Engine Chevrolet 1.8 F18D4 (141 hp) Cruz, Opel Mokka
Short description
The Chevrolet 1.8 F18D4 engine was installed on Chevrolet Cruze 1.8 (Chevrolet Cruze) and Opel Mokka cars. The engine has been produced since 2008.
Peculiarities. The Chevrolet 1.8 F18D4 engine is an advanced engine. The engine received a variable valve timing system VVT intake and exhaust channels and a system for changing the length of the intake pipe channels. The gas distribution mechanism drive remained belt-driven, but the belt resource was increased to 150 thousand km. The hydraulic compensators were removed, instead of them calibrated glasses appeared, which must be changed every 100 thousand km. There is no EGR on this engine. Engine 1.8 F18D4 140 hp was spared the typical problems of 1.8 F18D3.
The engine resource remained the same - in the region of 250,000 km.
Engine characteristics Chevrolet 1.8 F18D4 (141 hp) Cruz, Opel Mokka
| Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Configuration | L |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Volume, l | 1,796 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 80,5 |
| Piston stroke, mm | 88,2 |
| Compression ratio | 10,5 |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 4 (2-inlet; 2-outlet) |
| Gas distribution mechanism | DOHC |
| The order of operation of the cylinders | 1-3-4-2 |
| Rated engine power / at engine speed | 104 kW - (141 hp) / 6300 rpm |
| Maximum torque / at revs | 175 Nm / 3800 rpm |
| Supply system | Distributed fuel injection with electronic control |
| Recommended minimum octane number of gasoline | 95 |
| Environmental regulations | Euro 5 |
| Weight, kg | 115 |
Design
Four-stroke four-cylinder petrol with electronic fuel injection and ignition control, in-line arrangement of cylinders and pistons rotating one common crankshaft, with an overhead arrangement of two camshafts with a phase control system. The engine has a closed-type liquid cooling system with forced circulation. Lubrication system - combined.
Inlet and outlet valves
The diameter of the intake valve plate is 31.0 mm, the exhaust valve is 27.5 mm. The diameter of the inlet and outlet valve stem is 5.0 mm. The length of the intake valve is 114.0 mm, and the exhaust valve is 113.2 mm. The intake valve is made of chrome silicon alloy and the exhaust head is made of chrome manganese nickel alloy, the stem is made of chrome silicon alloy.
Service
Changing the oil in a Chevrolet 1.8 F18D4 engine. On a Chevrolet Cruze and Opel Mokka car with a 1.8 F18D4 engine (141 hp), an oil change every 15 thousand km or 12 months. The engine has 4.5 liters of oil. When changing the oil with a filter element, you will need 4.1-4.5 liters, without a filter - about 4 liters. Oil type: 5W-30, 5W-40, 0W-30 and 0W-40 (low temperatures), class - GM-LL-A-025. The approved oil is GM Dexos2.
Replacing the timing belt Chevrolet 1.8 F16D4 Cruz. Once every 100 thousand km, you need to check its condition. The timing belt is replaced along with the rollers every 150 thousand km (otherwise the belt will break and the valves will bend).
Change candles every 60 thousand kilometers. Candles NGK ZFR6U-11.
Air filter Chevrolet 1.8 must be replaced by 50 thousand km of its service.
Change coolant in 1.8 F14D4 according to the GM regulations, it is required every 240 thousand km or 5 years (for the conditions of the Russian Federation, it is better once every 2 years). Fill with GM Dex-Cool antifreeze.
The surface of the toothed part of the belt should not have cracks, undercut teeth and delamination of the fabric from the rubber, and the reverse side of the belt - wear, exposing the cord threads, and signs of burning. On the end surfaces of the belt there should be no delaminations and fraying. If there is damage, the belt must be replaced. The belt must also be replaced if traces of oil are found on it (before replacing the belt, the cause of its oiling should be eliminated) or when replacing a failed belt tensioner or guide roller.
Upon reaching a run of 150 thousand km, the belt must be replaced, regardless of its condition.
We carry out work with an assistant on a viewing ditch or overpass.
We start by removing the protection of the power unit.
From the bottom of the car with a “13” head, we unscrew the four bolts securing the protection of the power unit to the front suspension subframe.
We remove the protection of the power unit, supporting it with an adjustable stop.
We take out two pistons connecting the shield and the right wheel liner at the same time.
Using the “8” head, unscrew the three screws securing the shield to the subframe.
Sliding the right shield down, we remove it from under the wheel liner and remove it.
We unscrew the screws securing the fender liner of the right front wheel to the front bumper and fender and take out the caps for fastening the front part of the fender liner to the body, bend the front part of the fender liner and wind it behind the brake disc.
To check the condition of the belt with the E-10 head, unscrew the two screws securing the upper timing cover.
We remove the cover.
Turning the head E-18 the crankshaft clockwise for the screw securing the auxiliary drive pulley, ..
... we evaluate the condition of the timing belt.
The operation to replace the timing belt is quite complicated. At authorized dealer services, when replacing the belt, a special tool and fixtures are used to set the valve timing of the engine. Therefore, we recommend that you only replace the belt yourself by an experienced contractor who has the appropriate skills to repair modern engines.
To replace the timing belt, remove the accessory drive belt ...
To access the timing belt, the right support of the power unit must be dismantled.
We install a height-adjustable stop through a wooden block under the engine crankcase.
Remove the air filter.
With the “15” head, we unscrew the two bolts of the right support of the power unit to the side member, three bolts of the support to the engine bracket and the nut of the support to the mudguard of the body.
We take out the support from the engine compartment.
The right support of the power unit.
To access the ends of the camshafts, remove the cylinder head cover.
Pulling up, remove the covers of the engine control wiring harnesses from the holders of the cylinder head cover.
We shift the spring retainer of the tip of the crankcase ventilation tube.
Remove the tube tip from the fitting of the cylinder head cover.
Using the E-10 head, we unscrew 11 screws securing the cylinder head cover.
Remove the cylinder head cover.
For clarity, further operations are shown on a dismantled engine.
Before removing the belt, set the crankshaft and camshafts to the TDC (top dead center) position of the compression stroke of the first cylinder.
To do this, turn the crankshaft clockwise by the screw securing the auxiliary drive pulley until the mark on the auxiliary drive pulley coincides with the mark on the bottom cover of the timing drive.
In this case, the grooves made on the shanks of both camshafts should be located parallel and practically on the same level with the surface of the cylinder head adjacent to the head cover.
If the grooves on the camshaft shanks do not occupy the indicated position, turn the crankshaft one more turn (360º) clockwise and again check the correct installation of the crankshaft and camshafts.
Using the E-18 head, we unscrew the screw securing the auxiliary drive pulley. In order to keep the crankshaft from turning, we put stops under the wheels of the car, turn on the fifth gear in the gearbox and ask the assistant to strongly press and hold the brake pedal.
If it was not possible to unscrew the pulley fastening screw in this way, then, having unscrewed the two bolts with the “15” head, we dismantle the dirt-proof plate that covers the gap at the junction of the gearbox housing and the engine crankcase pan - next to the right wheel drive inner hinge housing.
Through the gap we insert a slotted screwdriver between the teeth of the flywheel and rest it on the differential bearing cover, thereby blocking the crankshaft from turning.
Having unscrewed, we take out the screw securing the auxiliary drive pulley.
We remove the pulley.
With the “15” head, we unscrew the three bolts securing the bracket of the right support of the power unit (the coolant pump pulley has been removed for clarity).
We remove the bracket.
With a slotted screwdriver, we release the lock of the middle timing cover on one side ...
…and on the other hand.
Lift and remove the middle timing cover.
Using the E-10 head with an extension, unscrew the four screws securing the lower timing cover.
Remove the cover .
2290–6_Dvigatel.indd
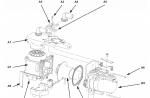
The drive of the gas distribution mechanism of the engine.
1 - belt tension roller; 2 - actuator of the intake camshaft phase control system; 3 - actuator of the exhaust camshaft phase control system; 4 - timing belt; 5 - belt guide roller; 6 - toothed pulley of the crankshaft
Again, we check the correct installation of the valve timing of the engine.
With the auxiliary drive pulley removed, we check the coincidence of the mark on the crankshaft toothed pulley with the mark on the cylinder block cover.
The marks on the toothed pulleys of both camshafts must be located opposite each other.
If necessary, turn the crankshaft to the required position by the accessory pulley screw, screwed into place through a suitable thrust sleeve.
In order to fix the camshafts from turning when replacing the belt, it is necessary to make a fixture from a metal plate or corner.
2290–6_Dvigatel.indd
Device for fixing camshafts.
We insert the device into the grooves on the camshaft shanks.
The plate will fix the shafts relative to each other.
Attention! To avoid damage to the camshaft position sensor drive discs, install the plate so that it does not touch the discs. For this, two recesses are made in the plate.
To loosen the belt tension, insert the “6” hexagon into the roller hole and, turning the roller clockwise with the hexagon, loosen the belt tension and pull the belt off the roller.
We remove the timing belt from the toothed pulleys of the camshafts and the crankshaft.
Timing belt, number of teeth 146, width 24 mm.
Attention! After removing the belt, the crankshaft must not be rotated to avoid sticking the valves into the pistons.
If it is necessary to replace the tension roller with a Torx T-50 key, unscrew its fastening screw.
We're filming a video.
To replace the belt guide roller with a Torx T-50 key, unscrew the roller fastening screw.
We're filming a video.
When installing the tension roller, we introduce the protruding end of its spring (on the reverse side of the roller) ...
... into the corresponding groove on the cylinder cover.
Before mounting the belt, we check the coincidence of the installation marks (see above) for the correct installation of the crankshaft and the housings of the actuators of the camshafts of the phase control system. If necessary, turn the crankshaft and camshaft pulleys to the desired position. We put the belt on the toothed pulleys of the crankshaft and camshafts and wind the belt behind the guide roller. By turning the tension roller clockwise, we start the belt behind it and release the roller. This will automatically tension the belt.
We take out the fixing device from the grooves of the camshaft shanks. We turn the crankshaft two turns clockwise for the screw securing the auxiliary drive pulley.
We again check the valve timing. If the alignment marks do not match, repeat the procedure for installing the timing belt.
We tighten the screw securing the auxiliary drive pulley at the beginning with a torque of 95N m. Next, turn it 30°, and then another 15°.
All other parts and assemblies are installed in the reverse order.
Any Chevrolet Cruze engine provides decent dynamics and smoothness for this car. Initially, two gasoline atmospheric chevrolet cruze engine volume of 1.6 and 1.8 liters, later there was a turbo engine with a working volume of 1.4 liters.
The turbo engine provides quite a lot of power, good torque and at the same time is very economical. It is worth noting that in many countries the Chevrolet Cruze engines have diesel options with a volume of 1.7 and 2 liters. The power units of the Chevrolet Cruze EcoTec series are 4-cylinder 16-valve engines with two camshafts on top, that is, it is DOHC.
An important question that worries many. Belt or chain stands in the timing drive of Chevrolet Cruze engines? There is a strong opinion that the chain is more reliable and does not need to be replaced frequently. However, modern belts today are also quite reliable. So let's reveal a big secret. in Chevrolet Cruze engines, a belt in the timing drive. According to the manufacturer, the belt itself has an extended service life.
Photo of the Chevrolet Cruze engine under the hood.

Engine characteristics Cruz Ecotec 1.6 (109 hp)
- Working volume - 1598 cm3
- Power - 109 hp at 6000 rpm
- Maximum speed - 185 (manual transmission) and 177 (automatic transmission) kilometers per hour
- Acceleration to the first hundred - 12.5 (manual transmission) and 13.5 (automatic transmission) seconds
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle - 7.3 (manual transmission) and 8.3 (automatic transmission) liters
And the parameters of the motor for the station wagon.
Characteristics of the Cruze SW 1.6 engine (124 hp)
- Working volume - 1598 cm3
- Power - 124 hp at 6000 rpm
- Torque - 150 Nm at 4000 rpm
- Maximum speed - 192 (manual transmission) kilometers per hour
- Acceleration to the first hundred - 12.6 (manual transmission) seconds
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle - 6.5 (manual transmission) liters
A more powerful 1.8-liter gasoline engine with a capacity of 141 hp. provides good dynamics, both on the Cruz sedan, and on the station wagon and hatch.
Characteristics of the Chevrolet Cruze Ecotec 1.8 liter engine
- Working volume - 1796 cm3
- Power - 141 hp at 6000 rpm
- Torque - 176 Nm at 3800 rpm
- Maximum speed - 200 (manual transmission) and 190 (automatic transmission) kilometers per hour
- Acceleration to the first hundred - 11 (manual transmission) and 11.5 (automatic transmission) seconds
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle - 6.8 (manual transmission) and 7.8 (automatic transmission) liters
Well, the most interesting engine is a turbo engine with a volume of only 1.4 liters. Small volume ensures minimum fuel consumption. At the same time, the presence of a turbine makes the power unit very dynamic. At 140 horsepower, the torque is 200 Nm, recall the atmospheric 1.8 produces 141 horses, but the torque is only 176 Nm, plus increased fuel consumption. At the same time, all the torque of the turbocharged engine is already available from 1,850 engine revolutions, and the aspirated 1.8 will have to be spun up to 3800. That is, already at the bottom, the 1.4 turbo is ready to give out a maximum. In addition to efficiency (5.7 liters on the highway), the Chevrolet Cruze turbo engine is also more environmentally friendly. Here are the specifications for this motor.
Engine characteristics Ecotec 1.4 Turbo
- Working volume - 1398 cm3
- Power - 140 hp at 4900 rpm
- Torque - 200 Nm at 1850 rpm
- Maximum speed - 200 (automatic) kilometers per hour
- Acceleration to the first hundred - 10.3 (automatic transmission) seconds
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle - 5.7 (automatic transmission) liters
The Chevrolet Cruze is one of the best-selling cars produced by an independent division of General Motors Corporation - Chevrolet (1911). The model first appeared on the car market in 2008 and, constantly improving, is being produced to this day.
In general, the range of engines that Chevrolet Cruze cars can be equipped with is very diverse. However, in Russia, models were initially supplied equipped only with atmospheric engines F16D4 and F18D4, having a cylinder capacity of 1.6 and 1.8 liters, respectively. A little later (2010) they added a turbocharged power unit A14NET / NEL with a cylinder capacity of 1.4 liters, which comes only with an automatic transmission and is capable of developing power up to 143 liters. With. At the same time, the F16D4 engine (EcoTec series) is considered the base engine of the Chevrolet Cruze.

One of the questions that worries buyers of any car is how the gas distribution mechanism (timing) of the power unit is actuated. Cars of the Chevrolet Cruze lineup are no exception, on which engines with different timing drive mechanisms can be installed.
Timing mechanism
The timing drive is one of the most critical components in an internal combustion engine (ICE). It is with its help that the camshaft of the power unit is driven, the rotational movement of which is transmitted from the crankshaft. In modern car engines, a rubber belt or a metal chain is used for this.
Belt drive
In atmospheric engines that power Chevrolet Cruze cars, the timing camshaft is driven by a rubber belt.

Among the advantages of a belt drive, experts note:
- ease of replacement;
- no additional lubrication;
- no noise;
A high strength rubber belt is mounted on the open gears of the crankshaft and camshaft. For a more precise synchronization of their rotation, the inner surface of the belt has teeth, which provide engagement with the gear teeth.
The main disadvantage of a belt drive is a small (compared to a chain) operational resource, which is no more than 90 thousand kilometers. At the same time, it is recommended to replace them every 50 ... 60 thousand km. In addition, during the operation of the car, it is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of the belt surfaces and, if cracks appear, immediately replace it. This will avoid more serious engine damage that can occur when a rubber belt breaks unexpectedly.
chain drive
In the A14NET / NEL engine, the camshaft drive is implemented using a steel chain.

The advantages of a chain drive include:
- long service life (more than 180,000 km of run);
- strength;
- increased reliability.
As for the disadvantages, the use of a chain drive leads to increased noise and the need to install a number of additional parts (tensioner, damper), with the help of which the chain is tensioned during operation and its vibrations are damped. In addition, the chain requires lubrication during operation.
Chain tension is a complex process and is provided by special tension rollers. In this case, the tensioner works in tandem with a special spring and, in addition, engine oil pressure is used. A steel toothed chain drives the camshafts by contacting the teeth of the “sprockets” attached to them. The condition of the chain and its service life largely depend on the pressure of the engine oil in the lubrication system of the power unit. The use of high-quality consumables also has a significant impact on the operation of the timing chain drive.
Which is better: chain or belt
It is impossible to unambiguously answer the question of which is better - a steel chain or a rubber belt. In practice, both chain and belt drives occur at about the same frequency. And if earlier the presence of a belt in the timing drive was misunderstood, now the belt drive has begun to dominate over the chain drive.
Important! This is primarily due to the fact that the quality of the drive belts has improved significantly.
For their manufacture, the most modern synthetic materials with high technical characteristics are used. They retain the necessary elasticity, while maintaining harsh operating conditions, characterized by high mechanical loads and ambient temperature fluctuations in the range from 45 to +120°C.
Many are attracted by the fact that the operational life of the chain is more than twice that of a belt drive, but we must not forget that the chain stretches during operation and requires periodic maintenance.
Car owners choosing an internal combustion engine with a timing belt believe that it is better to replace the belt several times, since this procedure is much simpler and cheaper. It is easy to carry out with your own hands.
- How to work in Uber on a company car and your own: a list of allowed cars
- How to profitably sell Volvo S60
- What to do if the Chevrolet Cruze does not start, how to fix it
- How to activate Navitel
Engine Chevrolet Cruze 1.6, 1.8 Chevrolet Cruze 1.4 turbo, belt or chain?

Any Chevrolet Cruze engine provides decent dynamics and smoothness for this car. Initially, two Chevrolet Cruze atmospheric gasoline engines with a volume of 1.6 and 1.8 liters were offered in Russia, later a turbo engine with a working volume of 1.4 liters appeared.
The turbo engine provides quite a lot of power, good torque and at the same time is very economical. It is worth noting that in many countries the Chevrolet Cruze engines have diesel options with a volume of 1.7 and 2 liters. The power units of the Chevrolet Cruze EcoTec series are 4-cylinder 16-valve engines with two camshafts on top, that is, it is DOHC.
An important question that worries many. Is there a belt or chain in the timing drive of Chevrolet Cruze engines? There is a strong opinion that the chain is more reliable and does not need to be replaced frequently. However, modern belts today are also quite reliable. So let's reveal a big secret in Chevrolet Cruze engines, a belt in the timing drive. According to the manufacturer, the belt itself has an extended service life.
Photo of the Chevrolet Cruze engine under the hood.

The base engine for the Cruise is a 1.6-liter engine. The most interesting thing is that the sedan and hatchback have a power unit of 109 hp, while the Cruze station wagon has 124 hp. The difference is explained by the fact that the version of the car in a universal body has a large mass and carrying capacity, so the base motor must be more enduring. Detailed characteristics of the Chevrolet Cruze sedan and hatchback engine below.
Engine characteristics Cruz Ecotec 1.6 (109 hp)
- Working volume - 1598 cm3
- Power - 109 hp at 6000 rpm
- Maximum speed - 185 (manual transmission) and 177 (automatic transmission) kilometers per hour
- Acceleration to the first hundred - 12.5 (manual transmission) and 13.5 (automatic transmission) seconds
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle - 7.3 (manual transmission) and 8.3 (automatic transmission) liters
And the parameters of the motor for the station wagon.
Characteristics of the Cruze SW 1.6 engine (124 hp)
- Working volume - 1598 cm3
- Power - 124 hp at 6000 rpm
- Torque - 150 Nm at 4000 rpm
- Maximum speed - 192 (manual transmission) kilometers per hour
- Acceleration to the first hundred - 12.6 (manual transmission) seconds
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle - 6.5 (manual transmission) liters
A more powerful 1.8-liter gasoline engine with a capacity of 141 hp. provides good dynamics, both on the Cruz sedan, and on the station wagon and hatch.
Characteristics of the Chevrolet Cruze Ecotec 1.8 liter engine
- Working volume - 1796 cm3
- Power - 141 hp at 6000 rpm
- Torque - 176 Nm at 3800 rpm
- Maximum speed - 200 (manual transmission) and 190 (automatic transmission) kilometers per hour
- Acceleration to the first hundred - 11 (manual transmission) and 11.5 (automatic transmission) seconds
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle - 6.8 (manual transmission) and 7.8 (automatic transmission) liters
Well, the most interesting engine is a turbo engine with a volume of only 1.4 liters. Small volume ensures minimum fuel consumption. At the same time, the presence of a turbine makes the power unit very dynamic. At 140 horsepower, the torque is 200 Nm, recall the atmospheric 1.8 produces 141 horses, but the torque is only 176 Nm, plus increased fuel consumption. At the same time, all the torque of the turbocharged engine is already available from 1,850 engine revolutions, and the aspirated 1.8 will have to be spun up to 3800. That is, already at the bottom, the 1.4 turbo is ready to give out a maximum. In addition to efficiency (5.7 liters on the highway), the Chevrolet Cruze turbo engine is also more environmentally friendly. Here are the specifications for this motor.
Engine characteristics Ecotec 1.4 Turbo
- Working volume - 1398 cm3
- Power - 140 hp at 4900 rpm
- Torque - 200 Nm at 1850 rpm
- Maximum speed - 200 (automatic) kilometers per hour
- Acceleration to the first hundred - 10.3 (automatic transmission) seconds
- Fuel consumption in the combined cycle - 5.7 (automatic transmission) liters
The Ecotec 1.4 Turbo engine is offered only with the Chevrolet Cruze automatic transmission.
Engine Specifications
Several different powertrains were installed on the Chevrolet Cruze. They differ in technical characteristics, this allows you to choose a car based on the requirements of a particular driver. For convenience, we have summarized all the main indicators in a table.
| A14NET | F16D3 | F18D4 | Z18XER | M13A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine volume, cc | 1364 | 1598 | 1598 | 1796 | 1328 |
| Maximum torque, N * m (kg * m) at rpm. | 175 (18) /3800 | 142(14)/4000 | 154(16)/4200 | 165 (17) / 4600 | 110 (11) / 4100 |
| 200 (20) /4900 | 150(15)/3600 | 155 (16)/4000 | 167 (17) / 3800 | 118 (12) / 3400 | |
| 150(15)/4000 | 170 (17) / 3800 | 118 (12) / 4000 | |||
| 118 (12) / 4400 | |||||
| Maximum power, hp | 140 | 109 | 115 — 124 | 122 — 125 | 85 — 94 |
| Maximum power, hp (kW) at rpm | 115 (85) /5600 | 109(80)/5800 | 115(85)/6000 | 122 (90) / 5600 | 85 (63) / 6000 |
| 140(103)/4900 | 109(80)/6000 | 124(91)/6400 | 122 (90) / 6000 | 88 (65) / 6000 | |
| 140(103)/6000 | 125 (92) / 3800 | 91 (67) / 6000 | |||
| 140(103)/6300 | 125 (92) / 5600 | 93 (68) / 5800 | |||
| 125 (92) / 6000 | 94 (69) / 6000 | ||||
| Fuel used | Gas/Petrol | Gasoline AI-92 | Gasoline AI-95 | Gasoline AI-92 | Regular (AI-92, AI-95) |
| Gasoline AI-95 | Gasoline AI-95 | Gasoline AI-95 | Gasoline AI-95 | ||
| Gasoline AI-98 | |||||
| Fuel consumption, l/100 km | 5.9 — 8.8 | 6.6 — 9.3 | 6.6 — 7.1 | 7.9 — 10.1 | 5.9 — 7.9 |
| engine's type | In-line, 4-cylinder | 4-cylinder, in-line | In-line, 4-cylinder | In-line, 4-cylinder | 4-cylinder, 16-valve, variable phase system (VVT) |
| CO2 emissions, g/km | 123 — 257 | 172 — 178 | 153 — 167 | 185 — 211 | 174 — 184 |
| Add. engine information | multipoint fuel injection | multipoint fuel injection | multipoint fuel injection | DOHC 16-valve | |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 72.5 | 79 | 80.5 | 80.5 | 78 |
| Piston stroke, mm | 82.6 | 81.5 | 88.2 | 88.2 | 69.5 |
| Compression ratio | 9.5 | 9.2 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 9.5 |
| Start-stop system | optional | No | Option | Option | No |
| Supercharger | Turbine | No | No | No | No |
| Resource thousand km. | 350 | 200-250 | 200-250 | 200-250 | 250 |
As you can see, technically all motors are quite diverse, this makes it possible to choose the most suitable options for a motorist.
At the moment, in accordance with the law, it is not necessary to check the number of the power plant when registering a car. But, sometimes it is still required, for example, when selecting certain types of parts. All engine models have a number stamped on the ebb of the cylinder head. You can see it right above the oil filter. Please note that it is prone to corrosion. This can lead to the destruction of the inscription. To avoid this, periodically inspect the site, clean it of rust, and lubricate with any grease.
Service
To begin with, it is worth considering the planned maintenance of the internal combustion engine. This is a mandatory procedure that ensures the normal operation of the engine. According to the manufacturer's recommendations, the minimum mileage between basic maintenance is 15 thousand kilometers. But, in practice, it is better to do it every 10 thousand, after all, operating conditions usually differ from ideal for the worse.
During basic maintenance, a visual inspection of all engine components is performed. Computer diagnostics are also mandatory. When defects are found, they are repaired. Also be sure to change the engine oil and filter. The following lubricants can be used for replacement.
| ICE model | Refueling volume l | Oil marking |
|---|---|---|
| F18D4 | 4.5 | 5W-30 |
| 5W-40 | ||
| 0W-40(Low temperature regions) | ||
| Z18XER | 4.5 | 5W-30 |
| 5W-40 | ||
| 0W-30 (Regions with low temperature) | ||
| 0W-40 (Regions with low temperature) | ||
| A14NET | 4 | 5W-30 |
| M13A | 4 | 5W-30 |
| 10W-30 | ||
| 10W-40 | ||
| F16D3 | 3.75 | 5W30 |
| 5W40 | ||
| 10W30 | ||
| 0W40 |
To ensure the smooth operation of the ignition, the candles are changed every 30 thousand kilometers. If they are of high quality, then they serve all this time without any problems and failures.
Timing belt always requires increased attention. All motors except the M13A use a belt drive. Replace it on a run of 60 thousand, but sometimes it may be required earlier. To avoid trouble, check the condition of the belt regularly. 
The M13A uses a timing chain drive. When used correctly, it is more reliable. As a rule, replacement is required after 150-200 thousand kilometers. Since by that time the motor was already quite worn out, the replacement of the timing drive was combined with a major overhaul of the power unit.
Typical malfunctions
Any motor has its drawbacks and malfunctions characteristic of it. This must be taken into account and the problems that arise should be addressed in a timely manner. Let's look at what difficulties the owners of the Chevrolet Cruze can face.
The main disadvantage of the A14NET is the insufficiently powerful turbine, it is also demanding on oil. If you fill it with low-quality grease, the risk of failure will increase. Also, do not constantly drive this engine at high speeds, this will also lead to premature "death" of the turbine and possibly the piston. There is also a problem characteristic of all Opel engines with leaking grease from under the valve cover. Quite often the pump bearing fails, it is worth replacing it.
On the Z18XER motor, the phase regulator sometimes fails, in which case the engine starts to rattle like a diesel engine. It is solved by replacing the solenoid valve, which is installed in the phase regulator, you can try to clean it from contamination. Another problem node here is the thermostat, it lasts no longer than 80 thousand kilometers, and in practice it often fails much earlier.
The problem of the F18D4 engine is the rapid wear of the main elements of the unit. Therefore, it has a relatively short service life. At the same time, minor breakdowns practically do not occur.
Considering the F16D3 power unit, one can generally note its reliability. But, at the same time, there may be problems with the failure of hydraulic valve compensators, they fail quite often. The engine also has a separate exhaust control system. This block also tends to fail regularly.
 The most reliable can be called M13A. This engine has a large margin of survivability, which saves the driver from many problems. If you properly care for it, breakdowns practically do not occur. Sometimes there may be a problem with the crankshaft position sensor, this is probably the most common malfunction of this motor. Also, when using low-quality fuel, the check lights up and a power system malfunction error appears.
The most reliable can be called M13A. This engine has a large margin of survivability, which saves the driver from many problems. If you properly care for it, breakdowns practically do not occur. Sometimes there may be a problem with the crankshaft position sensor, this is probably the most common malfunction of this motor. Also, when using low-quality fuel, the check lights up and a power system malfunction error appears.
tuning
Many drivers do not like the standard characteristics of the motors, so many ways have been invented that help increase power or improve other engine performance. We will analyze the most suitable for each specific power unit.
For the A14NET engine, chip tuning is the best solution. Here it is most effective, since a turbine is used. With the correct flashing of the control unit, you can get a 10-20% increase in power. It makes no sense to do other improvements on this motor, the increase will be small, and the costs will be significant.
There are many more opportunities to refine the Z18XER motor, but here you need to remember that most of the work will cost a round sum. The simplest option is chip tuning, with it you can add about 10% power to the motor. If you want to get a more significant increase, you will need to install a turbine, as well as replace the connecting rod and piston group, and the cylinders are bored at the same time. This approach makes it possible to obtain power up to 200 hp. At the same time, you will need to put another gearbox, strengthen the brakes and suspension.
The F18D4 usually requires a fairly large tuning investment, and the results will be highly debatable. Here, even chip tuning does not work, in order to achieve an increase of 15%, you will need to replace the standard exhaust pants with a “spider”. For a greater effect, you should look towards the turbine, it gives the biggest increase in power. But, in addition to this, it is also desirable to install new parts of the connecting rod and piston group that are resistant to such loads. Otherwise, you will have to do a major overhaul of the engine very often.
The F16D3 engine is mainly accelerated by boring cylinders. This allows you to achieve increased power at minimal cost. At the same time, chip tuning is also required.
M13A is most often overclocked using chip tuning, but this does not give a proper increase in power, usually no more than 10 hp. It is more efficient to use short connecting rods, this gives a significant increase in engine volume, and, accordingly, more power is obtained. This option is the most efficient, but you have to pay for it with increased fuel consumption.
SWAP
One of the popular tuning methods is SWAP, that is, a complete replacement of the engine. In practice, such refinement is complicated by the need to select an engine that fits the mounts, as well as to fit some standard units to the engine. Usually more powerful options are installed.
In fact, on the Chevrolet Cruze, such work is practically not carried out, the reason is the small number of suitable power units. Most often, they install z20let or 2.3 V5 AGZ. These motors require virtually no modifications, while they are quite powerful and reliable.
Forum: Chevrolet Cruze Sedan (2008-2015)
Hi all!
Over the past 3 years, I managed to ride Cruises with all types of engines and transmissions (except for diesel and turbocharged engines).
1600 automatic.
It was my first acquaintance - a test drive took place at the dealer. Externally and internally, I really liked the car, but in terms of driving characteristics - nowhere at all. Barely pulled to accelerate it was necessary to do peregazovku. on the on-board computer was about 15 liters of average consumption per 100 km. in general, 1.6-automatic - I do not advise anyone. People buy, and then the sites are filled with ads for the sale of such cars.
1600 mechanics.
A friend had one. He sat behind the wheel, it is quite acceptable if you drive calmly. Of course traction is not enough a little, but the city is the most. Although the price of 1.6 mechanics is lower, a friend complained about the average consumption.
1800 automatic.
I had it, skated 5 t.km on it in 8 months. It drives, it pulls, but it doesn’t like instant acceleration (overtaking, sudden lane changes, etc., etc.), the machine doesn’t have time, a few seconds of thought, the roar of the engine when switching to a lower one, and Cruz flew off.
On the highway, the consumption is 8.5, in the city, the consumption is 12-13 liters per 100 km.
Pros: automatic - convenience in the city, low consumption on the highway; tiptronic.
Cons: thoughtfulness during acceleration, long downshifts; high consumption; low reliability - several acquaintances complained about breakdowns, which the dealer nevertheless recognized.
1800 mechanics.
This is the engine and the box that this car needs. Everything else presented in Russia is just flaws. I've owned this Cruz for more than two years, I still can't get enough of it! I can't say anything negative. Hurry at least give back, at any moment you are driving a car, and not the machine is trying to adjust to the desired pace. The handle does not bother driving through traffic jams - probably such a car that it’s even nice to drive in traffic jams.
Average consumption (mostly city) - 9-9.5 liters. per 100 km.
I have the LS equipment - the only difference from the maximum speed is the lack of climate control (in principle, it is not needed) and cruise control (also a useless thing: if you drive a little on the tracks, you don’t need it, if you do a lot, it’s better to go yourself, less likely to fall asleep).
Completely satisfied with the machine, my Kuzya never let me down. A friend who sold his Cruz a year ago is still licking mine.
Comfortable beautiful interior, everything you need is at hand, there is nothing superfluous. The trunk is huge, fits everything you need. My wife really likes the car, the whole family doesn’t have tea.
Who doubts: Cruz or something else, I advise everyone: definitely Cruz. Only advice: do not take the 1.6 engine, you will regret it, it is better to pay a little extra and buy a normal package right away
Of course, most Chevrolet Cruze car owners are concerned about what will happen if the timing belt breaks. All motors have their own design differences. And what is practically safe for some (except for the delivery of the car by a tow truck to a car service, new belts, rollers and work). This can result in serious repairs for other engines.
Unfortunately, on all Cruz engines without exception, when the timing belt breaks, a “valve meeting” occurs. That is, they are oppressed, which requires at least the removal of the cylinder head, with their replacement. Therefore, it is necessary to take an extremely responsible approach both to observing the replacement interval and to choosing a car service that will install a new timing kit and provide a guarantee.
In conclusion, we note that the most optimal choice, after all, will be the Chevrolet Cruze 1.8 gasoline engine, cases of belt breakage on which are quite rare.
With the passage of regular maintenance, carried out every 15 thousand kilometers, a preventive inspection of the timing belt is carried out. Its serrated surface should not contain traces of cracks, tears of individual teeth, traces of delamination of tissues from the rubber base. From the outside, make sure that there are no signs of wear that exposes parts of the cord, and visible areas with soot. There should be no delamination on the end surface.
The presence of the damage listed above is a signal for the immediate installation of a new Chevrolet Cruze timing belt during the same maintenance. Similarly, it is worth doing if there are oil streaks on the belt, even in minimal quantities.
Technology for replacing the timing belt on a Chevrolet Cruze 1.6, 1.8:
- work is carried out, if possible, on a cooled motor
- dismantled lower engine protection and fender liner
- remove timing belt covers
- engine hung out
- remove the lower engine mount along with the bracket
- both camshaft pulleys are set according to the marks
- the rollers are loosened to remove the timing belt and dismantle it
- remove both camshaft pulleys
- then the tension rollers are removed
- if necessary, dismantled and replaced with a new water pump
- new rollers, auxiliary and main belt are installed
- Checking for correct labeling
- assembly is performed according to the reverse algorithm
It is important to remember that during the timing belt tension, the set lower mark can jump 1 tooth to the right. In order to prevent re-disassembly, you can immediately position it with a delay of 1 tooth, so that after tensioning the timing belt, all marks match. Then you need to scroll the motor two turns forward, making sure that the marks match.
A guarantee is provided for all types of work on replacing the timing belt, Chevrolet Cruze tensioner and auxiliary rollers, eliminating breakdowns that occurred due to a broken timing belt. A wide range of original and non-original spare parts is available. The vast experience of our masters and excellent knowledge of the features of servicing these engines allow us to offer our customers excellent quality and reasonable prices.