It will not be news to anyone that an incorrectly adjusted camber can lead not only to a deterioration in tire quality, but also to increase fuel consumption. That is why, it is worth approaching responsibly to exhibiting a collapse.
On your own adjust camber not at all difficult, as it may seem at first. We will try to consider this issue in detail and give best advice novice mechanics. Stabilization of a pair of steering wheels is the same important aspect, which affects the stability of the car on the road. What does it mean? The wheels should move in a straight line, and bypassing the turn, return to their original position.
Following from this, the urgent need for a wheel stabilization procedure is explained very simply. When the car is moving, wheels that are not stabilized move to the side as a result of shocks from the road. Then the driver must return the wheels to the desired (rectilinear) position. Given that this happens all the time, the person behind the wheel gets more tired. In addition, the steering gear contacts wear out faster. And with increasing speed, the growing instability becomes unsafe.
What determines the stabilization of the steered wheels? The answer is simple: from their convergence or collapse. Camber adjustment wheels can be produced in car workshops, but it is quite possible to solve this problem and do it yourself.
The first thing to do is to determine the need for camber adjustment.
Let's look at it point by point:
- Continuous departure of a car from a given course of rectilinear movement in one direction or another.
- Uneven tire wear.
- When examining the tread groove front wheel along the axis of rotation, it is necessary to examine the edges of this groove. The edges are the same - this means that there is no reason to worry, if one of them has some sharpness, and the other does not, then you have a problem. But you should pay attention to this only when driving calmly. If you are a fan fast speed, then this condition can be misleading.
- Difficulty in controlling during maneuvers. The presence of at least one of these symptoms indicates that it is necessary to install the camber. Drivers who have some experience in do-it-yourself car repair, with a strong desire, can perform wheel alignment on their own.
How is collapse regulated?
To repair you will need:
- ruler;
- standard set of tools;
- cord with a plumb line;
- a flat area with a pit or a lift.

First you need to find out: how accurately the convergence was made before. Those. “Zero” position at the steering rack during rectilinear movement. How to do it? We follow further instructions: put the car on a flat surface. Then turn the steering wheel as much as possible in one direction, making a mark on the top of the steering wheel (in the middle of the circle) turn the steering wheel all the way to the other side. In this case, it is necessary to count the number of whole revolutions and parts of a whole circle (shares). When calculated, divide the amount received by 2 and turn the steering wheel to this position. If given result coincides with the usual position of the steering wheel, then the “zero” position of the rack is set. If not, you will have to do it yourself.
How to set the "zero" position?
It is necessary to remove the steering wheel, to do this, unscrew the nut. After fixing it in the “zero” position calculated by us (the spokes of the steering wheel should be located symmetrically). Now we will focus on this position. In order to check yourself, you need to turn the steering wheel left / right alternately - in both directions it must turn the same number of revolutions, so turning the wheel to the side to the limit, protect them.
Next, you need to loosen the lock nuts of the tie rod ends. One rod should be unscrewed a little, and the second one should be twisted by the same number of revolutions (this is very important!). This procedure can be done once and no longer change the position of the steering wheel. And in the future - only to regulate the convergence.
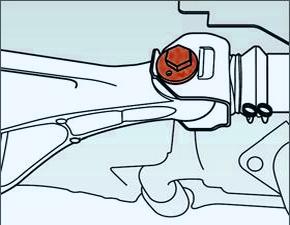
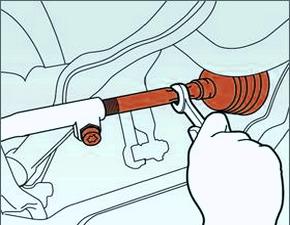
How to adjust wheel alignment?
After checking the straightness, you need to check the degree of congestion of the transport, tire pressure, whether the suspension and steering mechanism are securely fastened. After that, you can already proceed directly to checking and adjusting the convergence.
To determine the level of convergence of the wheels, you should calculate the difference between the points on the rim in front and behind its geometry axis. To do this, you need to use a special chain with a ruler or a tensioner.
To measure the toe-in, the ruler is installed between the wheels, so that the tips of the pipes rest against the side of the tires, and the chains touch the ground. When you set the arrow to the zero position, the car should be rolled forward a little so that the ruler is behind the wheel axle. In this case, the arrow should show the level of convergence. In case of non-compliance with the norm, it must be corrected.
In order to adjust the wheel alignment, you need to rotate couplings side tie rods. When this operation is carried out, the control nuts must be securely tightened.
Camber adjustment
by the most complex process there is a check and adjustment of the camber, but it is also possible to do it on your own. To do this, the car is raised so that the wheels do not touch the ground. After that, you need to calculate the places of the same runout on the side of the tires. With the wheels in the straight ahead position, hang a load next to the wheel. Chalk marks are made around the circumference of the wheel at the top and bottom. Using a plumb line, calculate the distance from the rim to the line.
The difference in distance between the weight thread and the upper part of the rim is the camber level. For the accuracy of the procedure, roll the car so that the wheel turns 90? .. Repeat several times and record the results.
Next, remove the car wheel and release 2 bolts securing the shock absorber strut bracket to knuckle. Then we shift the steering knuckle in or out, in which direction, and at what distance, depends on the results of your measurements. This is how you can set the desired camber angle. After the procedure, you need to tighten the bolts, put the wheel on and take measurements again.
Please note that on vehicles with rear wheel drive allow the norm of the camber angle of the front wheels, somewhere in the range of +1 - +3 mm, and for cars with front-wheel drive, this norm is from -1 to +1 mm.
After completing the entire procedure, do not forget to check the tightness of all those bolts that you adjusted. And after completing the camber adjustment, check the alignment of the vehicle on the road.
When doing the wheel alignment with your own hands, remember that it is necessary to take measurements several times (at least three), and then take the arithmetic mean. If the wheel alignment is adjusted correctly, vehicle will not go to the side when driving, and tire tread wear will be uniform.
The entire adjustment procedure is carried out again if, after the work carried out, the machine still “leaves” the trajectory of rectilinear motion. Incorrect camber or convergence will also be indicated by uneven tire wear, so tire diagnostics will also not be superfluous.

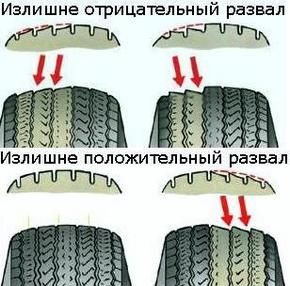
Doing such a difficult procedure yourself will save you a decent amount of money, but remember that for most modern cars it is recommended to carry out the descent / collapse in car services.
To ensure good stability and controllability of the car, the front wheels are set at certain angles relative to the body and suspension elements. Three parameters are adjusted: toe-in, camber angle, angle caster axis of rotation.
The pitch angle of the axis of rotation is the angle between the vertical and the line passing through the centers of rotation of the ball joint and the bearing of the telescopic strut support, in a plane parallel to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. It contributes to the stabilization of the steered wheels in the direction of rectilinear motion. This angle is adjusted by changing the number of shims on the brace tips. To reduce the angle, washers are added, and removed to increase. When installing / removing one washer, the angle changes by approximately 19 ". Symptoms of angle deviation from the norm: car pulling to the side when driving, different efforts on the steering wheel in left and right turns, one-sided tread wear.
Camber angle - the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the vertical. He contributes correct position rolling wheel during suspension operation. The angle is adjusted by turning the upper bolt of the telescopic strut to the steering knuckle. With a strong deviation of this angle from the norm, it is possible to take the car away from rectilinear movement, one-sided wear of the tread.
Toe-in is the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. Sometimes this angle is calculated from the difference in the distances between the rim flanges, measured behind and in front of the wheels at the level of their centers. Wheel alignment contributes to the correct position of the steered wheels at various speeds and angles of rotation of the vehicle.
The toe-in is adjusted by turning the adjusting rods with the tie rod end pinch bolts loosened. Before adjusting, the steering gear rack is set to the middle position (the steering wheel spokes are horizontal). Signs of deviation from the norm: severe sawtooth tire wear in the transverse direction (even with small deviations), tire squealing in corners, increased consumption fuel due to the high rolling resistance of the front wheels (the run-out of the car is much less than expected).
Control and adjustment of the angles of the front wheels is recommended to be carried out at the station Maintenance. The car is installed on a horizontal platform and loaded in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations (see below). (Checking and adjusting the angles on an unloaded vehicle is acceptable, but gives less accurate results. Before doing this, you should make sure that the tire pressure is correct, the tread wear on the left and right wheels is approximately the same, there are no play in the bearings and steering, wheel disks not deformed (radial runout - no more than 0.7 mm, axial runout - no more than 1 mm).
Checking the wheel alignment angles is mandatory if the suspension parts that affect these angles have been changed or repaired. Due to the fact that the installation angles of the front wheels are interconnected, first of all, they check and adjust the angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation, then the camber and, in last turn, convergence. For a run-in car in running order and with payload 320 kg (4 people) in the cabin and 40 kg of cargo in the trunk, the wheel alignment must be within the following limits.
Front wheel alignment
To ensure good stability and controllability of the car, the front wheels are set at certain angles relative to the body and suspension elements. Three parameters are adjusted: toe-in, camber angle, caster angle.
The pitch angle of the axis of rotation is the angle between the vertical and the line passing through the centers of rotation of the ball joint and the bearing of the telescopic strut support, in a plane parallel to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. It contributes to the stabilization of the steered wheels in the direction of rectilinear motion. This angle is adjusted by changing the number of shims on the brace tips. To reduce the angle, washers are added, and removed to increase. When installing / removing one washer, the angle changes by approximately 19 ". Symptoms of angle deviation from the norm: car pulling to the side when driving, different efforts on the steering wheel in left and right turns, one-sided tread wear.
Camber angle - the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the vertical. It contributes to the correct position of the rolling wheel during suspension operation. The angle is adjusted by turning the upper bolt of the telescopic strut to the steering knuckle. With a strong deviation of this angle from the norm, it is possible to take the car away from rectilinear movement, one-sided wear of the tread.
Toe-in is the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. Sometimes this angle is calculated from the difference in the distances between the rim flanges, measured behind and in front of the wheels at the level of their centers. Wheel alignment contributes to the correct position of the steered wheels at various speeds and angles of rotation of the vehicle.
The toe-in is adjusted by turning the adjusting rods with the tie rod end pinch bolts loosened. Before adjusting, the steering gear rack is set to the middle position (the steering wheel spokes are horizontal). Signs of deviation from the norm: strong sawtooth tire wear in the transverse direction (even with small deviations), tire squealing in corners, increased fuel consumption due to high rolling resistance of the front wheels (vehicle run-out is much less than expected).
The control and adjustment of the angles of the front wheels is recommended to be carried out at a service station. The car is installed on a horizontal platform and loaded in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations (see below). (Checking and adjusting the angles on an unloaded vehicle is acceptable, but gives less accurate results. Before doing this, you should make sure that the tire pressure is correct, the tread wear on the left and right wheels is approximately the same, there are no play in the bearings and steering, the rims are not deformed (radial runout - no more than 0.7 mm, axial - no more than 1 mm).
Checking the wheel alignment angles is mandatory if the suspension parts that affect these angles have been changed or repaired. Due to the fact that the angles of the front wheels are interconnected, first of all, the angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation is checked and adjusted, then the camber and, lastly, the convergence. For a run-in vehicle in curb condition and with a payload of 320 kg (4 people) in the cabin and 40 kg of cargo in the trunk, the wheel alignment must be within the following limits:
Wheel alignment angles of the vehicle in running order.
Page 2 of 2
To ensure good stability and controllability of the car, the front wheels are set at certain angles relative to the body and suspension elements. Three parameters are adjusted: toe-in, camber angle, caster angle.
The angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation (Fig. 1) is the angle between the vertical and the line passing through the centers of rotation of the ball joint and the bearing of the telescopic strut support, in a plane parallel to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. It contributes to the stabilization of the steered wheels in the direction of rectilinear motion. This angle is adjusted by changing the number of shims on the brace tips. To reduce the angle, washers are added, and removed to increase. When installing / removing one washer, the angle changes by approximately 19 ". Symptoms of angle deviation from the norm: car pulling to the side when driving, different efforts on the steering wheel in left and right turns, one-sided tread wear.

Camber angle (Fig. 2) - the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the vertical. It contributes to the correct position of the rolling wheel during suspension operation. The angle is adjusted by turning the upper bolt of the telescopic strut to the steering knuckle. With a strong deviation of this angle from the norm, it is possible to take the car away from rectilinear movement, one-sided wear of the tread.
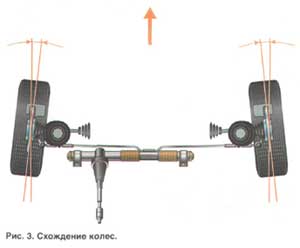
Toe-in (Fig. 3) - the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. Sometimes this angle is calculated from the difference in the distances between the rim flanges, measured behind and in front of the wheels at the level of their centers. Wheel alignment contributes to the correct position of the steered wheels at various speeds and angles of rotation of the vehicle.
The toe-in is adjusted by turning the adjusting rods with the tie rod end pinch bolts loosened. Before adjusting, the steering rack is set to the middle position (the steering wheel spokes are horizontal). Signs of deviation from the norm: strong sawtooth tire wear in the transverse direction (even with small deviations), tire squealing in corners, increased fuel consumption due to high rolling resistance of the front wheels (vehicle run-out is much less than expected).
The control and adjustment of the angles of the front wheels is recommended to be carried out at a service station. The car is installed on a horizontal platform and loaded in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations (see below). (Checking and adjusting the angles on an unloaded vehicle is acceptable, but gives less accurate results. Before doing this, you should make sure that the tire pressure is correct, the tread wear on the left and right wheels is approximately the same, there are no play in the bearings and steering, the rims are not deformed (radial runout - no more than 0.7 mm, axial - no more than 1 mm).
Checking the wheel alignment angles is mandatory if the suspension parts that affect these angles have been changed or repaired. Due to the fact that the angles of the front wheels are interconnected, first of all, the angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation is checked and adjusted, then the camber and, lastly, the convergence.
For a run-in vehicle in curb condition and with a payload of 320 kg (4 people) in the cabin and 40 kg of cargo in the trunk, the wheel alignment must be within the following limits:
camber angle ............................................... ...........0°±30"
convergence................................................. .............0°00"±10" (0±1mm)
Pitch Angle.......................1°30"±30"
Vehicle wheel alignment angles in running order:
camber angle ............................................... ...........0°30"±30"
convergence................................................. .............0°15"±10" (1.5±1mm)
Pitch Angle......................0°20"±30"
Front suspension angles
To ensure good stability and controllability of the car, the front wheels are set at certain angles relative to the body and suspension elements. Three parameters are adjusted: toe-in, camber angle, caster angle.
The angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation (Fig. 1) is the angle between the vertical and the line passing through the centers of rotation of the ball joint and the bearing of the telescopic strut support, in a plane parallel to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. It contributes to the stabilization of the steered wheels in the direction of rectilinear motion. This angle is adjusted by changing the number of shims on the brace tips. To reduce the angle, washers are added, and removed to increase. When installing / removing one washer, the angle changes by approximately 19 ". Symptoms of angle deviation from the norm: car pulling to the side when driving, different efforts on the steering wheel in left and right turns, one-sided tread wear.
Camber angle (Fig. 2) - the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the vertical. It contributes to the correct position of the rolling wheel during suspension operation. The angle is adjusted by turning the upper bolt of the telescopic strut to the steering knuckle. With a strong deviation of this angle from the norm, it is possible to take the car away from rectilinear movement, one-sided wear of the tread.
Toe-in (Fig. 3) - the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. Sometimes this angle is calculated from the difference in the distances between the rim flanges, measured behind and in front of the wheels at the level of their centers. Wheel alignment contributes to the correct position of the steered wheels at various speeds and angles of rotation of the vehicle.
The toe-in is adjusted by turning the adjusting rods with the tie rod end pinch bolts loosened. Before adjusting, the steering rack is set to the middle position (the steering wheel spokes are horizontal). Signs of deviation from the norm: strong sawtooth tire wear in the transverse direction (even with small deviations), tire squealing in corners, increased fuel consumption due to high rolling resistance of the front wheels (vehicle run-out is much less than expected).
The control and adjustment of the angles of the front wheels is recommended to be carried out at a service station. The car is installed on a horizontal platform and loaded in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations (see below). (Checking and adjusting the angles on an unloaded vehicle is acceptable, but gives less accurate results. Before doing this, you should make sure that the tire pressure is correct, the tread wear on the left and right wheels is approximately the same, there are no play in the bearings and steering, the rims are not deformed (radial runout - no more than 0.7 mm, axial - no more than 1 mm).
Checking the wheel alignment angles is mandatory if the suspension parts that affect these angles have been changed or repaired. Due to the fact that the angles of the front wheels are interconnected, first of all, the angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation is checked and adjusted, then the camber and, lastly, the convergence.
For a run-in vehicle in curb condition and with a payload of 320 kg (4 people) in the cabin and 40 kg of cargo in the trunk, the wheel alignment must be within the following limits:
camber angle ............................................... ........0°±30"
toe-in ...............................0°00"±10" (0± 1 mm)
Pitch Angle.......................................................1°30"±30 "
Vehicle wheel alignment angles in running order:
camber angle ............................................... ...0°30"±30"
toe-in.................................0°15"±10" (1.5±1 mm)
Pitch angle......................................................0°20"±30 "







