Transfer case(RK) is installed in vehicles suitable for driving. In other words, it is present in vehicles with all-wheel drive, but not in those with front- or rear-wheel drive.
The purpose of the transfer case is to adjust the torque working in the undercarriage of the machine. She comes to the aid of cars in the passage of complex and landscape routes.
But let's talk about this device in more detail. First, let's figure out where to look for it.
Where can I find a transfer box?
The location of the PK may differ depending on the make and model of the vehicle.
Sometimes the creators of the car put it on, sharing it with this device.

However, you can often find gearboxes that include transfer cases.
What are transfer boxes?
The purpose and design of the transfer case are inextricably linked. Not all vehicles have the same RC. Most often, these mechanisms differ from each other in their type and structure. There are three main criteria by which one such mechanism differs from another.
- Types of drive shafts. In step-down boxes, they can be misaligned and, conversely, coaxial.
- Locations of drive shafts.
- The number of gears available. This number determines the gradation of the box. They are one-, two- and three-stage.
What is the distribution box made of?
The distribution mechanism itself may differ. There are several ways to collect it. However, there are components that a transfer case device cannot do without.

- First, it is the drive shaft. When using one gear, he is responsible for receiving torque.
- Second, there are four drive shaft. They are placed on the axle at the back and front. They are connected in pairs.
- Thirdly, in such a mechanism there is necessarily a gear or chain transmission of torque.
- Most all-wheel drive cars there is also a downshift. However, we draw your attention to the fact that it is not present in all transfer boxes. So, this link in the chain of the mechanism is absent, for example, in crossovers, which, although they have all-wheel drive, are not designed to drive through difficult landscapes.
- Also in the boxes of some cars with all-wheel drive there is a differential that is installed between the axles, and a lock for the differential.
How does the box work and is it needed?
How does it work?
First, let's figure out how the transfer case works. The principle of operation of the transfer case is that differentials, which are of two types (symmetrical and asymmetrical), divide the torque into axles. The first type of mechanism distributes the torque equally, and the second - not equally, depending on the specified indicators. One way or another, thanks to this device, the drive shafts can operate at different speeds, which increases the maneuverability and stability of the machine when turning and when.
The principle of operation of the dispenser:
Also, a lock can be installed under the differential. This device helps to lock the differential that distributes the torque. After such blocking, the wheels will rotate strictly at the same speed. You can control this function yourself from the inside of the car, or you can set up automatic locking. Such a function is in demand on those machines that have to drive, for example, through long fields.
The transfer box has several modes of operation. It can function:
- with two active axles and differential lock, which is carried out in automatic mode;
- with two active axles, but in a reduction gear with the condition of permanent differential lock;
- with two working axles and with the condition of permanent differential lock;
- with two working bridges;
- provided that only the rear axle is working.
If the box doesn't work
Transfer case malfunctions are different. However, there are several most common ailments of the device:
- Difficult to shift into gear. If you have such a problem, check the rods and plugs of the device. They could wear out as a result long service life. If so, they should be replaced as soon as possible. Also, the cause may be seizures formed on the gears. If none of these reasons applies to you, it remains only to check the latches. Perhaps this problem is caused by their laxity.
- Gears are automatically disengaged while driving. Most likely the gears need to be replaced. Their teeth must have already worn out. If the gears are in order, check the integrity of the fork fasteners. They can jump.
- The box is terribly noisy. First, remember what lubricants do you use? Perhaps their viscosity is not enough and you need to pick up something thicker. The gears could be worn out. Then they need to be replaced. The same reason can be caused by problems with the operation of the clutch or wear of the bearings.
- Oil is leaking from the AC. If you have determined that the oil is flowing from it, just buy new gaskets and ask the master to install them.

Unfortunately, it is almost impossible for an amateur to repair the box on his own. The only thing that a beginner in the repair business can do with his own hands is to produce. For all other procedures, specialist assistance will be required.
Do you need a transfer case?
Like any mechanism, RK has its advantages and disadvantages.
Let's start with the cons. More precisely, from one, but significant minus of the transfer case. The fact is that most of its parts are quite expensive. Therefore, their replacement will be expensive. And those parts that are sold by reasonable prices, are difficult to repair, therefore, they may also require funds from the car owner for the work of the master.
Now the pros:
- When the “razdatka” is operating while the car is moving at low speed, the torque is transmitted to the axles. This increases the cross-country ability of the SUV.
- It is noteworthy that during the operation of the "razdatka" a large torque cannot be lost. This is achieved thanks to the demultiplier. He is an assistant to the machine in reducing the intensity of torsion of the drive shafts.
- Also, the driver of a car equipped with a transfer case has the opportunity to independently determine the gear number.
- When driving in difficult conditions RK will become a friend and assistant to the motorist, helping him " iron horse» overcome terrain obstacles effectively.
- And, of course, one of the leading benefits is that the operation of the transfer case extends the life of the transmission.

But do not forget that no transfer case detracts from the importance of the skill of the driver who decides to drive through difficult sections. After all, even when driving the most “fancy” car, the rider’s inexperience can play a cruel joke on him.
Cars off-road popular with car enthusiasts. The difference between such machines from conventional ones - with a drive to one of the axles, comes down to the fact that both axles are leading them. This increases the likelihood of passing difficult area roads (mud, snowdrift, etc.). To make both axles drive on a car allows the transmission to be equipped with an additional unit - a transfer case, or, in simple terms, a transfer case.
The transfer case is a gearbox that distributes torque along two axes. This unit is located behind the gearbox.
On off-road vehicles, several types of transfer boxes are used, differing in:
- device
- connection type;
- moment distribution ratio;
- control method;
- type of connection to the checkpoint.
There are several designs of transfer boxes, but the principle of operation for all types is the same.
DEVICE AND VARIETIES

For example, consider the device of the simplest dispenser - gear type. Such units have already been somewhat supplanted by other types, but at the same time they are considered one of the most reliable and “real” transfer cases.
The gear transfer case consists of 4 shafts placed in the housing - the driving, driven, intermediate shaft and the drive of the second axle. On all shafts there are gears interacting with each other.

The driving and driven shafts are mounted on the same axis and have constant engagement with each other. This gives a constant transmission of rotation to one of the axles, that is, one drive axle on the car works all the time.
The intermediate shaft in the razdatka, through its gears, geared simultaneously with the gears of the input shaft and the drive of the second axle, ensures the transmission of torque to the latter, therefore the second axle also receives rotation and is the leading one.
The principle of operation of such a gearbox is very simple - the drive shaft receives rotation from the gearbox, immediately gives it to the driven shaft and, through the intermediate one, transmits torque to the drive shaft of the second axle. But the operation of a machine with this type of transfer case and a constant supply of rotation to both axles is difficult, because due to the rigid connection of the shafts, the controllability of the car drops, and there is a strong load on the transmission elements.
Designers solve this problem in two ways - by installing a differential (interaxle) and equipping the assembly with a mechanism for disabling one drive axle.
The differential in the design of the transfer case performs the same role as in the main gear - the ability to rotate shafts with different angular velocities. Its presence reduces the patency of the car due to the possible transfer of all torque to one axle if the second one has lost traction, but it has a positive effect on handling. In order to raise off-road qualities differential is additionally equipped with a lock.

In units with a shutdown mechanism, a car in normal operation has one drive axle, and the second is activated if necessary.
Additionally, the gear transfer case can be equipped with a reduction gear, which increases pulling force by changing the gear ratio in the transfer case. A reduction gear is implemented by installing additional gears on the shafts. That is, each shaft has two gears of different diameters. When one of them is engaged, the gear ratio in the unit is 1: 1, there is no reduction, but if you use the second group of gears, the ratio changes. On some vehicles it is 2:1, on others it is 2.5:1. As a result, the speed of the machine is reduced, but the traction force increases proportionally. It is noteworthy that downshifting is used only when turned on. all-wheel drive.
In addition to gear transfer cases, chain ones are also used on machines. In them, there is no intermediate shaft, and the rotation on the drive shaft of the second axle is carried out by a chain. This design is characterized by a lower metal content of the assembly, but is inferior to the gear type in terms of reliability.

IN modern designs abandoned the use of differentials, and their place was taken by couplings - mechanical (synchronizers), friction, electromagnetic, viscous couplings. A number of cars use Torsen differentials.
TYPE OF DRIVE AND INFLUENCE OF THE TRANSFER BOX ON IT
Features of the transfer case affect the type of all-wheel drive, of which there are only three:
- Permanent full.
- All-wheel drive, manually connected.
- Drive that operates automatically.
An example of a permanent four-wheel drive is a transfer case with a conventional differential equipped with a lock (the common name is Full Time). In vehicles with such a system, the transfer case provides a constant transmission of rotation along two axes.
A drive connected manually is called Part Time. In a car with such a drive system, the transfer case in normal driving mode supplies rotation to only one axis, while the second is activated when needed. In such units, the differential is not used, but instead of it, couplings are installed - mechanical, electromagnetic, which connect / disconnect the second bridge.
The system that uses both bridges in automatic mode is OnDemand. It is used on passenger cars, and in this case, the razdatka is aimed at increasing cross-country ability and improving handling. The control is carried out by electronics that interact with the ABS. In such transfer cases, there is no differential, and an electrically driven clutch is installed instead.
In the OnDemand system, the transfer case, by default, provides rotation to only one axle. But when certain driving conditions occur, the electronics activate the clutch drive and the second axle is connected.
TORQUE DISTRIBUTION
The distribution of torque by the transfer case is equal and unequal. In the first case, rotation is applied to both bridges in a 50/50 ratio. This distribution is provided by a transfer case that is not equipped with a differential or with it, but with a lock.
In boxes with unequal distribution, the ratio is different. In Full Time and Part Time handouts, the proportions are fixed and are 40/60 or 60/40.
As for OnDemand systems, the proportions of distribution are “floating” in them and vary from 50/50 to 100/0. That is, such handouts in automatic mode can evenly distribute rotation or transfer to one axis.
CONTROL METHODS
Transfer boxes installed on a car have three control methods:
- manual;
- electric drive;
- electronic control system.
Hand drive razdatki - old and primitive. With such a drive, the driver, by means of levers, disconnects / connects the second axle, locks the differential, and engages a downshift.

The electric drive differs in that the switching in the transfer case is carried out by servo drives. The driver controls with the keys. This is a convenient type of drive, but not as reliable as manual mechanical.

On some cars, there is a combined control, in which the switching on / off of the second axle is performed by a servo drive, and the downshift is activated using a lever installed in the cabin.
The electronic control system is used in OnDemand drive dispensers. Since the switching in the node is carried out in automatic mode, there are no transfer case controls for the driver.
Transfer boxes are installed in the transmission in different ways. More often this node is connected to the checkpoint, which reduces the number constituent elements transmission. But there are also cars in which the transfer case is installed separately from the gearbox, and they are connected to each other by an additional cardan shaft.
Despite the single principle of operation of transfer boxes, there are many features of their functioning. On some SUVs, the main drive axle is the rear, and the front is connected. But there are cross-country vehicles in which the transfer case allows the driver to make any drive axle the main one without any problems.
In order to simultaneously distribute torque between the front and rear axles, cars are equipped with a transfer case or transfer case - a mechanism in the car's transmission, which, in addition to distributing torque, performs several more functions:
- an increase in the torque required to overcome the rolling resistance of the drive wheels when driving off-road;
- ensuring the stability of the car during slow movement while reaching the maximum torque.
Audi transfer case.
World Automotive industry produces hundreds of car models equipped with transfer boxes of various designs, which consist of several basic elements:
- metal case;
- main (drive) shaft through which rotation is transmitted from the gearbox;
- shafts of the rear and front axle;
- center differential that distributes rotation between the front and rear axle car;
- gear or chain transmission;
- oil collector - a chamber in which oil accumulates;
The design of the center differential allows the wheels of the front and rear axles to rotate at different speeds if the unit is not equipped with a locking mechanism. If the transfer case has a self-locking or manual locking differential, the transfer case will forcibly adjust the rotation of the rear and front axle shafts depending on the road conditions.
Auto manufacturers equip transfer cases with several basic types of differentials:
- viscous couplings;
- Torsen locks;
- friction clutches.
The first option is the most common, easy to manufacture and relatively inexpensive. Among the shortcomings - the impossibility forced blocking differential, the possibility of failure as a result of overheating under continuous load.
Torsen are installed on SUVs, since the fragile design of the assembly does not allow the car to move off-road. Friction clutches have a more advanced design, as well as the possibility of manual and automatic locking.
Types of transfer boxes

Control levers for a manual transfer case of a Niva car.
Depending on destination, design features and types of transport produce several types of units designed to distribute torque:
- simple (non-switchable);
- manual;
- semi-automatic;
- automatic.
The most significant advantages simple mechanisms— high wear resistance, ease of use and non-failure operation. Boxes of this type are installed on foreign and domestic models SUVs, and sports cars specially designed for high-speed driving off-road. The peculiarity of such handouts is that they function constantly, regardless of the type of road.
To control the manual dispenser, a mechanical lever is used, which in most cases is located between the passenger and driver's seat. manual box does not depend on the operation of the car's electronics, it is trouble-free in operation.
Semi-automatic operation is characterized by the ability to control the drive axles by pressing the keys located on the panel. Of the pluses - simple control, of the disadvantages - the driver's attention is diverted to switching buttons.
The automatic transfer case is controlled by actuation electronic systems, which equip modern cars. Connection / disconnection of bridges, differential lock is carried out by servo drives or a torque converter. The automatic transfer box is able to sensitively control the car on roads with different surface conditions, the disadvantage is the possibility of failure as a result of moisture.
Transfer case operating modes
Depending on the design of the dispenser, the driver can use several modes of operation:
- inclusion of the rear axle;
- the inclusion of the front and rear axles;
- the inclusion of both bridges, the center differential is blocked;
- both axles are on, downshift is on, differential is locked;
- both axles are included with automatic differential lock.
Common faults
Repair of a transfer case is associated with a significant investment of money, therefore, in order to minimize the wear of components, it is necessary to carefully operate the car and carry out timely Maintenance. The main malfunctions of the dispenser are called.
Welcome to the blog pages! This material will discuss the transfer case, a mechanism that is behind all-wheel drive vehicles. What is a transfer box? Many have heard such a definition - razdatka, but do not quite understand its important field. Consider the device of the transfer case and its varieties.
Before considering the devices, you need to understand what the transfer case is. Here, as it were, everything is simple, the razdatka is designed to redistribute torque between the front and rear axles.
In addition, on special equipment (tractors, trucks), a power take-off shaft comes out of it to connect additional equipment such as pumps, compressors, etc. Also, the transfer case may have a demultiplier in its device, which includes a lower gear. This is necessary on the road to increase traction from the engine.
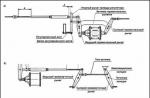
Well, now let's move on to the most interesting, namely the consideration of the transfer case diagram and the nodes of which it consists:
- Frame;
- input shaft;
- output shafts;
- gears;
- Differential;
- Control system.
Frame
It can be either combined with the main box or stand as a separate unit. In a separate position, the connection between the gearbox and the transfer case is carried out by a separate shaft, which is the input for the unit.
It should also be noted that the transfer case, like the gearbox, is filled with special gear oil.
Input and output shafts
The input shaft receives torque from the gearbox and then with the help of a differential, if it is integrated into the design, it is transferred to the output shafts, which go respectively to the front and rear axles.
The role of the differential is to redistribute the moment of forces between the shafts to the front and rear wheels. The need for this procedure is due to the fact that the wheels travel an unequal distance. For example, if the front wheels hit a bump, but the rear wheels are still driving on a straight road, the result is that the number of revolutions made by the front and rear axles will be different.
Gears
The gears in the transfer case are needed to link all the shafts together. In addition, the implementation of a lower gear is also assigned to gears, only with a different ratio of teeth. It's like in a conventional gearbox, only there are two gears, a regular (direct) and a reduced one.
Sometimes, instead of gears, automakers use a metal chain. It is considered less reliable than a gear drive.
Differential
It should be mentioned that there is also a differential lock mechanism. It blocks its work and the revolutions are divided into the front and building wheels equally. This function significantly raises the level of off-road patency of the car.
Control system
It serves to switch between the operating modes of the transfer case. On older cars, control took place with the help of mechanical rods and levers that the driver moved in the cabin. On modern cars, the razdatka is controlled through special vacuum or electric drives. And the driver presses only buttons or turns special washers.
Types of transfer boxes
We will make a conditional division of transfer boxes according to the vehicles on which they are installed, since this parameter most accurately characterizes the requirement for the unit. And cars with all-wheel drive are divided into:
- crossovers;
- SUVs.
Not everyone knows that crossovers, also called SUVs, belong to the class of cars for which off-road driving is a very conditional thing. Passenger cars can also be attributed to them according to the structure of the transmission.
They can drive through a small puddle or climb a curb, but it's not worth kneading mud on them. And all due to the fact that the transfer case they have a differential lock with a tendency to overheat with frequent slipping. It is done on the basis of one of three systems:
- Viscous coupling;
- Thorsen differential;
- Multi-plate clutch.
Let's take a brief look at each system.
viscous coupling
Built on the basis special liquid, which is located between numerous, rotating relative to each other with small gaps, transfer case plates. The plates are connected to the output shafts, and when the difference between the turns of the plates becomes very large (one of the axles slips), the liquid sharply increases its viscosity and binds (rigidly glues) the plates together, blocking the differential.
But for a long time it cannot be in this state because the liquid overheats and loses its properties.
Differential Thorsen
Such a differential is based on worm gears and its main ability is to quickly and accurately redistribute torque between the axles. Very good mechanical design based on worm gears, but its main drawback is unreliability, that is, in critical situations, it is prone to rapid destruction.
Multi-plate clutch
This is a more reliable mechanism, which all modern crossovers switch to.
Its device is a set of disks that rub against each other depending on the force that presses on them. And the greater the force, the more they block the differential.
The clamp is commanded by the computer based on the readings from the sensors and the position of the selector.
It should be said that the two previous systems did not require participation from the driver and worked independently.
The multi-plate clutch also, with prolonged slippage, begins to overheat, and in order to save the mechanism, the electronics turn off its operation, the car becomes a monodrive. This is a wise decision for "gentle" SUVs, which are sometimes tested, out of ignorance, for off-road, keeping them from breaking.
Also an important factor in crossovers is the absence of a reduced range in the transmission.
As for SUVs, it is worth noting highest reliability their transmissions when driving off-road. Locks in them are carried out rigidly, without the possibility of a smooth change in torque between the axles.
Yes, it has a bad effect on management when high speeds, but you can skid as much as you like, without fear of overheating.
In addition, in the razdatka of such cars there is a demultiplier for switching on a lower gear. There may be one or two reduced modes.
Thanks to this, off-road vehicles can climb very steep hills or drive through mud without fear that the engine will not have enough thrust.
Also downshift makes it possible to move at very low speeds (1-2 km / h), which gives the driver time to more accurately choose the trajectory of movement without stopping the car.
Summing up, you can see that the transfer case is a very useful unit. And if you do not rape him in vain, but take into account the purpose vehicle the service life will be very long.
Allow me to bow out on this.
Cars. Thanks to this unit, there is a distribution of torque along the axes, as well as its increase when the vehicle moves through terrain with difficult terrain.
A look into the past
The first all-wheel drive vehicles appeared at the beginning of the twentieth century. These were cars designed for road and off-road racing. The public reacted coolly to the invention, considering it pampering, and was not going to overpay big money for dubious pleasure.
It seemed that the idea had died, no one needed it. But already in the tenth years of the last century, the designers revived it by developing all-wheel drive trucks.
The developers faced the question: how to distribute the torque between the two drive axles. It was clear that a conventional gearbox could not solve this problem.
After some manipulations appeared committed new unit who performed the following tasks:
- created a number gear ratios, contributing to the coordination of the speed of rotation of the crankshaft, the torque coming out of it, and the speed of the car;
- distributed torque between drive axles;
- did not prevent movement back.
Out of habit, this new mechanism has long been called a gearbox. But, unlike the familiar all-wheel drive vehicles, this box had two output shafts.
But this development was not successful due to the high cost. Perhaps she would have sunk into oblivion, but then the first World War. And, as you know, military operations are conducted not only along paved roads, you have to drag guns off-road, and even in the spring thaw. This is where the finest hour of all-wheel drive vehicles has come.
The purpose of the transfer case
The transfer case serves to distribute the force to all the drive axles of the vehicle. In addition, it is used to turn on and off the leading front axle. The transfer case, as a rule, has a two-stage gearbox. Under its influence, the gear ratios change, and the number of gears of the car doubles.
First row gear ratios obtained when you turn on the direct (higher) gear. The second row is activated when downshifting. This allows you to use vehicles in different road conditions.
In car design high cross there is a device that does not allow downshifting at the moment when front axle included. Such a device protects the rear axle from overload with a large torque.
Transfer case types
1. With coaxial drive shafts leading bridges. This type is widely used due to the possibility of using a single main gear for front and rear axles.
2. With misaligned driven shafts. They don't have an intermediate shaft. Compactness, noiselessness, high efficiency- these are the main advantages of this type of transfer case. In addition, it has a low metal content.
3. With a blocked drive axles. Allows you to use the full traction force without wheel spin. With such a transfer case, the front axle is switched on only on difficult sections of the road. When driving on hard surfaces, the front axle is disengaged to save fuel and reduce tire wear.
4. With differential drive of driving axles. In boxes of this type, it is used that allows the rotation of the drive shafts with different speeds. In a car equipped with such a box, the front axle is constantly on. To increase the cross-country ability, center differentials are made with forced locking.
Transfer box device
Despite the differences in the design of transfer boxes, depending on the all-wheel drive system, they all have common main components:
- drive shaft;
- center differential;
- a mechanism that blocks the center differential;
- rear axle drive shaft;
- gear or chain transmission;
- reduction gear;
- front axle drive shaft.

Transfer box diagram
Torque from the gearbox to the transfer case is transmitted through the drive shaft.
Distributes the torque between the axles - center differential. Thanks to him, the axes can rotate with different angular velocities. center differential there are two types:
- symmetrical (distributes torque equally);
- asymmetrical (distributes torque in various ratios).
Serves for rigid coupling of the front and rear axles.
The chain drive transmits torque to the front axle. It consists of gears (driver and driven) and drive chain. Instead of a chain, a gear (cylindrical) is often used. In the all-wheel drive system, automatically connected, the transfer case is made in the form of a bevel gear.
The purpose of the downshift is to increase the torque when the car is driving off-road. It has a planetary gear design.
Operating modes
The transfer box operates in five modes.
1. Neutral on.
2. Differential unlocked with overdrive engaged: torque split 1:2.
3. Differential locked with overdrive engaged: torque is divided according to road grip.
4. Differential unlocked with downshift: torque is distributed in a ratio of 1:2.
5. Locked differential with downshift: forward and rear axles work as a whole. Torque is distributed depending on the degree of adhesion of the wheels to the road. In this mode, the car's cross-country ability is the highest.
Video: transfer case.