 2-4,5 |
| Kinematic viscosity at 40 °С, mm?/s – for class 1 | 1,5-4 |
| Fractional composition: | |
| for class 1, at a temperature of 180 °С, % (by volume), no more | 10 |
| at a temperature of 250 °С, % (by volume), less | 65 |
| for class 1, at a temperature of 340 °С, % (by volume), not less than | 95 |
| at a temperature of 350 °С, % (by volume), not less than | 85 |
| 95% (by volume) is distilled at a temperature, °C, not higher | 360 |
| Cloud point, °С, not higher | -16 - for class 1 |
| Limiting filterability temperature, °С, not higher | -5 - for grade C; -15 - for grade E; -26 - for class 1 |
Russia's accession to the Geneva Convention led to the introduction of regulations in the country that set standards for the emission of harmful substances contained in exhaust gases and released into the air. These documents clearly spelled out articles that indicate that only those cars that fully comply with European standards for emissions of harmful substances should be in operation.
Environmental classes of cars
After conducting a huge number of laboratory studies, data was obtained indicating that during the year an average car consumes almost 4 tons of oxygen from the environment, and after processing, the following substances are emitted into the air:
- carbon monoxide - about 800 kg;
- carbons - 200 kg;
- nitrogen oxides - 40 kg.
If we take into account the statistics that the number of cars is increasing every day, then one can only guess what this threatens environment. Environmental services have long begun to pay attention to this issue. Special attention. It is clear that it is impossible to ban the operation of cars, so it was decided to develop regulations governing the regulation of emissions of harmful substances with exhausts. All car manufacturers are required to comply with them.
What is the environmental class of a car?
This concept implies the separation of all existing vehicles into separate categories. Assignment to one or another category is carried out depending on the content of harmful substances in the exhaust gases. Also important is the level of harmfulness from the fumes of the fuel that is used for specific vehicle.
Harmful fumes include:
- CO - carbon monoxide;
- NO - nitric oxide;
- hydrocarbons;
- fine solids;
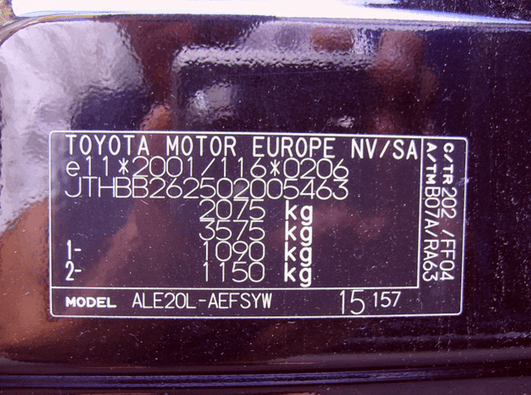
Attention! The ratio of the car to the environmental class is determined at the stage of customs control, when the car crosses the border of the Russian Federation. The eco-class mark is placed in technical passport going along with the car.

Classification of cars by standards
Euro-1 is one of the very first standards that controls the amount of harmful components contained in exhaust gases. It applies only to vehicles equipped with petrol type engine. The standard regulated the amount of oxides of carbon, nitrogen and hydrocarbons in the exhaust. Since this was the very first standard, it is considered the most loyal to transport, but at the same time quite cruel to the environment.
Euro-2 is already an improved standard, which refers to a 3-fold reduction in the content of harmful substances in exhaust gases. On the territory of the Russian Federation, it entered into force in 2005. Full application only started in 2006.
Euro 3 - this standard refers to the regulation of the content of negative components in the exhaust gases of a vehicle equipped not only with gasoline, but also diesel engine. The Euro-3 norm has even greater requirements for emissions. Compared to previous standards, a reduction of almost 40% is envisaged.
Euro 4 - This standard has been actively used in Europe since 2005. On the territory of Russia, it began to operate only in 2010. According to him, the reduction in the composition of negative components in the exhaust gases should be 40% compared to the previous standard.
Euro 5 is one of the most popular standards in use today. It has become mandatory since 2008. It must comply with all new vehicles with a high load capacity, the sale of which is carried out in the European Union. Correspondence passenger transport These regulations have been required since 2009. In Russia, the norms have been introduced since 2015.

How can I find out what class a car belongs to?
There are three most right way, thanks to which you can find out if the vehicle belongs to the environmental class:
- analysis vehicle title- it is quite possible that there is a mark indicating a certain standard;
- search in the Rosstandart table;
- query through the online database, specifying only the VIN.
Environmental class in TCP
First of all, you can find out which standard the car's exhausts meet with the help of PTS. This is a vehicle passport containing basic technical data. If this is a new type of document, then find out necessary information you can in column 13. Most often, the class is written in words.
In the event that the document is not a new sample, then this note may be in the column "Additional notes".
Attention! If the PTS did not find an answer to this question, then you can find the information in the Rosstandart table.

Ecological class in the Rosstandart table
The agency that certifies vehicles, in accordance with the special standards of the Russian Federation, has developed a special table with which you can find out which environmental class the car belongs to.
The main criteria that are taken into account when determining the class of a car include the year of production and the country of manufacture. The list of manufacturers includes not only European countries, but also located outside of it. When compiling the table, not only the UNECE requirements were taken into account, but also other standards that are used on the territory of other producing countries.

Surprisingly, the Russian departments are developing this table, but our country is not on the list. The reason for this is that all the above criteria have been introduced in the country recently. That is why it is not entirely correct to compare cars of old production and produced in the early 2000s with European-made cars that meet all the necessary standards.
If, after you have learned the class of the car from the table, there are any incomprehensible moments or questions, then you can additionally find out by VIN code.
Advice! You can find the ID in different places depending on the manufacturer: on the engine, on the body pillar next to the driver's seat, on the dashboard on the driver's side, under the floor trim or door sills and always in the PRT.
Find out the emission class using VIN
You can find out about the class of the vehicle by the VIN code on the special website of Rosstandart. On the website of the department for this there is a special online service. It is through him that you can make the appropriate request.
This method has its own great dignity is the accuracy of the result. In a certain column is entered VIN number and the request is sent. After recognizing the identifier, a result is produced that describes the following data:
- car model;
- type of transport;
- approval number;
- date of issue of the document and its validity period;
- environmental class type.
Attention! The information you need can only be obtained if given VIN is in the Rosstandart database. It is quite possible that it is not there. In this case, the owner of the vehicle will have to independently contact the relevant department.
Conclusion
The introduction into force of special environmental standards regarding the content of certain harmful components contained in the exhaust gases of a car made it possible to divide cars into environmental classes. In the event that the composition of negative substances in the exhaust is very high, the car owner will have to pay a transport fee and a duty, the amount of which depends on the class.
More detailed information learn about the new environmental class Euro-5 in next video:
In order to fight for the improvement of the environmental situation in the world, special environmental standards have been introduced that characterize all vehicles according to the amount of harmful substances they emit into the atmosphere. To date, in Russia, since 2010, the Euro-4 standard has been in force.
The environmental class of a car is a special classification code that characterizes automotive equipment according to the level of pollutant emissions. Pollutants include traffic fumes engines and fuel vapors containing carbon monoxide - CO, derivatives of hydrocarbons - CmHn, nitrogen oxides - NOx, as well as dispersed particles.
All cars imported into Russia must comply with certain environmental standards. Today, the Euro-4 environmental standard is in force on the territory of Russia, which applies to any vehicles located on the territory of the country, regardless of their type. This means that not only cars, but also trucks and special equipment.
Characteristics of environmental standards
Environmental standard "Euro-1"
This standard was introduced in 1992 in Europe, the USA and Japan, becoming the first step towards improving environmental situation in the world. Operated until 1995.
Environmental standard "Euro-2"
It replaced the Euro-1 standard in 1995, significantly tightening the requirements for both the fuel itself and the level of harmful substances emitted by diesel and gasoline engines. It was from this standard that Russia joined the fight for the environment by adopting Euro-2 in 2006. Starting from 2006, the import of cars that did not have a certificate of compliance with the Euro-2 standard was banned into Russia.
Ecological standard "Euro-3"
In 2000, Europe adopted new standard"Euro-3", reducing the allowable performance harmful emissions by 30-40%. Russia adopted this standard in 2008, and it was valid until 2010.
Ecological standard "Euro-4"
In any case, the EU is ahead of Russia in the fight for the environment, so the Euro-4 standard, which began to operate in Russia only in 2010 and caused a lot of controversy, was introduced in Europe back in 2005. This standard has tightened the previous standards by 65-70%.
Ecological standard "Euro-5"
A similar rule has been in force in Europe since 2009. In Russia, it is possible to introduce the Euro-5 standard in 2014. To date, the issuance of a certificate of conformity "Euro-5" is possible in Russia, but this procedure not yet required.
Ecological standard "Euro-6"
The EU plans to introduce a new environmental standard "Euro-6" in 2014.
Below is comparison table with the requirements of each of the environmental standards in relation to passenger cars with gasoline and diesel engines.
| Class | date | SO | TNS | NMHC | NOx | HC+NOx | PM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel engines | |||||||
| Euro 1 | July 1992 | 2,72 (3,16) | - | - | - | 0,97(1,13) | 0,14 (0,18) |
| Euro 2 | January 1996 | 1,0 | - | - | - | 0,7 | 0,08 |
| Euro 3 | January 2000 | 0,64 | - | - | 0,50 | 0,56 | 0,05 |
| Euro 4 | January 2005 | 0,50 | - | - | 0,25 | 0,30 | 0,025 |
| Euro 5 | September 2009 | 0,500 | - | - | 0,180 | 0,230 | 0,005 |
| Euro 6 | September 2014 | 0,500 | - | - | 0,080 | 0,170 | 0,005 |
| Gasoline engines | |||||||
| Euro 1 | July 1992 | 2,72 (3,16) | - | - | - | 0,97 (1,13) | - |
| Euro 2 | January 1996 | 2,2 | - | - | - | 0,5 | - |
| Euro 3 | January 2000 | 1,3 | 0,20 | - | 0,15 | - | - |
| Euro 4 | January 2005 | 1,0 | 0,10 | - | 0,08 | - | - |
| Euro 5 | September 2009 | 1,00 | 0,100 | 0,068 | 0,060 | - | 0,005 |
| Euro 6 | September 2014 | 1,00 | 0,100 | 0,068 | 0,060 | - | 0,005 |
Symbols: CO - carbon dioxide, HHC - hydrocarbon, NMHC - volatile organic substances, NOx - nitrogen oxide, PM - particulate matter.
Implementation of environmental standards in Russia
On the territory of Russia today the environmental standard "Euro-4" is in force. Cars that do not meet this standard cannot be imported into the country.
If we talk about AvtoVAZ, basically Russian manufacturer cars, then in December 2011 production began Lada cars that fully comply with Euro-4 standards. It is worth noting that the Ladas, produced for export, were converted to Euro-4 back in 2005.
Today, AvtoVAZ is actively preparing for the introduction of the new Euro-5 standard in the country. Therefore, talk about the fact that Russia cannot fully switch to strict environmental standards only because the manufacturer domestic cars unable to re-equip their factories to new requirements, have no real ground.
The main problem today is not even in the cars themselves, but in the fuel, the quality of which leaves much to be desired. But, in theory, some requirements are also imposed on fuel. Nevertheless, already in 2014 Russia is expected to switch to the Euro-5 environmental standard.







