Now we spend more and more time in the car. The provision of transport in Russia is approximately 250 vehicles per 1,000 people and is constantly growing, even despite a slight decrease in sales.
Almost every newly produced car has an air conditioning system installed as standard. Let's see what a car air conditioning system consists of and how it works.
Automotive air conditioning system works on the same principle as well-known domestic air conditioners installed in apartments and offices. It allows you to cool the air in the car, as well as clean it from moisture and odors. In modern cars, it is an integral part of the ventilation and interior heating system.
The main purpose of an air conditioning system in a car control) to ensure the comfort of passengers. Basically, she shouldmust perform four functions.
Main:
1.temperature control;
2. humidity control;
Additional:
1. air purification;
2. air circulation control.
A bit of history: The first car air conditioners appeared in the USA, which was then a trendsetter in the automotive industry. In the 40s and 50s, they were installed as an expensive option on premium and high-end cars. The growth took place in the 60s of the 20th century and by the beginning of the 70s already about half of the cars in the USA had air conditioners, air conditioners came to Europe in large quantities a little later.
An automobile air conditioner is a sealed system filled with freon and compressor oil, which is partially dissolved in liquid freon. The oil is used to lubricate the compressor.
To date, the main refrigerant automotive air conditioning systems is freon R134a, but there are still cars on the previously used R12. In the future, there is a prospect of switching to the new refrigerant R1234yf.
Picture 1- Approximate view of the air conditioning system of an SUV. Views of all the main elements of the air conditioning system.
At the moment, modern cars use two main air conditioning schemes:
- with receiver-drier and expansion valve;
- with accumulator and expansion tube.
Figure 2- Scheme of an air conditioner with a receiver-drier and a thermostatic expansion valve
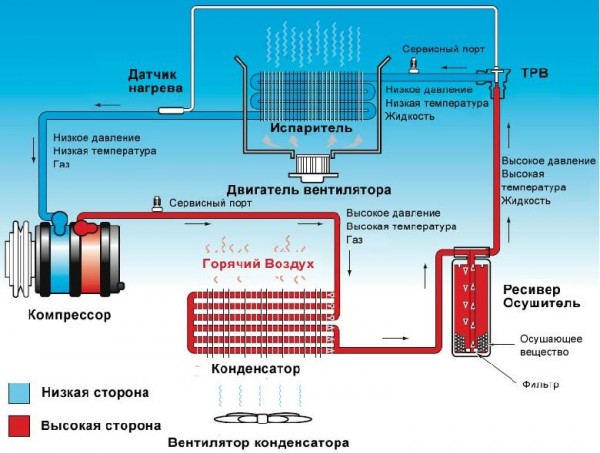
IN receiver systemand thermostatic valve non the low pressure (suction) side is the evaporator and part of the pipeline from the expansion valve to the compressor suction port, on which the low pressure sensor and the low pressure service port are located. On the high pressure (discharge) side are locatedcondenser, receiver-drier, thermal expansion valve (hereinafter referred to as tdv), and pipeline from the compressor discharge port to tdv, on which is locatedhigh pressure sensor andhigh pressure service port.
As it is already clear, the system is divided by pressure into high And low sides.
When the electromagnetic clutch is turned on, the compressor starts to work - the gaseous refrigerant is sucked in and compressed to a high pressure, after which it is pumped through the pipeline into the condenser, where the gas with high pressure and temperature condenses: it passes from a gaseous state to a liquid, giving off heat to the environment.The temperature of the refrigerant at the outlet of the compressor is about 60 degrees C. IN air passing through the condensermuch colder, it corresponds to the ambient temperature (as a rule, not higher than +35 ºС),Next, liquid freon enters the receiver-drier, where it is dried - moisture is removed and filtered (removal of suspended particles). The receiver also provides compensation for the supply of refrigerant to the evaporator. The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then enters the expansion valve, where it is throttled.The flow resistance created by the expansion valve causes rapidrefrigerant pressure drop.This refrigerant then enters the evaporator where it boils. Liquid freon boils at low pressure, absorbing heat fromrelatively hot car interior air(for example, +30 ºС), thereby leading tochanging the state of the refrigerant from liquid to gaseous andre-absorbed by the compressor. Then the cycle repeats.
Those. the simpler path of freon looks like this: compression of gaseous freon into compressor- condensation in condenser- dehumidification of liquid freon in receiver dryer- throttling in trv, where there is a pressure loss - boiling in evaporator, where freon passes from liquid to gas - absorption into compressor. Cycle repetition.
Figure 3- Scheme of an air conditioner with an accumulator and an expansion tube
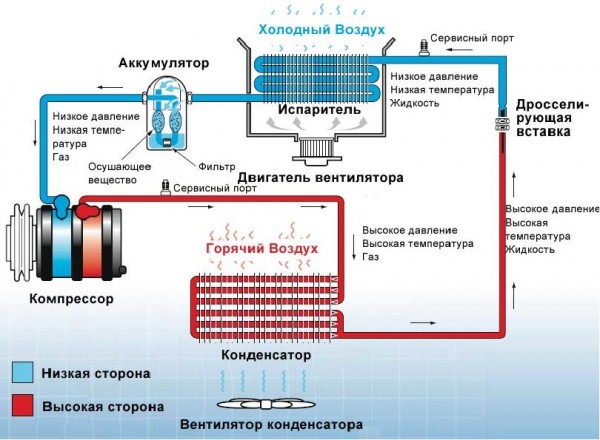
difference systems with accumulator and expansion tube, in the fact that an accumulator is installed at the outlet of the evaporator, and a throttling insert is installed instead of the TRV.The throttling insert replaces the expansion valve, and the battery replaces the receiver dryer.
A the battery contains a drying agent,which removes moisture from freon. Also in the accumulator there is an additional evaporation of liquid refrigerant, which can get from the evaporator. That is The accumulator protects the compressor from liquid refrigerant entering it, which can damage it due to water hammer.
The throttle insert is a calibratedan insert that doses the flow of liquid refrigerant into the evaporator.Since the throttling insert hasfixed diameter of the passage hole, then the evaporator in this scheme will beflooded evaporator.
The compressor in this circuit operates cyclically, receiving start-stop commands from the control unit based on signals from pressure and temperature sensors.
Visual display of the car air conditioning system with an emphasis on the compressor (sorry, if this manufacturer's advertisement, I have nothing to do with it - the video is successful).
The video shows a diagram air conditioner with receiver-drier and expansion valve in dynamics.
The main feature of the operation of automobile air conditioners, for example, from ordinary household split systems, is that it does not use electricity for its operation, but part of the power of the internal combustion engine, which is taken from its crankshaft using a clutch.
Essential elements:
The car air conditioner consists of the following main elements: compressor, evaporator, condenser, thermostatic valve (or expansion tube), receiver-drier (or accumulator), connecting pipelines and auxiliary elements (sensors, relays, etc.).
In general, compressor called a mechanism in which mechanical energy is used to increase the pressure of freon. In this case, the energy of the car's internal combustion engine. The compressor circulates freon and oil through the air conditioning system. air.
The drive shaft of the compressor rotates from the electromagnetic clutch. If the clutch is not energized, then only its pulley rotates and the torque is not transmitted to the compressor shaft. When the air conditioner is turned on, voltage is applied to the clutch coil, it is attracted to the compressor shaft and transmits torque from the car engine to the compressor shaft. The air conditioning system starts up.
Figure 4- Photo of a typical compressor for a car air conditioning system, as well as its section
Evaporator is a heat exchanger, the main function of which is to absorb the heat contained in the passenger compartment and cool the air inside the car. It also dehumidifies the passing air.. In the evaporator, a phase transition of liquid freon into a gaseous state (boiling) occurs.
Figure 5- Appearance of the evaporator I
Capacitoris a heat exchanger, the main function of which isremoval to the environment of the heat absorbed from the cab. In the condenser, a phase transition of gaseous freon into a liquid state (condensation) occurs.
Figure 6- Appearance of the capacitorcar air conditioning systems I
expansion valve And throttling insert are devices designed to regulate the supply of refrigerant to the evaporator air conditioning systems. Their mainfunction is to supply a certain amount of refrigerant to the evaporator independing on the overheating of the refrigerant at the outlet of the evaporator.
Figure 7- Appearance of expansion valves and expansion insert (upper right corner)car air conditioning systems I
Receiver dryer performs the following main functions:
Removal of moisture from refrigerant and oil;
Removal of foreign impurities (solid particles) from freon;
Performing liquid-vapor separation, thus providing liquid supply to the TRV.
Battery, used in systems with throttlinginsert to preventcontact with liquid refrigerantlow side compressor(water hammer).
Figure 8- Appearance of the receiver-dryer (right) and battery (left). The port for the pressure sensor is visible on the battery.
Also, many auxiliary elements are used in automotive air conditioning systems: fans, sensors and pressure switches (high and low), thermostats, filters, couplings, and so on.
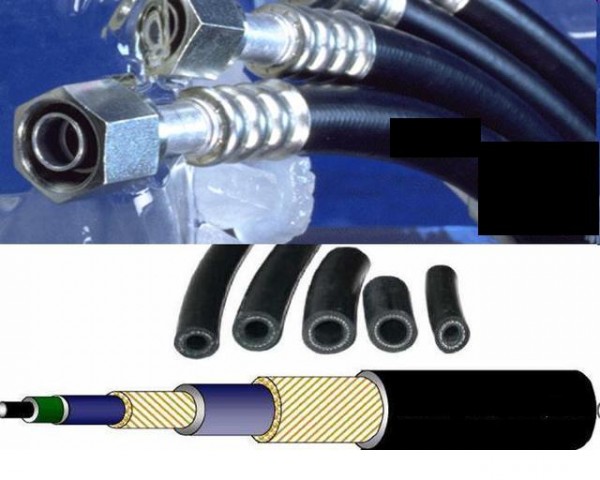
In addition to aluminum lines, pipelines auto air conditioning systems are often made from special reinforced hoses. Repair of pipelines is almost always performed from such hoses.
I removed the manufacturer's name so as not to confuse anyone. The hoses are trimmed with special devices - crimpers for the required connection fitting. The top picture shows the already crimped hose. On the lower hose in section, as you can see, this is a multilayer product.
Figure 9- Automotive Air Conditioning Hoses

The air conditioning system is simply controlled from the car's control panel: as a rule, the operating modes are controlled through the control of the control valve cable and the fan control knob. The intensity of air supply to the car interior is determined by the fan speed. On vehicles not equipped with a climate control system, the blower motor can rotate at four different speeds.
The distribution of air throughout the cabin is carried out through a system of air ducts.
Figure 10- Simple panel ventilation, air conditioning and heating of a Ford car
1 - switch of operating modes of the air blower fan; 2 - recirculation mode switch; 3 - temperature regulator of the air entering the passenger compartment;; 4 - air conditioner switch; 5 - air flow distribution regulator.
A rather simple system has been disassembled here, but the principle of operation and the scheme are absolutely the same everywhere.
Climate control systems are somewhat more complicated.
In general, if we talk about repairs, then the repair of car air conditioners is always fraught with difficulties due to the huge line of elements included in it. For example, on cars of the same manufacturer of the same year of manufacture, air conditioning systems may differ. For example, there may be different compressors and so on.
in addition, the elements of an automobile air conditioner are subject to severe corrosive wear, especially in our winter conditions. Plus mechanical and vibration loads. Therefore, car air conditioning needs to be monitored.))) But this is a completely different topic.
It is clear that it is shown somewhat simplified, but in my opinion it is clear and accessible.
All photos are taken from open sources on the Internet.