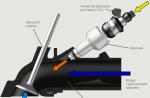
The constant velocity joint, or in the popular "grenade", is an integral part of the transmission of a front-wheel drive car. Its main role is the continuous transmission of rotation from the gearbox to the wheels at different angles. Despite the same principle of operation of all CV joints, they differ in design features for different car models. In addition, different operating conditions cause differences in the design of the external and internal CV joints.
The device of the internal CV joint
The inner CV joint is designed to transmit torque from the transmission to the outer CV joint. It differs from the external one in size (in a big way) and cost, although it consists of the same parts:
- Cases in the form of a bowl with a driven shaft.
- The inner cage is a spherical fist with a drive shaft.
- Separator in the form of a ring with holes to hold the balls.
- metal balls.

The roller version of the hinge is characterized by the presence of a support, which, with the help of three rollers, moves along the tracks cut in the inner part of the body. The balls or rollers are located in the grooves of the housing and are held by a cage, which is connected to the drive shaft by a spline connection. When changing the angle of the drive and driven shafts, the balls move along the grooves, continuously transmitting force.
Symptoms
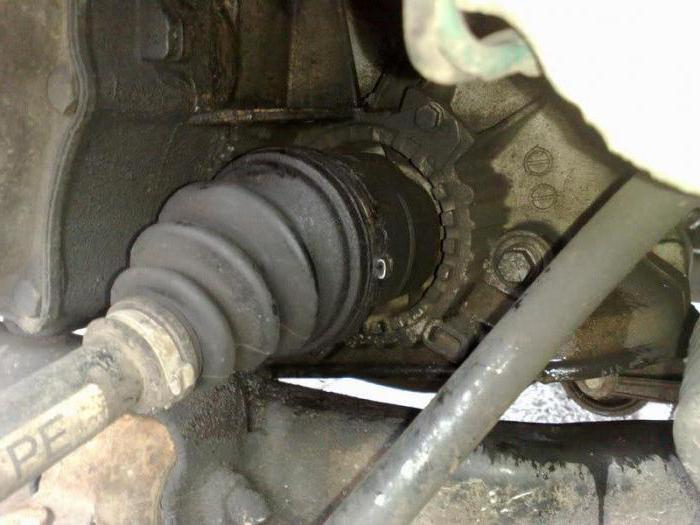

The work of the SHRUS is always associated with the impact of huge loads. Despite the use of high-strength materials in the design of the assembly, it is sometimes capable of failing. The following reasons contribute to this:
- The use of poor quality materials in the manufacture of assembly parts, the use of counterfeit or defective spare parts.
- Lack of lubricant inside the mechanism or its poor quality.
- Ingress of water or abrasive debris into the mechanism due to damage to the anther.
- Excessive load on the mechanism due to unsatisfactory road surface conditions or aggressive driving style.
- Long-term operation, during which the resource of parts is developed.
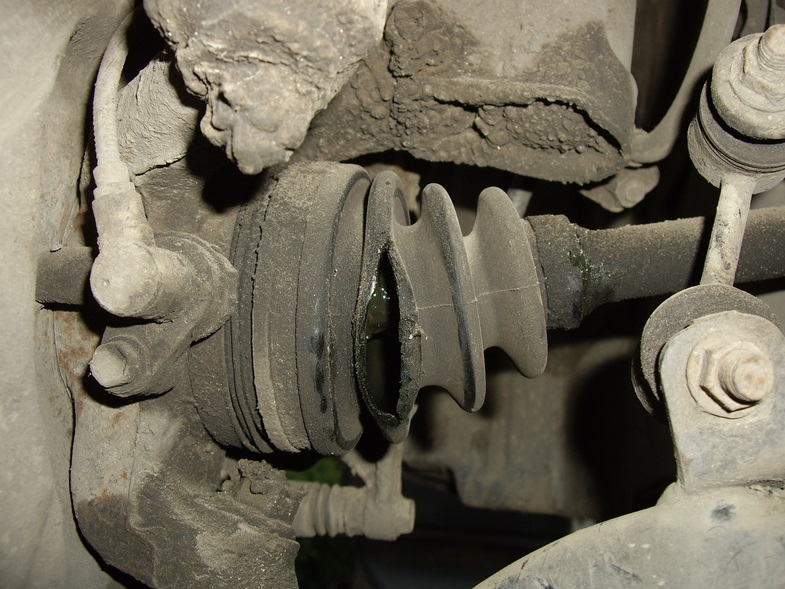

A malfunction of the internal CV joint manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- A characteristic crunch when hitting obstacles, pulling away or hard acceleration.
- Jerks and vibration during acceleration.
- Play in the joints of the hinge when the wheel is suspended.
How to check the internal CV joint
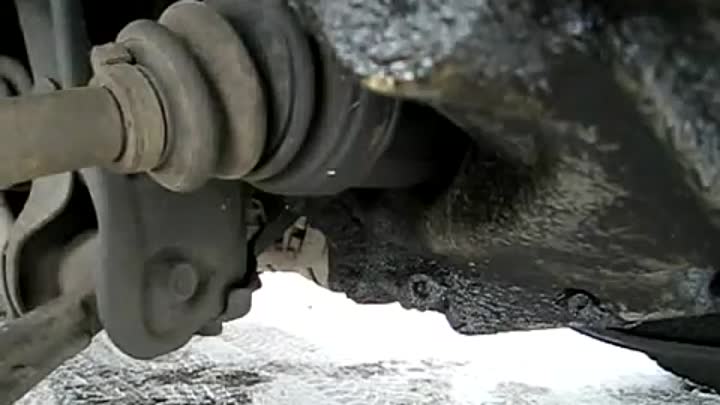

The breakdown of any part of the car is associated with a change in its size, physical properties, or the appearance of wear on the rubbing parts. A CV joint is a swivel joint in which the elements of the mechanism are in close contact and are under constant load. Over time, in the places of interaction of parts, a development is formed and the gap increases, which manifests itself in an increase in the characteristic “crunch” during sharp acceleration or overcoming obstacles.
Unlike the outer CV joint, which is easy to check when driving at the maximum angle of rotation, the inner CV joint is rarely in a state of maximum curvature. You can verify the serviceability or breakdown of the assembly when hanging the wheel. To do this, on the lift with the engine running, turn on the first gear so that the wheels rotate slowly. If at the same time a crunch is heard from the faulty part, and when exposed to the shaft, play is felt, then the CV joint is faulty.
What lubricant to use for CV joints
The main tasks of lubricants used in CV joints are friction protection and prevention of corrosion development. Also, the lubricant must be inert with respect to polymer anthers, which prevent moisture and debris from entering the mechanism. Most of the above requirements are met by the following types of lubricants:

1. Lithium. These are viscous yellowish compounds, which at low temperatures acquire an even thicker consistency, hardly spreading on parts. They are able to significantly reduce friction and loads acting on the hinge elements, protect them from moisture and neutralize accidentally ingested dirt. Their only drawback is the ability to dissolve some types of anthers made from organic polymers. One of the representatives of this type of lubricant is the domestic Litol-24, which is replaced after a run of 100 thousand km.
2. Based on molybdenum disulfide. More versatile lubricants that are characterized by increased resistance to corrosion. In their composition, the content of organic acids is reduced, due to which the aggressiveness in relation to polymer products is reduced. Such lubricants are recommended for use in CV joints of cars of any manufacturer. Their main drawback is their sensitivity to moisture ingress in case of anther leakage, due to which the lubricant loses its properties. Domestic manufacturers produce lubricants with molybdenum disulfide under the general name SHRUS-4.

3. Barium grease. Resistant to moisture ingress into the mechanism, successfully resists corrosion, and is also neutral to any polymers from which the anthers are made. Its main disadvantage is poor resistance to low temperatures. Lubrication at the moment, due to the high cost, is not very common. All domestic formulations made using this technology are labeled under the name ShRB-4.
- Graphite lubricants, since they are designed to work in bearings, and when used in a CV joint, its service life will not exceed 25 thousand km.
- Hydrocarbon lubricants, including technical vaseline, as they are destroyed at t o exceeding 45 o C, and lead to failure of the hinge after a short time.
- Consistent compositions made on the basis of calcium and sodium, since they are not able to work in units with high mechanical stress, and will lead to failure of the hinge after a run of 15-30 thousand km.
- Compositions made on the basis of zinc or iron.
When changing the lubricant of the hinge, they are guided by the operating instructions for the car and the lubricant itself. Its planned replacement should be carried out every 100 thousand kilometers, as well as when installing a new CV joint or anther.
Replacing the inner CV joint

A faulty internal CV joint is capable of falling apart while driving, depriving the car of mobility. To avoid breakage and unexpected costs, the assembly should be replaced at the first sign of failure. It is desirable to carry out all work at a specialized service station, since the operation requires certain knowledge and skills from the master. But if you have the necessary tool, relevant experience and self-confidence, the motorist is able to do everything on his own in a garage.
Before replacement, prepare the following spare parts:
- The hinge itself.
- Boot with new clamps.
- Lubricant.
- Hub nut.
The replacement procedure is carried out in the following order:
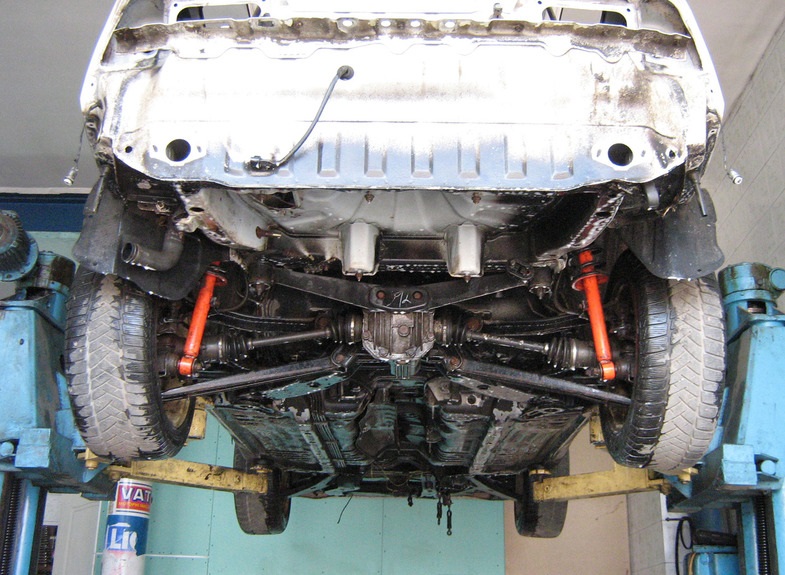

1. The car is jacked up from the side of the CV joint to be replaced or placed on a lift, after which oil is drained from the gearbox.
2. The hub nut is unscrewed and the wheel is removed.
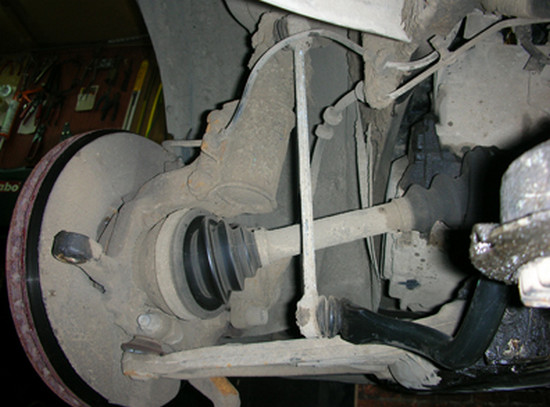

3. Disconnecting the rack from the steering tip and mounting the ball joint.
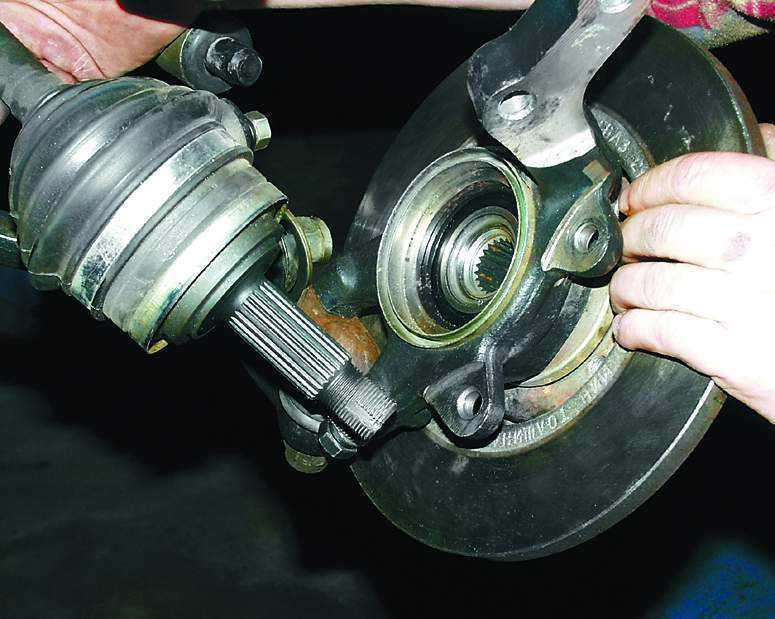

4. Pulling off the brake disc with the caliper from the slots and moving the structure to the side.
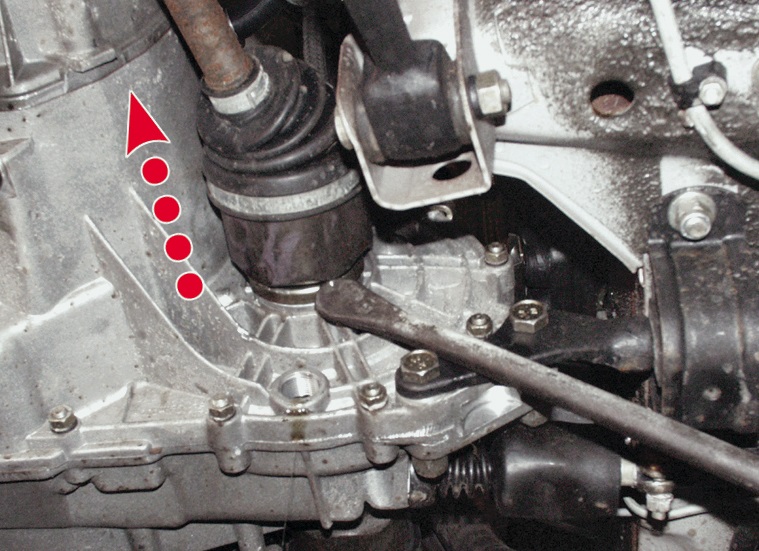
5. Pulling off the inner CV joint from the splines using a metal guide and a hammer.

6. Removing the entire drive to the outside.
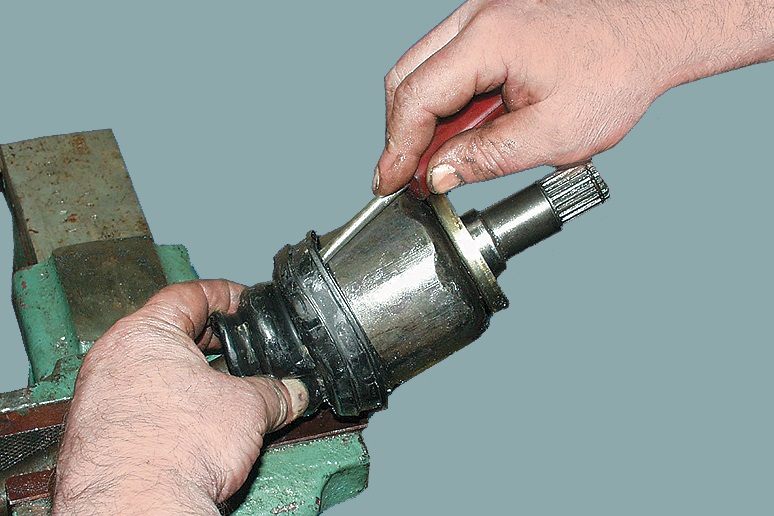

7. Removing the anther clamps, the anther itself and the faulty CV joint after clamping the drive in a vise.
8. Laying lubricant in the new CV joint.
9. Mounting the anther and putting the CV joint on the splines.
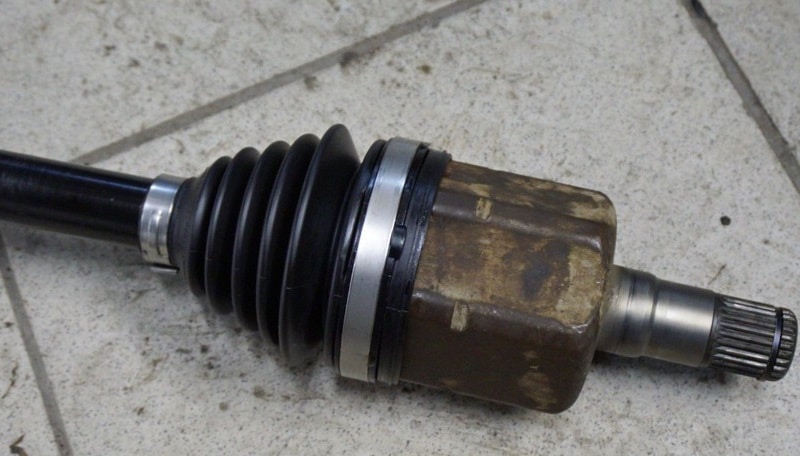

10. Installation of clamps on the anther.
11. Installation of the assembled drive in the gearbox. When hit in the slots, a characteristic click is heard, after which the drive is hammered into place.

12. Further assembly is carried out in the reverse order.
The described method allows you to replace the inner CV joint of all VAZ models: 2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106, 2107, 2108, 2109, 21099, 2110, 2111, 2112, 2113, 2114, Niva, Lada Priora, Kalina, Grant, Vesta and most foreign cars.