I marginally mentioned that the second one is controlled by a bunch of various sensors and, in fact, without them, its operation is not possible. Some of my viewers and readers began to ask questions - how many are there, what do they control and what do they influence? I think this information is really necessary (for general development), so I decided to write an article. So read it, it will be useful ...
It is worth noting that the injector is the same on almost all cars, respectively, its sensors are almost the same. But it is worth noting that for some manufacturers they may differ slightly.
What are the differences
Yet the total mass is the SAME. They may have different names, but the essence remains the same. BUT for some modern machines, instead of DMRV (explanations and decoding will be below), DBP + DTV can be installed.
Also, some cars have an advanced gas distribution system, on which phase shifters are installed, they are hydraulic or electric, and both can have control "points"
If you do not take complex motors, as we say SKYACTIV from MAZDA, because they also have "ion sensors" and do not take into account turbocharged engines (a few more are added there), otherwise the similarity is very large.
That is, we will consider conventional atmospherics without phase control systems.
Which is exactly what a large number of simple motors are. Well, let's start and analyze each separately.
MAF (Mass Air Flow Sensor)
Usually mounted on the air filter housing and measures the amount of air taken in (calculated in kilograms per hour). It is IMPOSSIBLE to say that it constantly breaks down, yet the reliability is at a fairly high level. However, it can still fail due to ingress of moisture, oil, grains of sand or dust, this happens if a filter of zero resistance is installed (or there is no filter at all). Another big MINUS - if you tune the engine and swing the regular VAZ to 150 - 160 hp, then it cannot calculate the amount of air anymore, because it is not corny designed for this.

PROBLEMS:
- Overestimation. At idle by 10-20% - unstable operation, constantly floating speed, poor start-up.
- Underreporting. At high speeds, the dullness of the motor manifests itself, an increase in fuel consumption.
The normal indication for VAZ cars is idling - 8-10 kg / h. At 3000 rpm - 28 - 32 kg / h
Replacement is about 2000-2500 rubles, along with diagnostics.
TPS (Throttle Position Sensor)
Mounted on the side of the throttle itself and on the same axis with the throttle. It reads the indications of opening or closing, respectively, pressing the gas pedal.

At one time there were many fakes that did not live even a month, so it’s worth choosing time-tested ones, preferably those that are installed at the factory. There were also cases when they were knocked down and broken by a high-pressure jet at car washes. Given these rules, they can live long enough.
Faults: The manifestation of failures when pressing the gas pedal. Increase in speed (for no apparent reason) at idle. Jerks and dips under load
The cost is about 250 - 350 rubles with diagnostics
DTOZH (Coolant Temperature Sensor)
ON VAZ is installed between the head of the block and the thermostat. It has two contacts in the structure (it should be noted that a single-contact for the instrument panel is often fixed nearby - they cannot be confused). The main task is to regulate the fuel mixture. Here you can draw an analogy with a carburetor, where you do it with suction, but here everything is done automatically using this sensor. The colder the engine, the richer the fuel mixture.

In fact, this is a resistor (thermistor) whose resistance changes depending on temperature. The standard values for the VAZ are 100 degrees Celsius - the resistance is about 176 ohms, "25 gr." - 2795 Ohm, "0gr." - 9420 ohms, "-20" degrees Celsius - 28680 ohms.
It should be noted that the temperature of the coolant affects almost all engine control characteristics.
Structurally, the sensor is very reliable, there is essentially nothing to break. The main problems may be related :
- Violation of contact inside the sensor, occurs from a VERY long operation
- Insulation failure or broken wiring before it
If it fails:
- Turning on the fan on a cold engine
- Not turning on when hot (temperature limits)
- Difficulty starting a hot engine
- Increased fuel consumption
The price itself is about 150-200 rubles + replacement. Changes fast enough
DD (Knock Sensor)
Usually installed on the cylinder block, between the second and third cylinders. There are currently two options:
- Detonation-resonant (similar to a barrel).
- Broadband (similar to a tablet)
They are not interchangeable, it is IMPOSSIBLE to put in place of another, because they work with slightly different algorithms.
![]()
Structurally, it is very reliable (again, there is nothing special to break there). The principle of operation is this - (it can be compared with a piezo lighter for a stove), the more the motor oscillations (shocks) go, the more it increases the voltage. Thus, detonation knocks are monitored. reads the readings and sets the ignition timing. There is a large detonation - a later ignition is installed.
PROBLEMS: If it fails, the engine does not develop power (dull), it does not work smoothly, and fuel consumption also increases.
The price is about 250 - 400 rubles + installation.
DC (Oxygen Sensor) - lambda - umbrella
It is installed either next to or on the exhaust pipe of the muffler. In some foreign cars, there are two pieces (before and after the catalyst). The main task is to determine the residual oxygen in the exhaust. If detected - lean fuel mixture, if not detected - rich. The readings, as usual, go to the ECU and are used to adjust the fuel supply.

This is a fairly reliable electrochemical design, however, it can also fail. If it breaks down, fuel consumption increases, as well as emissions of harmful substances.
Cost from 1000 to 2500
DPKV (Crankshaft Position Sensor)
It should be noted that this is one of the main sensors that is needed for the operation of the entire engine as a whole.

Generates an electrical signal when changing the angular position of a special toothed disk, which is mounted on the crankshaft. Very hardy and very simple element. Mounted on the cover of the oil pump, structurally similar to a piece of magnet with a coil of thin wire. Designed to determine - the cylinder, the fuel supply time, and the spark supply time.
BREAKDOWN: If it fails, the motor stops working! It also happens that the engine speed is limited in the region of 3000 - 5000.
Cost - 400 - 600 rubles
DS (Speed sensor)
Generates impulses in the ECU, the number of which per unit time is proportional to the speed of the car. Installed on the gearbox, sees the rotation of the shafts, thus the speed is calculated. It is necessary to develop the optimal mode of engine operation.

The sensor itself can work for a long time, but contacts or connectors are often oxidized. Failure leads to a deterioration in driving performance, the ECU simply cannot understand whether the car is standing or moving and at what speed.
NEI REQUIREMENTS: Reduced idling, rev dips during heavy braking, the engine is a little dull. On some Chevrolet vehicles, driving will not be possible.
Price around 200 - 300 rubles
DF (Phase Sensor) or DPRV (Camshaft Position Sensor)
Determines the angular position of the camshaft. For eight-valve engines, it is fixed at the end of the block head. ON the sixteen-valve on the head of the block about 1 cylinder.

Until about 2005, it was not installed on 8-valve engines, which means that fuel injection into the intake manifold will be carried out in pair-parallel mode. That is, two nozzles open at once.
The power units in which it is installed are characterized by phased injection, that is, only one injector nozzle opens into which fuel should be injected.
FAULTS: If it fails, the car automatically switches to a pair-parallel mode, which leads to an overrun of 10-15% of fuel.
It costs about 250 - 400 rubles
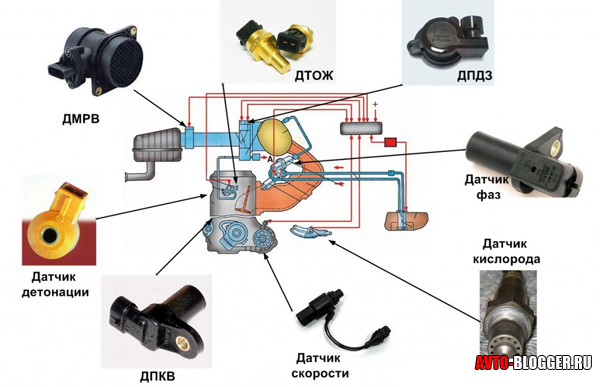
As you can see, there are about eight main sensors in the system, I want to remind you once again that in some modern units there can be much more of them. These same are in any simple motor, which is installed on hundreds of simple machines.
I end here, sincerely your AUTOBLOGGER