Insufficient visibility is a condition caused by external factors and the location of the car, in which the driver cannot distinguish the observed object at a distance of less than three hundred meters.
The following natural phenomena can lead to a decrease in the specified distance:
- fog;
- rain;
- snowfall;
- blizzard;
- twilight;
- smoke;
- dust;
- splashes of water and dirt;
- blinding sun.
The allowable distance, determined by the value of 300 meters, is based on the calculation of the braking distance at a permitted speed of 90 km / h. Taking into account the adhesion coefficient equal to 0.35 for a wet roadway.
Driving in low visibility conditions
Driving in poor visibility can be summarized in four main categories:
- During rain;
- At fog;
- At blinded by the sun;
- Under influenced by other weather events.
During the rain
An important feature when driving in rainy weather- Decreased adhesion of tires to the road surface. On a wet surface, the coefficient of adhesion drops by one and a half to two times, the controllability of the car worsens, and braking distances increases.
Particular attention should be paid to hazards such as:
- asphalt concrete pavement hidden under fallen tree leaves or dirt;
- the period immediately after the start and after the end rain.
When driving at high speed wet road, a water wedge may form between the road surface and the wheels of the car, or as it is also called " hydroplaning effect.
Unlike low speed driving, where water between the road surface and the vehicle tire is forced into the tread pattern, high speed it doesn't happen.
A sign of the onset of hydroplaning can be sudden ease of driving. To combat the phenomenon, it is necessary to apply engine braking.
In fog
In the case where visibility is limited by fog, the driver requires much more attention and experience than when driving in rainy weather. Often in accidents caused by fog, the number damaged cars measured in dozens, many people get injured.
In the event of thick fog, stop driving immediately and wait for better weather conditions.
For this weather phenomenon may have the following effects on the driver:
- much reduce visibility distance;
- forms an optical illusion;
- disturbs orientation in space;
- distorted perception of speed and distance to objects;
- strong stress has an effect on the mind of the driver.
If you continue driving, you must:
- slow down so that its value does not exceed half of the visible distance in meters;
- use low beam along with fog lights;
- to increase the distance visible in front of the car periodically bring your eyes closer to the windshield.
- open a window driver's door listen to the noise emitted by vehicles.
Under no circumstances should you:
- approach the one ahead auto;
- carry out car parking within the road;
- overtake or advance.
When blinded by the sun
Direct sunlight directed into the eyes reduces the visibility of the driver, reduces his concentration and leads to overwork. This is especially true in the morning and evening period, the sun is directly above the horizon and the sun's rays fall parallel to the earth.
In case when pavement, alternating, passes through sunny and shaded areas, the driver experiences a sharp deterioration in visibility. In such cases, the driver will require increased attention.
With sunlight directed towards back car, the colors of traffic signals become difficult to distinguish, and rear lights leading Vehicle. With side sunlight, areas with a low contrast shadow are formed on the roadway.
The optimal solution would be using a sun visor to protect from direct sunlight.
Influenced by other weather events
When the first snow falls, the road surface is especially dangerous. Snow quickly rolls and forms an ice cover or roll, which, together with significantly reduced visibility, leads to an increase in the number of accidents.
Visibility on the road is essential.
Up to ninety percent of the information necessary for the safe continuation of the movement, the driver receives through vision. The device of human eyes requires time to adapt to the dark. However, at night vision is largely dulled.
Yes, in dark time day, or at dusk, the driver distinguishes the situation on the road much worse. The perception of colors is distorted. Green appears lighter than red, which in turn appears black. The reaction rate decreases several times. On average, for a time of 0.6 seconds or more.
If for night traffic you can use high beam headlights, then at dusk it already poorly illuminates the road. Must be enabled fog lights, lower the engine speed and increase attention.
Speed in low visibility
 When driving in sunny weather on a dry road surface, i.e. in ideal conditions, drivers can drive at the speed allowed by the rules traffic for the section of the road.
When driving in sunny weather on a dry road surface, i.e. in ideal conditions, drivers can drive at the speed allowed by the rules traffic for the section of the road.
However, in slippery road conditions or poor visibility, it is necessary to reduce the speed to a safe value for specific conditions.
At difficult conditions movement, the choice of speed is subjective. How fast to travel dangerous area The road is determined by the driver, guided by his experience and feelings.
The universal rule still applies:
safe speed is the speed at which the stopping distance will have a distance less than visibility.
traffic rules poor visibility
Insufficient visibility is understood as the deterioration of visibility caused by the temporary state of natural conditions (environment).
Reducing visibility due to weather conditions is the most dangerous, because in most cases it is not possible to convey the necessary warning with the help of road signs.
The visibility range defined by the rules is considered the maximum distance at which it is possible to distinguish a pedestrian against the background of the road surface.
The distance of 300 meters was taken from the calculation of the possibility of stopping cars when approaching at the maximum allowable speed at 90 km / h, subject to the value of the coefficient of adhesion characteristic of a wet road surface.
The driver, being in conditions of insufficient visibility, must be guided by paragraphs 19.1 - 19.8 of the traffic rules. An error in determining insufficient visibility often leads to the inability to quickly make the right decision in a complex environment. traffic situation.
What is the difference between low visibility and limited visibility?
At first glance, it is not easy to distinguish between insufficient and limited visibility. But the rules of the road contain exhaustive definitions of these terms, as follows:
Visibility limited by permanent or temporary traffic obstructions.
Permanent ones include:
- mountains;
- hills;
- the buildings;
- winding turns.
For temporary:
- stopped vehicles;
- repair work;
- other obstacles.
Conditions of insufficient visibility are temporary natural phenomena, such as:
- rain;
- snow;
- fog;
- twilight time.
At the same time, the intensity of these phenomena should limit the visibility of the road at a distance of less than 300 m. Insufficient visibility is the result of limited lighting caused by natural phenomena, and limited is the result of a physical restriction of the view.
Where is visibility needed and what should it be?
 It would seem that, good visibility required in all cases, but in relation to different conditions, the requirements will vary significantly.
It would seem that, good visibility required in all cases, but in relation to different conditions, the requirements will vary significantly.
Conventionally, situations can be divided into such points as:
- movement in the flow without maneuvers. The speed or distance must comply with the conditions of safe movement, for the timely adoption of measures to avoid accidents;
- when performing an overtaking manoeuvre. It is necessary to correctly estimate the distance both to cars moving towards, and for those moving behind in the direction of travel;
- visibility to exit from adjacent. You will need to estimate the distance to passing vehicles.
- visibility when turning left. It will be necessary to estimate the distance to cars approaching from the left, and after crossing the lane, make the same estimate on the right side.
To perform a safe maneuver, the estimated time must be multiplied by the maximum possible speed movement. The probability of a traffic accident will be the lower, the more stock remains in the calculation.
What to do if visibility is not enough?
When buying a new car, you need to make sure that the fog lights in the selected configuration are available. Recently, most foreign cars have them as standard.
In addition to ease of use during poor visibility, there will be the ability to use fog lights instead of daytime running lights. They may consist of sets of LEDs located at the headlights.
Possibly additionally install on the car daytime running lights in the form of rings, the so-called angel eyes.
https://my.mail.ru/mail/zemfira-ionova/video/1223/1392.html" align="center" mode="normal"]
How to increase visibility?
When faced with deteriorating weather conditions, there are several ways to improve visibility:
- reduce the speed so that its value corresponds to the traffic conditions that have arisen. Its value should be less than half of the distance for which the road is viewed;
- turn on additional lighting. Fog lights, dipped or high beam. IN without fail pre-equip the car with fog lights in case of their absence;
- improve driving awareness. Do not fix your eyes on one point, which increases fatigue. Periodically bring your eyes closer to the windshield. If necessary, it is allowed to move by sticking your head out the window of the driver's door.
What can interfere with visibility?
Obstacles to visibility can be both permanent or temporary obstacles, as well as changing weather.
Road visibility is determined by parameters such as:
- weather(rain, snowfall, fog);
- Night time(dawn, sunset, dusk);
- the physical characteristics of the road(radii of horizontal and vertical curves);
- intensity of building and green spaces.
It's worth remembering insufficient visibility, this is the result of a decrease in light levels and a lack of light in general.
Visibility, corresponding to the existing road conditions, takes a leading position in respect of road safety. The more limited it becomes, the more attention and caution the driver must exercise. It is also worth noting that the choice of driving style is highly dependent on visibility while driving.
In the last - the seventh - block of concepts, we will consider the visibility conditions in which the driver has to move on the vehicle.
Driving in fog, rain or snow, on the one hand, night riding, on the other side, sharp turns with practically “zero” visibility, on the third hand, all these are visibility conditions that have specific names. Let's talk about them.
NIGHT TIME
It would seem, well, what is easier ... We will not argue with this assessment and quote the traffic rules.
"Dark time of the day" - the period of time from the end of evening twilight to the beginning of morning twilight.
Agree, it smacks of the style of the general military regulations of the armed forces of the Russian Federation. And if it is simpler, then the dark time of the day is a period of time when it is impossible to move without special additional road lighting.
The driver must remember that in the conditions of the dark time of the day there are special rules for driving. So, for example, the movement of a vehicle must be carried out exclusively with the use of dipped or main beam headlights. (We will talk in more detail about the use of external lighting devices when analyzing the corresponding section of the SDA).
The antipode of the dark time of the day is the daylight time, that is, the period of time during which natural (solar) lighting operates.
LOW VISIBILITY
"Insufficient visibility" means visibility of the road less than 300 m in conditions of fog, rain, snowfall and the like, as well as at dusk.
Bad weather and twilight very significantly reduce the visibility distance, making it impossible to distinguish even the outlines of objects that are at some distance.
Agree, this state of affairs is an extremely dangerous phenomenon when driving a vehicle. That is why the Rules introduce the concept of insufficient visibility, outlining its boundaries - the visibility of the road is less than 300 meters in bad weather or twilight.
And one moment. The term "inadequate" means that there is visibility of the road, but there is not enough natural light at the moment. And, therefore, in conditions of insufficient visibility (as well as at night), the driver is obliged to use external lighting fixtures(high or low beam headlights).
This will compensate for the lack of natural light.
Our similar, at first glance, tautology around insufficiency will be fully justified in the analysis of the following concept.
LIMITED VISIBILITY
"Limited visibility" - the driver's visibility of the road in the direction of travel, limited by the terrain, geometric parameters roads, vegetation, buildings, structures or other objects, including vehicles.
Limited visibility prevents the driver from seeing the road at a safe distance.
Unfortunately, the SDA does not indicate a specific numerical characteristic (footage) of limited visibility. But the methodology for applying the Rules allows us to conclude that it is less than 100 meters.
The driver must remember that in conditions of limited visibility it is strictly forbidden for him to carry out:
- U-turn;
- Reversing;
- Overtaking;
- Stop and parking on the roadway.
We will talk about this and many other things (regarding the conditions of limited visibility) in the relevant sections of the SDA.
Another significant point. Agree, it is very easy to confuse two similar-sounding concepts - “insufficient visibility” and “ limited visibility". Especially often this error manifests itself when solving problems on traffic rules and passing the final qualifying exam.
This is where the previously used technique can help. Lack of visibility is the product of a lack of light (insufficient light), and reduced visibility is the result of some physical restriction on the view.
Let's summarize. Visibility conditions play a significant role in ensuring traffic safety. The worse the visibility, the more careful the driver must be. The choice of manner of movement (especially speed) is directly dependent on visibility conditions.
If this information was useful to you, please write about it in the comments. If you have any questions, write, we will definitely try to help you.
- limited visibility
- limited visibility is
- limited visibility
- poor visibility
Discussion: 3 comments
Hello.
Help is needed.
The situation is this:
The road has four lanes, two in one direction and, accordingly, two in the other (opposite), between them there is a dividing lawn, which has a technological gap. It's in the heart of the city. Sign 6.3.1 “Place for U-turn. Left turns are prohibited. I am driving in the left lane in one of the directions. Another participant in the movement moves in the opposite direction, enters a technological gap in order to perform a U-turn maneuver. So here's the question: he, referring to limited visibility, leaves the front of his car on left lane oncoming traffic, that is, along which I am moving ... which traffic rules He violated the Russian Federation??? I ask you to explain. As a result, there was a serious accident as he drove very close in front of me. Now, of course, he is trying to deny his guilt and his only argument is that I was driving with a huge speed limit and could not stop in front of him. My speed was 60 km/h. The braking distance was 17.2 meters. I will be grateful for help.
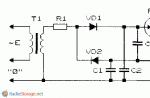
Regardless of the lighting of the road, as well as in the tunnels on a moving vehicle, the following lighting devices must be turned on:
- On all motor vehicles - headlamps or dipped beam; on bicycles - headlamps or lanterns; on horse-drawn carts- lights (if any);
- On trailers and towed motor vehicles - parking lights.
What external lighting devices can you use when driving at night on unlit sections of roads?
Answer. When driving at night on unlit sections of roads, you must use, depending on road conditions, speed and the presence of oncoming and passing vehicles in front, dipped or main beam headlights.
What external lighting devices should you use when driving at night on illuminated sections of roads in a settlement?
Answer. In built-up areas, the Rules require you to use only dipped-beam headlights when driving at night on illuminated sections of roads. Driving with side lights on is prohibited, as they do not identify your vehicle well enough for other road users. High beam headlights, given its dazzling effect on other drivers, are also prohibited.
What external lighting devices should be included in a tunnel with artificial lighting?
Answer. In a tunnel with artificial lighting, depending on the presence of oncoming or passing vehicles, dipped or main beam headlights should be turned on. Driving only with position or daytime running lights is prohibited, as they do not provide traffic safety in the event of a sudden shutdown of lighting.
What external lighting devices should be turned on at night and in conditions of insufficient visibility, regardless of road lighting, as well as in tunnels on towed motor vehicles?
| 1. | Daytime Running Lights. | |
| 2. | Parking lights. | |
| 3. | Rear fog lights. |
Answer. On towed mechanical vehicles and on trailers at night and in conditions of insufficient visibility, regardless of the illumination of the road, as well as in tunnels on a moving vehicle, the marker lights must be switched on.
Is it sufficient during daylight hours to turn on daytime running lights to identify a vehicle when driving in fog, when the visibility of the road is less than 300 m?
| 1. | Enough. | |
| 2. | Not enough. |
Answer. Brightness of LEDs used in daytime running lights, is considered sufficient to designate the vehicle instead of dipped headlights when driving during daylight hours. However, when driving in fog and other conditions of insufficient visibility, the vehicle must have high or low beam headlights on.
Can you use fog lights instead of low beam headlights during daylight hours?
Answer. IN daytime to designate a vehicle, the driver can use
Driving at night is very different from driving during the day. Nature is arranged in such a way that a person sees worse at night than during the day, and with age, the quality of night vision deteriorates. But most of the decisions that the driver makes are based on what he sees. When driving in the dark, the driver can see and evaluate the situation only in the area limited by the headlights. Moreover, objects appear in the illuminated area suddenly, and it takes more time to identify them than during the day.
Therefore, the reliability of driving at night is significantly reduced and, as a result, more errors are made. The most common of these are distance and speed estimation errors, as at night the driver has less time to estimate, less room to maneuver, and less time and opportunity to correct these errors. And the response time to night road increases.
Main condition safe ride in the dark- movement at a lower speed than during the day. The speed must be chosen so that, if necessary, you can stop the car within sight. Those. stopping way should not exceed the distance illuminated by headlights. Car windows must be clean. Firstly, it is always more pleasant to look at the road through clean glass, and secondly, dirty glass plus the light of oncoming headlights further worsen the already.
When driving in traffic, always keep an eye on the traffic ahead. It is very important not to miss the moment of the beginning of its braking. This will be prompted by his brake lights, which, however, may be faulty or partially serviceable. IN similar cases you will need to double your vigilance and increase your distance.
Always remember that there may be unlit objects on the road and near it. If you spot something ahead, always slow down. What it is - you will figure it out later when you drive closer or stop. Perhaps it is a standing unlit car, perhaps something else.
Pedestrians are the greatest danger when driving at night. They do not always fall into the field of view of the driver, they are more difficult to detect on an unlit section of the road. A separate risk group is drunken pedestrians. Their actions are unpredictable, therefore, near “such” pedestrians, one should reduce the speed as much as possible and anticipate the possibility of a detour in advance, or be ready to apply emergency braking.
Stop zones public transport you have to be especially careful. When there are a lot of cars, and then partial blinding occurs with the light of the position lights, plus the light of oncoming headlights. It is not always possible to immediately notice a pedestrian who is on the roadway, therefore, when passing stops, always slow down. When a shuttle vehicle is standing at a stop, pay attention to the light spot in front of it. If a shadow suddenly flashed on it, it is possible that because of this transport a pedestrian will now appear on the road, or maybe not one.
Therefore, once again - slow down in advance - you will have more time to react and you need to make it clear to those following you that there is a possible danger ahead. When they see your brake lights, they will understand that you are slowing down and slow down themselves. Then even the emergency braking of your car will not be a surprise to them.
Movement in the dark. Oncoming traffic
When driving on an unlit road, it is preferable to use high beam headlights. But you should always remember that there is a possibility of blinding oncoming drivers. You can also be blinded, so you need to develop the habit of looking to the right at the road at the time of the departure, and not at the oncoming headlights. First, to the right of the road, most often, there may be obstacles that you may not see, being blinded. Secondly, you can navigate by the markings, the bump stop, the right edge of the carriageway, the roadside.
You need to switch the headlights from high beam to low beam in advance - at least 150m before the oncoming car. But if the oncoming driver signals with a short-term switching “near-far-near”, then this must be done earlier. When the oncoming vehicle is level with yours, you can switch to high beam again.
It happens that an oncoming driver does not switch to low beam, but continues to drive with high beam, blinding you. In this case, you can remind him to switch by blinking briefly from low beam to high beam several times. But in no case should he, so to speak, be “taught” by reciprocal blindness. An oncoming car may have a headlight adjustment problem - it is driving with a low beam and its driver does not understand why you are blinking at him, maybe his driver just forgot to switch the light, or maybe he only has a high beam at that moment. And what could be worse than two blinded drivers who are driving towards each other and do not see anything?
If you are still blinded, and you can hardly distinguish what is happening on the road - smoothly turn off the speed, immediately turn on the emergency light signaling and without changing lanes, stop the car. After the sight is restored, it will be possible to go further.

It is very dangerous to be suddenly blinded by an oncoming car leaving because of the transverse profile of the road break (at the top of the hill). Approaching such a site and seeing the glow of oncoming headlights, be prepared for the fact that the oncoming car may not have time to switch the headlights to low beam - blink your headlights in advance so that he does not forget to do this. When an oncoming vehicle appears on the descent, it is also necessary to switch to the dipped beam earlier.
There are situations when the driver sees that a vehicle is moving towards it with one headlight on. It could be a motorcycle or it could be a car. If it is not possible to consider, then you should always assume that this is a car and its only working headlight is the right one! In this case, for the siding, take as far to the right as possible, and if this is not possible, stop and turn on the hazard warning lights. This is necessary so that those driving behind you can better see your car on the road and react in time.
When two cars, moving at night, meet on a turning arc, it turns out that one driver drives on the outer arc, and the other on the inner one. Thus, the headlights of a car driving “inside” the turn begin to blind the oncoming car earlier. Therefore, he needs to switch to low beam a little earlier. The driver of a car that is driving on the outer arc of a turn may switch to low beam a little later if he sees that his headlights do not interfere with oncoming traffic.
Night traffic outside the city
The most important thing when driving on night country roads is. Many factors need to be taken into account: the type and condition of the road surface, weather conditions, traffic intensity, and of course, how familiar you are with the road you are driving on. On an unlit road outside a built-up area, keep in mind that in most cases obstacles are located on the edge of the road. There may be a pit, there may be a standing unlit car, or there may be anything. Therefore, do not snuggle close to the edge of the roadway.
When you are following the vehicle in front (leadership), switch your headlights from high beam to low beam and pay close attention to safe distance. In this case, the leader takes control of all kinds of obstacles and dangers on the road. Your task is to carefully monitor its side lights and warning lights. And again, distance. In the dark, all objects appear further than they really are.

If you are in the lead role, then, if the situation allows, turn on the high beam headlights so that you can see obstacles on the road earlier. If you have to drive with low beams (for example, you often have to pass with oncoming people whom you can blind) and the road is hard to see, then slow down. But in this case, they can catch up with you and, as they say, “sit on the bumper”. And seeing the headlights reflected in your rearview mirror is very unpleasant. In this case, do not look in the mirror, but let yourself be overtaken. How in this case to behave to the drivers of the overtaken and overtaking cars has already been said in the article. Be sure to read.
If you intend to stop on an unlit road, it is not safe to do so even on the side of the road. Choose a place for such a stop where you can either pull off the road or pull away from the roadway as far as possible. If this is not possible, try to pull over to the side of the road and turn on your hazard warning lights to be more visible on the road.
During a long night trip while driving on a good level country road, a so-called state of monotony can occur. Why is it dangerous?
Smooth and calm movement slowly lulls vigilance and the level of attention to the environment decreases. Sometimes the driver imperceptibly "disconnects" from reality. In other words, he falls asleep right with his eyes open. This is very dangerous, because at this moment the driver is not able to monitor the traffic situation. Fatigue affects, especially since biologically nighttime is reserved for sleep. Therefore, at the slightest sign of fatigue, stop immediately, get out of the car and warm up.
There is one way for a driver to determine whether he is tired or not. In a normal situation, the driver looks directly at the road, steers, slows down, accelerates, in general, rides. And everything seems to be fine. But fatigue accumulates gradually, and it is difficult to determine the moment when the body is tired. Experienced drivers, especially truckers, know for themselves what fatigue is, but for those who have been driving recently, this advice may come in handy.
Now attention: first look at the road in front of the car, then turn your head and look at the road through the left window. If the road "floated" before your eyes, then you are tired and it's time to stop for a rest. Try to get out of the car, but not abruptly. Shaking? The brain seems to be aware of everything, but the body does not seem to obey. In this case, all the more you need to stop and rest - you are very tired. Further movement may not be safe. But it’s better not to bring yourself to such a state and make stops for rest as often as possible, especially if the trip is at night.
Navigating a series of articles
1. Movement at night
night car trip safety
When driving, be sure to take into account the fact that at night a person sees worse than during the day - a fact that has scientific confirmation. Moreover, with age, night vision becomes worse, so you should not drive often at night for people of advanced age.
If you are to night trip, it is necessary to perform whole line preparatory actions. The first thing to do is to check the condition of the car's lighting fixtures: are the parking lights on, are the direction indicators working, dipped and main beam headlights, brake lights, lights reversing, fog lights. The backlight of the instrument panel must be in good working order - otherwise you will not be able to control the speed of movement, as well as monitor the presence of fuel in the tank and the temperature of the coolant.
Be sure to check that the windshield wipers are working properly, the brushes are not worn out, and there is a enough liquids. Also check the condition of the side mirrors, if necessary, clean them of dust and dirt. Remember: when driving at night, many nuances that are invisible during the day take on special meaning. For example, "wipers" do not clean well Windshield- at night, because of this, visibility can deteriorate greatly (up to the point that you will not be able to drive normally). The same applies to rear-view mirrors: during the day it is still possible (but strongly discouraged) to drive with dirty mirrors, but at night they can be completely useless in this state.
If you haven't had to drive at night yet, be sure to study the location of the toggle switches and buttons designed to turn lights on and off - otherwise you will have to look for them on the go, distracting from driving. This is especially inconvenient in cases where you need to turn on or off one or another device as quickly as possible (the most typical example is the need to switch high beam headlights to low beam when oncoming vehicles appear).
You can check the operation of the rear lights by inviting an assistant who will stand behind the car while you turn on all the lights in turn. If there is no assistant - put your car with the hood against any wall - you can easily determine by the reflections on it whether the rear lighting or one of them is out of order.
About 90% of all actions that a driver performs while driving a car and all decisions he makes are based on what he sees. Consequently, the reliability of driving is much reduced in the dark: firstly, at night a person sees worse than during the day, and secondly, at night the driver's field of view is limited only to the area illuminated by the headlights of the car. That is why at night motorists commit more bugs, the bulk of which is associated with an incorrect estimate of the distance to the object, the wrong choice of speed and the determination of the speed of other vehicles.
At night, on an unlit road, the visibility zone is limited by headlights
At night, the driver has less time to make a decision, to perform a particular maneuver, as well as to correct a mistake. Ultimately, all this leads to the fact that the reaction time to changes in traffic conditions increases significantly.
The first thing the driver should do to improve visibility at night is to reduce the speed of movement down to the minimum. In any case, the same road should be driven much more slowly at night than during the day. The speed mode should be chosen based on the fact that, if necessary, it would be possible to quickly stop the vehicle within its visibility. In other words, when driving at night, the stopping distance of the vehicle should not exceed the distance that is illuminated by the headlights.
Do not drive faster than your visibility allows under current road conditions. Keep in mind that at night, a person’s vision can present him with various unpleasant “surprises”: the most typical example is objects that suddenly appear from the darkness, which in the daytime are perfectly visible from afar. In such situations, the driver needs twice as much time to detect such objects as during the day.
Many motorists neglect glasses prescribed by a doctor. This is completely unacceptable even in the daytime, and even more so in the dark. Ultimately, your neglect can lead to the fact that you may not notice an obstacle on the road in time and not have time to respond to its appearance, and this will lead to an accident. It’s good if this obstacle turns out to be a stone on the road, a pit or some kind of foreign object - much worse if such neglect causes a collision with a person (a tragic outcome is also possible). Remember: if you have minor defect vision, wearing them while driving is a must. If you don’t like glasses so much, you don’t even have to take them out of the car, but while driving, they should be your indispensable “ammunition”.
When driving on a night road, do not forget that there may be unlit obstacles and objects on it, as well as in its immediate vicinity. In particular, this may be an unlit vehicle. For this reason, when driving at night, try to ensure traffic safety. When it seems that there is some kind of obstacle ahead, immediately reduce the speed of movement until it comes to a complete stop: even if it only seemed to you, it is better to play it safe.
The most serious danger when driving at night is associated with pedestrians. If during the day you can easily notice a person who is standing by the side of the road and wants to cross the road (even if wrong place- you will have time to react), then at night you will hardly notice it. A pedestrian standing at the curb may well be out of your line of sight, so he will appear unexpectedly on the roadway. Particular vigilance should be shown in relation to children: because of their small stature, you discover them later than an adult. In addition, the actions of children are particularly unpredictable and at the same time fast. special attention elderly pedestrians are also worthy: they often do not look at the road at all and cross carriageway where they please. In addition, they are distinguished by a slow reaction, as well as an erroneous assessment of the traffic situation. However, the worst thing is drunken pedestrians: they are able to “throw out” such “tricks” on the road that one wonders how a person is capable of this?
If you see that in the immediate vicinity of the roadway there are representatives of these "dangerous" categories of pedestrians, prepare in advance for the worst case scenario. Reduce the speed of movement, "blink" the headlights, switching the dipped and main beam headlights, if necessary, apply sound signal, plan in advance the trajectory of a possible change in direction of movement, and also be prepared to brake urgently.
When driving at night, pay close attention to the vehicle in front of you so as not to miss the moment of its possible braking. Remember: in the dark, the only sign by which you can determine the beginning of its braking is the lit brake lights.
If you feel tired, stop and rest.
When you have a long night trip, it is best to take a partner with you who has driver license. This will allow you to change places with him and take turns resting.
Drivers of vehicles should turn on their parking lights in advance to compensate for poor visibility at night. Remember - in the dark you need to drive at a lower speed than during the day. First, so you get the opportunity to get in this situation best review, secondly, there will be more time to follow the road, detect obstacles and react in case of an unexpected change in traffic conditions. If a critical situation happens, then you will have more chances to get out of it with the least losses.
Before performing any maneuver, turn on the appropriate direction indicator in advance: this rule is many times more relevant at night. Due to limited visibility, it is necessary to notify other road users of any, even little change the trajectory of your vehicle. At the same time, please note that the drivers of other vehicles must have enough time to respond appropriately to your maneuver.
"Performing a right turn" (at night)

At night, keep an increased distance between your car and the vehicle ahead.
"Keeping your distance when driving at night"

As far as possible, try to avoid overtaking, and if this is not possible, exercise extra caution.
Before the trip, think over and prepare the route. If you “rush around” along the night road, looking for the right turn, you will noticeably complicate traffic situation and create unnecessary problems not only for yourself, but also for other road users.
The location of the car on the road "(during the dark)

Don't let yourself relax. There are fewer vehicles on the roads at night than during the daytime, which causes many drivers to be completely inappropriately complacent and unjustifiably relaxed. Despite the fact that there are fewer vehicles on the road at night, there are much more dangers when driving than during the day.
Always keep an eye on the speedometer: the intuition of any driver is not enough to adequately assess the speed of his car.
Of exceptional importance when driving at night on a suburban highway is the choice of the optimal speed mode. Remember: if traffic rules allow cars move outside settlements at a speed of 90 km / h - this does not mean that at night you need to drive along a country road at this speed. Perhaps, in your case, 60-70 km / h will be enough. Choosing speed mode when driving at night outside the city, consider the following factors.
- 1. The number of lanes for traffic in each direction, available on a given road. If the road has only one lane in each direction, it is obvious that to go from high speed it would be too dangerous. When the road is two- or even three-lane, the speed can be increased (of course, within reasonable limits).
- 2. Type and condition of the road surface. Obviously, when driving on an asphalt road, you can develop a higher speed than on dirt road. If there are pits, potholes and potholes on the road, it is dangerous to drive at high speed: the car can end up in a ditch or into oncoming traffic, and this the right way quickly disable parts and suspension assemblies.
- 3. Your degree of familiarity with the road you are on. It's one thing when you drive along a well-known road where you know every bump, every turn and every road sign, and quite another - if the track is unfamiliar, and you are intensely peering ahead.
- 4. The technical condition of your car. If you have, for example, wheel tires in not very good condition, shock absorbers are unreliable, or the camber and toe-in are not adjusted, etc. - you should not drive at high speed at night. It may happen that due to poor visibility you notice an obstacle late and technical condition your vehicle will not prevent an accident.
- 5. Current weather conditions. If it is raining or snowing outside, the road surface is wet and slippery, visibility is poor, you need to drive minimum speed. It happens that in the headlights of snowfall or heavy rain appears as a solid wall, limiting visibility in front of the car by literally two or three meters (and sometimes even less). When in such a situation there is some kind of obstacle in front of the car, then when driving at a speed of more than 10 km / h, you simply do not have enough time to respond in a timely manner and prevent an accident.
- 6. Current situation on the road. It is one thing when you are alone on the track, and quite another if there is traffic on the road. a large number of both passing and oncoming vehicles.
In the absence of oncoming vehicles, turn on the high beam headlights - this will significantly improve visibility. As soon as an oncoming vehicle appears, immediately switch to low beam headlights so as not to dazzle the driver. At the same time, it is recommended to slow down, because even the dipped headlights of an oncoming vehicle will noticeably worsen visibility (in addition, you will also switch to dipped headlights, and this will also negatively affect your line of sight).
If the driver of an oncoming car, when approaching you, did not switch to dipped headlights, “blink” him. But in no case do not turn on the high beam "in retaliation" - this is fraught with the most backfire. As a result of unexpected blinding, the driver of an oncoming vehicle may accidentally enter your lane of oncoming traffic - you will provoke a head-on collision.
Therefore, in similar situation(when an oncoming vehicle is driving with high beam headlights) the first thing to do is to slow down and, if necessary, stop completely. It is also recommended that you turn on your hazard warning lights (before you stop) to warn other road users of possible danger. If you decide that you will not stop - direct the car closer to the curb and continue to move at low speed with low beam headlights.
In no case do not look at the headlights of an oncoming vehicle - this is the shortest way to dazzle. Direct your gaze to the right, but in such a way as to control the situation on the road, and while driving, be guided by the right edge of the carriageway. Drive at a slower speed until visibility is fully restored.
Sometimes there are situations when the driver is blinded not by an oncoming car, but by a passing car that moves behind (this happens through a rear-view mirror located in the passenger compartment). IN this case try as far as possible not to look into this mirror, and even better - temporarily move it to another position, turning away from you. It is for this reason that you should never forget to switch to low beam headlights when approaching another vehicle from behind. Another way to get rid of rear glare is to allow the vehicle behind you to overtake your vehicle.
There are times when, when driving at night, the car's lights suddenly fail. Needless to say, how dangerous this is: after all, your car in such a situation becomes completely invisible to other road users, and if drivers of other vehicles can still somehow notice your car in the light of their headlights, then a pedestrian may well step right under the wheels .
Note
Most often, lighting devices fail due to a blown fuse - this is one of the simplest breakdowns that can be easily fixed on your own. Therefore, always keep a spare set of fuses in the glove compartment.