A manual gearbox is a unit in which the choice of gears and their inclusion is carried out manually, mechanically. Due to the limited range of operation of motor vehicles, a transmission is used to expand the capabilities of the internal combustion engine and adapt to different driving conditions.
The main function of a manual transmission, like any other, is to adapt and transmit torque to the wheels by changing the gear ratio. In a manual transmission, it is carried out manually, by selecting the step appropriate for the situation. Torque in a manual transmission is carried out in stages.
The prototype for the creation of an automatic transmission was a manual transmission. Understanding the principle of its operation will give an understanding of the essence of the functioning of almost any transmission.
According to the number of steps are:
- four-stage (mainly on older cars, now they are extremely rare);
- five-speed (most common);
- six-speed.
Types of manual transmission according to the number of shafts available:
- two-shaft (mainly installed on front-wheel drive cars);
- three-shaft (installed on front-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive vehicles, both in cars and trucks).
The robotic gearbox is a modern advanced manual transmission, gear shifting occurs using electrical mechanisms controlled by an electronic unit. Some modes in the "robot" are similar to automatic transmission modes, while others require the selection of a mode. The clutch pedal is missing.
Manual transmission device
A mechanical transmission consists of a clutch basket and the box itself.
The power unit includes:
- crankcase (body);
- primary, secondary and intermediate shafts;
- stage selection device;
- driven and leading sets of gears;
- synchronizers;
- bearings, couplings and seals.
All these components are located in the housing and interacting with each other transmit torque.
Clutch
The clutch is an integral component of a manual transmission, disengaging the engine and gearbox at the time of gear shifting without consequences for the units. If you exaggerate, the clutch turns off the torque, while both the engine and the wheels of the car spin at idle.

The clutch is designed to neatly connect the motor and wheels. It consists of two discs, one of which is connected to the motor of the car, the second - to the wheels of the vehicle. The transmission of torque is carried out through the input shaft of the transmission.
Clutch engagement (release) and disengagement (squeezing) of the clutch is controlled via the pedal.
Gears and shafts
In standard manual transmissions, the shaft axes are arranged in parallel, gears are located on them.
The drive (primary) shaft is connected to the flywheel of the motor through the clutch basket, the longitudinal protrusions on it move the second clutch disc and transmit torque to the intermediate one through a rigidly fixed drive gear.

A bearing is located in the shank of the drive shaft, to which the end of the secondary adjoins. The absence of a fixed connection makes it possible for the shafts to rotate independently of each other in different directions and at different speeds.
On the driven shaft there is a whole set of different gears, both rigidly fixed and freely rotating.
The movement and selection of the required pair of gears for the distribution of the torque corresponding to the conditions of movement is carried out by switching forks by means of a two-way control mechanism.
The gearshift rod consists of a lock, a gearshift clutch, drives, sliders with forks that move up and down using the gearshift handle located in the passenger compartment of the machine, and a drive.
The gear selection mechanism can be located both in the transmission housing and located on the vehicle body and, in rare cases, on the steering column. In most cases, a rocker gear drive device is used.
Synchronizers
The angular speeds of the primary and secondary shafts are equalized with the assistance of the synchronizer and it becomes possible to change the stage. Synchronizers provide a more gentle operation of the gearbox and reduced noise.
Special equipment and some sports cars are not equipped with synchronizers.
The principle of operation and the device of a two-shaft manual transmission

The essence of the functioning of the manual transmission is to create connections between the primary and secondary shafts by varying gears with a different number of teeth, which adapts the transmission to the constantly changing circumstances of the vehicle's movement.
For people who are ignorant of these issues, the essence of the functioning of the manual transmission can be explained in a simplified way, in order to understand the essence of the issue.
This power unit provides the necessary modes of operation of the motor by changing the number of revolutions, changing the transmitted force to the drive wheels. Accordingly, with a decrease in the number of revolutions, the transmitted force decreases, and with an increase, it increases. This is necessary when maintaining the required mode of operation of the motor when starting to move, reducing speed or accelerating.
The two-shaft manual transmission consists of:
- driving and driven shaft;
- gears of the driving and driven shafts;
- main gear;
- differential;
- synchronizers;
- gear shift mechanism;
- body - crankcase.
Most modern front-wheel drive cars are equipped with a two-shaft manual transmission.
In such transmissions, the torque is transmitted from the input shaft gears to the driven gears. The drive shaft is connected to the motor through the flywheel, and the driven shaft transmits torque to the front wheels. They are located in parallel.
Without an intermediate shaft, which is typical for three-shaft manual transmissions, the dimensions of the unit are smaller, as is the weight, but an increased number of gears leads to a decrease in efficiency. The compact size of such a transmission allows it to be installed on heavy motorcycles.
Parallel to the primary shaft, on which the gears are fixed, there is a secondary one with a set of gears. The gears of the shafts constantly interact with each other and at the same time spin freely on the axis.
The drive gear of the final drive on the secondary shaft is firmly fixed. Between the gears are synchronizer clutches.
To reduce the dimensions of the unit and to increase the number of stages, up to three secondary shafts are installed, each of them has a main gear gear that constantly interacts with the driven gear.

The main gear and differential transform the torque of the secondary shaft to the drive wheels of the machine. The differential makes it possible to rotate the wheels at different speeds, which becomes noticeable when one of the drive wheels hits a slippery surface.
The gearshift mechanism is usually located outside the transmission housing. The connection between it and the transmission is carried out using cables and rods. The simplest and most common is switching using cables.
The device of the gearshift mechanism:
- step selection cable and control lever;
- a cable for switching on speeds and a lever for their selection;
- gear shift rod with forks and gear shift handle;
- blocking lock.
When choosing steps, the control lever moves transversely, when turned on, it moves longitudinally.
The principle of operation of a two-shaft box is in many respects similar to the functioning of a three-shaft box. The main distinguishing principle is some specifics of the operation of the switching stage of the mechanism.
When you turn on a specific speed, the control lever will move both longitudinally and transversely. During transverse movement, the force is transferred to the cable, which acts on the stage selection lever, which, in turn, rotates the rod around the axis and contributes to the selection of the desired gear.
The principle of operation and the device of a three-shaft manual transmission

The fundamental principle of the functioning of a manual transmission is the gear interaction of gears, which are enveloped in the transmission fluid in the crankcase.
The structure of such an MCP includes:
- driving and driven shafts;
- intermediate and additional shafts;
- frame;
- synchronizers;
- gear sets;
- step changeover mechanism with locks and locking mechanisms;
- step change lever.
Bearings located in the housing ensure the rotation of the shafts. Each shaft has a set of gears with a different number of teeth.
The drive shaft is adjacent to the engine by means of a clutch basket, driven with a cardan shaft, the intermediate shaft transmits torque to the secondary.
There is a drive gear on the input shaft, which spins the intermediate one with a firmly fixed set of gears located on it. The driven shaft has its own set of gears moving along the splines.
Between the gears of the secondary shaft there are synchronizer clutches that align the angular speeds of the gears with the revolutions of the shaft itself. Synchronizers are firmly fixed on the shafts and move in the longitudinal direction along the splines. On modern manual transmissions, such clutches are located at each stage.
The gearshift device in a three-shaft manual transmission is most often located on its body. The basis of its design are the control handle and sliders with forks. There is a blocking mechanism to prevent synchronous selection of two degrees. The gearshift device can be remotely controlled from the steering column.
In the neutral stage, the torque is not given to the wheels, since the input shaft is disconnected from the motor by the clutch.
When the position of the control handle is changed, the fork similar to the position moves the synchronizer clutch, which equalizes the speed of rotation of the corresponding gear and the output shaft. The toothed part of the synchronizer begins to interact with the toothed halo of the gear and it is blocked on the secondary shaft and the torque (torque) moment is transferred with the necessary gear ratio to the wheels.
The movement of vehicles back is carried out with the assistance of the appropriate stage. The change of direction of rotation occurs with the participation of the intermediate reverse gear, which is located on a separate axis.
Three-shaft manual transmissions are bulky and heavy, but their clear advantage is the direct transmission of torque from the first shaft to the second, which gives greater efficiency.
It is installed on rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive cars, trucks.
How to use a manual transmission
Driving a car with a manual transmission and competently managing such vehicles has specific features that any driver needs to know.
How to start a car on a mechanic
The correct one has a positive effect on the resource of its work and ensures the safety of the surrounding machines and people. To avoid creating interference, it is periodically necessary to quickly drive off.

The sequence of actions when starting the machine:
- depress the clutch pedal to the stop and move the gearshift lever to the neutral gear position, if there is any doubt whether the speed is selected correctly, move the lever handle to the sides, when the gearshift handle is in the neutral position, the lever moves freely to the right and left;
- when transferring the car to the neutral stage, it is necessary to fix the transport in order to avoid uncontrolled movement, for this the car is put on the hand brake or the brake pedal is depressed;
- when the clutch is depressed and the car is held by the brake, it is necessary to turn the ignition key, while the icons on the instrument panel should light up, as soon as almost all the icons go out, turn the key further and release the key after starting the engine.
Experienced drivers and mechanics advise:
- turn the starter, that is, start the engine for no more than 10 seconds to avoid breakdowns, if the car does not start, the key is turned back and after a minute the procedure for starting the engine is repeated again;
- when starting in sub-zero temperatures, it is necessary to warm up the car for several minutes with the clutch pedal depressed to reduce the load on the engine and transmission due to the thickening of the oil from frost.
How to switch speeds
The gearshift diagram for a manual transmission is most often located on the outside of the lever handle.

The process of switching speeds consists of several stages:
- depress the clutch pedal with your left foot to the stop;
- move the lever to the desired position with your right hand;
- gently release the clutch pedal and slowly depress the accelerator pedal.
- driving in direct gear (fourth on most boxes) will significantly reduce fuel consumption;
- the choice of the reverse speed is made only after the complete cessation of the movement of the vehicle;
- the pedal must be pressed quickly and all the way, and it should be released with a careful, measured movement, avoiding jerks;
- on roads with insufficient grip (ice, clay, wet surfaces), driving in neutral or with the clutch pedal depressed is contraindicated;
- when making a turn, it is not recommended to squeeze the clutch, even to change gear;
- with free movement on the road, it is possible to effectively brake the engine by gradually lowering the steps.
Oil
Regularly checking the fluid level and replacing it according to the manufacturer's instructions will extend the life of a manual transmission.

In most mechanical transmissions, the replacement of the working fluid is carried out at intervals of 50-60 thousand kilometers due to the accumulation of by-products of work and the decrease in the properties of oils.
A special transmission fluid designed for manual transmission is poured into the box, the brand and other indicators are selected according to the manufacturer's requirements specified in the service book and operating instructions. Using the wrong oil can result in increased wear or failure.
Most manual transmissions have a dipstick and drain plug, which allows you to change the transmission fluid yourself and without much effort.
Pros and cons of manual transmission
Advantages of manual transmission:
- it is possible to tow the car for any distance of the route, even with the engine turned off;
- it is possible to start the car from the "pusher" with a discharged battery or malfunctions in the ignition system;
- smaller dimensions and weight than an automatic transmission;
- the dynamism of the vehicle, the ability to choose the manner of control, by a suitable change in engine speed;
- it is possible to use to the maximum all the capabilities of the engine at the revolutions regulated by the manufacturers at each speed, at which the torque is maximum or close to it;
- dynamic acceleration and fuel economy in comparison with an automatic (with aggressive and sporty driving styles, consumption increases);
- simplicity of design;
- reasonable price for maintenance and repair, especially in comparison with automatic transmission;
- great work resource.

Disadvantages of MTPL include:
- the difficulty of driving cars with manual transmission, especially for beginners;
- clutch, which can be burned by inexperienced drivers or with regular slipping in snow and ice;
- due to inexperience, there is a possibility of damaging the transmission when switching to reverse gear when moving forward or improperly working with the clutch;
- reduced engine life due to too low or vice versa high revs, the automatic transmission will not allow this to be done;
- when switching gears is not fast enough and when switching at too low speeds, a significant loss of motor power occurs;
- increased fatigue due to the need to control the clutch, selection and gear shifting, especially for inexperienced drivers;
The advantages of a manual transmission are many, and the disadvantages will disappear with the acquisition of driving experience in a manual transmission.
The main malfunctions of the manual transmission and their symptoms
"Mechanics" refers to reliable units with a long service life, but improper work with it, poor-quality transmission fluid and time lead to malfunctions.

For mechanical transmissions, malfunctions are inherent:
- extraneous noise during operation or when choosing a speed;
- does not turn on any speed or all speeds;
- difficult inclusion of speeds;
- self-shutdown speed;
- transmission fluid leakage.
Transmission fluid leakage occurs due to worn oil seals, damaged seals, a loose drain plug or incorrectly inserted dipstick, or damage to the manual transmission housing.
The appearance of noise when the lever is in the neutral stage about an insufficient level of transmission fluid or excessive wear on the input shaft bearing.
The appearance of extraneous sounds when choosing a speed:
- wear or deformation of the locking mechanisms of the gear selection device;
- wear of synchronizers;
- insufficient clutch release;
- boxes are loosened.
Extraneous noises during the operation of the manual transmission may indicate wear of the bearings, synchronizers, or an insufficient level of transmission fluid.
The reasons for the difficult inclusion of speeds can be:
- excessive wear of synchronizers;
- severe gear wear;
- worn out or faulty gear shift mechanism;
- loose fixation or malfunction of the switching mechanism rods;
- insufficient clutch release.
Knockout speeds:
- loose manual transmission mounts;
- faulty engine mounts;
- jamming of drive control rods;
- excessive wear of synchronizers, gears, gearshift mechanism, shift forks, secondary or intermediate shaft bearings.
If there are alarming symptoms associated with the operation of the manual transmission, it is necessary to contact a specialist to eliminate them.
Malfunctions that are not fixed in time can lead to breakdowns of other elements of the box, where repairs will cost much more.
manual transmission, she is Manual Transmission, sometimes, in the circles of auto mechanics, you can hear it as a "box" or "korobas" - it is a device made up of a set of gears that mesh with each other in various variations, forming gears with different gear ratios.
Each gear is designed for a certain speed and load on the engine, their alternate use allows you to use the engine as efficiently as possible with minimal risk of overloading it. The more gears in the car, the better its adaptability to different driving conditions.
Gear box device
The device and principle of operation of the gearbox
The mechanical box is arranged in this way:
- At the bottom of the box is the crankcase (structurally, this is the gearbox housing);
- Inside the shafts with gears - primary, secondary and intermediate shafts;
- Also in the manual transmission there is an additional shaft and reverse gear;
- Synchronizers;
- On top of the box is a gear shift mechanism () with locking and locking devices;
- In the cabin, the gearshift lever is displayed.
Carter in place with the entire body contains all the main components and parts. The crankcase is half filled with gear oil, which is needed to lubricate the internal mechanism. Since during operation, the gears of the gearbox are subjected to heavy loads and must be lubricated in order to eliminate friction and cool the parts.
Shafts rotate in bearings that are pressed into the crankcase. The gearbox shafts have a large set of gears with different numbers of teeth.
Synchronizers gears are needed to smoothly and silently switch gears by equalizing the angular velocities of the gears.
gear shift mechanism designed to change gears and control it from the passenger compartment using a lever. The locking device, at the same time, does not allow two gears to be switched on at the same time, and the blocking device keeps the gear from spontaneously turning off.
Since the gear ratio is determined through the ratio of the number of gear teeth in interaction. All manual transmissions are divided into types according to the number of steps. There are 4, 5 and six speed gearboxes. In addition to steps, manual transmissions are also divided into types according to the number of shafts.
Types and design of manual transmission
Manual transmission box can be done according to one of two common concepts: three-shaft or twin-shaft. Boxes of the first type are installed mainly on rear-wheel drive cars, while the second ones are used on rear-engine and front-wheel drive cars. box diagram transmissions of each type has its own fundamental differences, so they should be considered separately.

Diagram of a manual transmission.
Three-shaft checkpoint
The scheme of this type of gearbox assumes the presence of three shafts, called driven, intermediate and leading. The drive shaft is connected to the clutch through splines. Intermediate shaft located in parallel. The moment is transmitted to it by a rigidly fixed gear.
The driven shaft with a number of gears rotates independently of the drive shaft. The gears of this shaft are not rigidly attached. Rigidly fixed synchronizer couplings are installed between them, having the possibility of only longitudinal sliding along the shaft.
Operation of a mechanical transmission
In any modern manual transmission, all three shafts are constantly in contact through gears. When the neutral gear is on, the driven shaft is not fixed by anything, rotating freely. Engaging the gear leads to the longitudinal movement of the synchronizer to docking with the gear, which ensures a rigid connection of the driven shaft and the entire gearbox with the engine. This allows you to start transferring the selected torque directly to the wheels. To turn on the reverse gear, a separate shaft with its own gear is used.
As a rule, three-shaft gearbox mechanics has helical gears, which guarantees their strength, noiselessness and wear resistance.
Two-shaft gearbox
Here, on the drive shaft connected to the clutch, gears are fixed relative to it. The main difference with the previous design is the absence of an intermediate shaft, since here the driven shaft immediately goes parallel to the drive one, also equipped with movable gears that are constantly in contact with the elements of the drive shaft.
The principle of operation here is the same as in 3-shaft boxes, except for the absence of a direct transmission. Such boxes are distinguished by greater reliability and durability with good efficiency, but less variability in gear ratios, which determines the fact that a 2-shaft mechanics box is used exclusively in passenger cars.
Advantages and disadvantages
mechanical box is not the only, but the most common type of gearbox. It has both obvious advantages and obvious disadvantages, which are still much less.
Repairing a gearbox is a rather complicated procedure and should only be entrusted to a specialist.
So, the advantages of the manual transmission can be called:
- minimum cost and weight;
- good acceleration dynamics;
- simplicity and clarity of design;
- reliability;
- cheapness in maintenance.
Mechanical speed gearbox rigidly connects the power unit to the drive pair, which allows you to achieve maximum driving efficiency on icy and off-road conditions. In addition, the manual transmission can be completely decoupled from the engine, allowing the vehicle to be started with an external force (towing, pushing) without restriction.
But this system also has certain disadvantages, including:
- the need to constantly shift gears, which is tiring when driving for a long time;
- long-term development of skills for correct gear shifting;
- only step change of gear ratios;
- relatively low clutch life.
For these reasons today mechanic box is the main, but not the only demanded gearshift system.
Common manual transmission malfunctions
A manual gearbox can have a wide variety, being a complex system with a large number of moving parts. Most often, the box fails due to:
To extend the service line, in addition to a gentle driving mode, it is recommended change oil on time.
- wear of certain nodes;
- a stable lack of oil in the box;
- weakening the fastening of the elements of the box.
The causes of these breakdowns can be the following factors:
- incorrect operation;
- low-quality mechanisms;
- natural operational wear;
- poor quality repair or lack of .
Almost always, a faulty mechanical box is determined by certain external signs. For example, noise in the neutral position of the gearbox indicates wear on the bearing on the drive shaft or simply a lack of oil in the box. If noises are observed when shifting gears, this may be a sign of worn synchromesh clutches or problems with clutch disengagement.
Difficult gear shifting indicates probable wear on the connecting or moving parts of the box.
The same problems can lead to a spontaneous disengagement of the transmission.
No matter how simple and reliable a manual transmission is, it also periodically fails, especially with improper care or the wrong driving style, and you need to be prepared for this.
How to use the manual
Operating a car with such a gearbox requires certain skills and abilities, so for many, especially women, shifting gears on the mechanics is difficult.
How to change gears
Gear shift
The first thing to remember is the position of the gearshift lever for each gear. The second is to learn how to choose a speed mode, and the range of operation of each of the gears.
Speed modes:
- In 1st gear 15-20 km / h;
- In 2nd gear 30-40 km/h;
- In 3rd gear 50-60 km/h;
- On the 4th up to 80 km/h;
- 5th for speeds over 80 km / h.
But best of all, when shifting gears, focus on the tachometer. You can switch to an increased speed by spinning the engine speed 1500 - 2000 rpm diesel engine, or if it is gasoline, then up to 2000 - 2500 thousand rpm.
Before starting the movement, always make sure that the shift lever is in the neutral position. Then, with your left foot, depress the clutch and move the gearshift knobs to the position corresponding to first gear. In order to move off without jerks and the roar of the engine, you need to smoothly release the clutch and also lightly press the accelerator (gas) pedal. Further, upon reaching the speed threshold, we switch to second gear, again depressing the clutch and releasing the gas pedal, then smoothly repeat everything.
Including speeds, they cannot be skipped, they can only be switched one by one.
When slowing down by pressing the "brake" pedal or when braking by the engine, the gears decrease in the same way, only turn on not the next one down in order, but select the most suitable speed mode.
Despite the fact that the mechanical box is a reliable unit, if it is not used correctly, the box can fail very quickly. Therefore, it is recommended to follow these tips:
- Shift gears smoothly and carefully, more than half of the breakdowns of a manual transmission are associated with the failure of gears and synchronizers through careless gear shifting.
- Check the oil level in the box. The number and replacement lines are regulated in the repair manual.
- Protect gearbox housing. The pallet is very fragile and can be accidentally damaged by catching on some kind of obstacle, therefore, as a rule, I protect the crankcase of the engine and gearbox from mechanical damage with an additional screen.
Related terms
Gear shifting is a device that every car with an internal combustion engine needs. The need for this mechanism is due to the fact that any engine has a rather narrow speed range, where torque and power reach their maximum. And, in addition, each engine has a so-called “red zone” - a speed limit that must not be exceeded in order to avoid engine breakdowns.
This article will be completely devoted to the subject of the checkpoint, namely, its mechanical variety (manual transmission). After all, both an “experienced” driver and a novice motorist need to know the device of a manual gearbox and its principle of operation. Also, the article will present the graphic diagrams of the manual transmission, consider its main malfunctions and give advice on the proper operation of this vital mechanism for the car.
Types of gearboxes
In addition to mechanical, there are other types of gearboxes - CVT, and automatic.
The CVT gearbox is stepless. The most important parts of the variator are the sliding pulleys (there are two of them) and the belt that connects them. The connecting belt in a section has the form of a trapezoid. The main advantage of the variator is the constant operation of the car engine in optimal mode. There are also additional benefits, which include dynamism of acceleration, smoothness of movement and economy. In comparison with the "automatic" (, automatic transmission), the variator has a very simple design. But if we compare it with a manual gearbox, then the variator is still inferior to it in terms of dynamics and efficiency.
In addition, a CVT gearbox is almost impossible to combine with a powerful motor, since the fragility of the belt will not allow this. Maintaining and repairing the variator is quite an expensive pleasure, it will be easier and cheaper to replace the gearbox. And one more minus is the need for additional mechanisms for reversing and starting off.
A robotic gearbox is almost no different from a mechanical one - the torque is also transmitted from the engine to the transmission using the classic “dry” single-plate clutch. But still there is such a nuance: in the robotic box, the processes of gear shifting and on / off are automated. clutch. Therefore, the "robot" is able to greatly simplify the process of driving a vehicle - there is no need to manually and, losing precious time, think about which gear to turn on at a given moment. Also, to the advantages of the “robot” box, you can add its relative cheapness, efficiency and low weight.

However, there are also disadvantages. The robotic gearbox does not work too smoothly, and gear shifting occurs with a significant delay. In addition, at high speeds, the “robot” can react to switching with jerks and jerks. Manual mode will not help here, since the same electronics “commands” the clutch. If we compare a robotic box even with a simple automatic transmission, then the clarity of the “robot” switching is much inferior to the “automatic”. It should also be remembered that when starting to move, a car with a robotic box makes a small rollback. Based on all these disadvantages, manual transmission is traditionally put on the most "budget" car models.
Manual transmission device
Now let's move on to our "hero of the occasion", to whom this material is dedicated - to. As you know, a manual transmission is a mechanism that transmits, converts and changes the direction of torque from the engine flywheel. In the "mechanics" the steps are switched mechanically, respectively - by moving the gear lever. The torque is first transmitted to the output shaft, and then to the wheel drive.
What is meant by the term "step transmission"? Traditionally, it determines a stable transmission coefficient (the so-called gear ratio) between the interacting gears of the shafts - the driving and the driven. This "mechanic" differs from, for example, a variator, where the mentioned coefficient is not tied to the gear ratio and is floating. In other words, the ratio of the number of teeth on the driven gear to the number of teeth on the drive gear gives the gear ratio. These numbers differ at different stages of the checkpoint. The largest gear ratio is obtained at the lowest stage, and the smallest, on the contrary, at the highest.
In general, the principle of operation of a manual transmission is quite simple, and the set of its parts is small.
A manual transmission can be called relatively uncomplicated. The manual transmission package includes:
- shafts with gears (primary, intermediate and secondary);
- additional shaft with reverse gears;
- crankcase;
- synchronizers;
- directly the gearshift mechanism, equipped with devices for blocking and locks;
- shift lever.
Bearings are installed in the crankcase, in which the gearbox shafts rotate. The shafts are equipped with sets of gears with different numbers of teeth. For noiselessness and smooth gear shifting, synchronizers are used - they equalize the angular speeds of the gears during their rotation. The operation of the gear shift mechanism is to change gears - it is controlled by the driver using a lever. The locking device allows you to keep the transmission from unwanted self-shutdown. The locking device is designed to avoid switching on two gears at the same time.
Stages and shafts manual transmission
As mentioned above, the gear ratio is determined through the ratio of the number of gear teeth that are in interaction. For example: first gear = lower gear = highest gear ratio. All manual transmissions are divided into types according to the number of steps. There are four-, five- and six-speed manual transmissions. Nowadays, the most common “five-step” is a 5-speed gearbox, but a 4-speed one can be found very rarely.
In addition to the number of steps, manual transmissions are also divided into types according to the number of shafts. There are three-shaft and two-shaft boxes. Three-shaft gearboxes are equipped with rear-wheel drive vehicles (including heavy trucks), and two-shaft gearboxes are most often installed mainly on passenger cars with front-wheel drive.

Three-shaft gearbox device
The package of the three-shaft gearbox includes:
- drive shaft, also called primary and its gear;
- intermediate shaft with a block of gears;
- secondary shaft (driven), also with a gear block;
- the gearbox housing, called the crankcase;
- synchronizer clutches;
- direct gearshift.
In three-shaft gearboxes, as their name implies, three shafts work - the drive (primary), intermediate and driven (secondary). The drive shaft provides the transmission of torque to the intermediate shaft, with which it is connected using a gear. The intermediate shaft is also equipped with a gear block. The secondary (driven) shaft rotates independently of the primary, although it is located on the same axis with it and also has a block of its gears.
The body of the manual transmission is made of light metal. The entire gearbox mechanism is attached inside the case, and lubricant is poured there (most often, gear oil, although nigrol was used in old Soviet-style models).
The location of the shift lever can be different: sometimes the lever is located directly in the box, and sometimes it is mounted on the body. The mechanism responsible for remote gear shifting is colloquially called the "scene".
Two-shaft gearbox device
The package of a two-shaft gearbox includes:
- drive (primary) shaft, equipped with a block of gears;
- driven (secondary) shaft, also with a gear block;
- gear shift mechanism;
- main gear;
- synchronizer clutches;
- differential;
- gearbox housing.
So, this type of manual transmission has only two shafts. In general, the location and purpose of the parts of a two-shaft box is similar to a three-shaft one. The difference is only in the arrangement of the shafts (they stand in parallel) and in the principle of creating a transmission - if in a three-shaft it is created by two pairs of gears, then in a two-shaft one pair works. The two-shaft manual transmission does not have a direct transmission. Also, in two-shaft boxes, not one, but several driven shafts can be used at once.
For reverse gear in both two- and three-shaft boxes, an additional shaft and an intermediate gear are used. To keep the gear engaged (also for all types of gearboxes), clamps are used. To prevent two gears from being engaged at the same time, a blocking device is provided.
Synchronizers in gearboxes are used to silently engage the gear by equalizing the angular velocity of the gear and shaft. The standard package of the synchronizer includes two blocking rings, a coupling, crackers and wire rings. Using a synchronizer, you can alternately turn on the two gears of the secondary (driven) shaft.

The main breakdowns of the gearbox and their causes
- Oil leakage. Most often it can be associated with damage to seals and seals. Also, the cause may be a loose fastening of the housing cover (crankcase). To get rid of leakage, it is necessary to change the seals and gaskets to new ones and / or tighten the covers.
- The checkpoint is noisy. Most likely, the noise of the box is associated with a malfunction of the synchronizer. It can also be caused by worn gears, splines and/or bearings. In this case, wear parts should be identified and replaced.
- The gearbox is hard to turn on. This may be due to a breakdown of some of the parts of the switching mechanism. Wear of gears and/or synchronizers is also possible. Check these parts and replace if necessary.
- Transfers turn off by themselves. Most often this occurs due to a malfunction of the locking device, as well as severe wear of the synchronizers and / or gears. The method of troubleshooting is still the same - replacing the blocking device, gears, synchronizers - depending on which of them the breakdown is associated with.
In order for the checkpoint to serve you faithfully for a long time, treat it accordingly. The main advice when using the shift lever is to be literate in this process. Also, do not forget to change the oil in the crankcase from time to time. If you follow these simple points, the gearbox can last as long as the car itself, without reminding yourself of any malfunctions.

The main part of gearbox breakdowns is connected precisely with incorrect handling of the control lever. Do not pull the lever with quick and sharp movements - such tough operation may eventually lead to a major overhaul of the entire box, since the switching mechanism and synchronizers will fail very quickly (in fact, the same applies to shafts with gears).
Move the lever smoothly, take mini-pauses in the neutral position - then the synchronizers will work, which will protect the gear from breaking.
Do not forget to periodically check the oil level in the crankcase! Top it up if the need arises. Also, in due time, a complete oil change will be required - its terms are indicated in the operating instructions for the machine.
Video - The principle of operation of a manual transmission manual transmission
Conclusion!
And, of course - the classic, always relevant advice: listen to your car! A good driver always feels his iron friend and treats him with care. With this approach, you will not have to repair either the gearbox or other devices in your car.
- News
- Workshop
The Prosecutor General's Office began checking auto-lawyers
According to the Prosecutor General's Office, the number of litigations conducted by "unscrupulous auto-lawyers" who work "not to protect the rights of citizens, but to extract super profits" has sharply increased in Russia. According to Vedomosti, the department sent information about this to law enforcement agencies, the Central Bank and the Russian Union of Motor Insurers. The Prosecutor General's Office explains that intermediaries take advantage of the lack of due diligence...
Tesla crossover owners complain about build quality
According to motorists, problems arise with the opening of doors and power windows. The Wall Street Journal reports this in its material. The Tesla Model X is priced around $138,000, but according to the original owners, the quality of the crossover leaves a lot to be desired. For example, several owners at once jammed opening up ...
It will be possible to pay for parking in Moscow with a Troika card
Troika plastic cards used to pay for public transport will get a useful feature for motorists this summer. With their help, it will be possible to pay for parking in the paid parking zone. To do this, parking meters are equipped with a special module for communication with the transport transaction processing center of the Moscow Metro. The system will be able to check if there are enough funds on the balance...
Traffic jams in Moscow will be warned a week in advance
The specialists of the center took such a measure because of the work in the center of Moscow under the My Street program, the Official Portal of the Mayor and the government of the capital reports. The TsODD is already analyzing car flows in the Central Administrative District. At the moment, there are difficulties on the roads in the center, including on Tverskaya Street, Boulevard and Garden Ring and Novy Arbat. The press office of the department...
Volkswagen Touareg review reached Russia
As stated in the official statement of Rosstandart, the reason for the recall was the possibility of weakening the fixation of the retaining ring on the support bracket of the pedal mechanism. Earlier, Volkswagen announced a recall of 391,000 Tuareg vehicles worldwide for the same reason. As Rosstandart explains, as part of the recall campaign in Russia, all cars will have...
Mercedes owners will forget what parking problems are
According to Zetsche, cited by Autocar, in the near future, cars will become not just vehicles, but personal assistants that will greatly simplify people's lives by ceasing to provoke stress. In particular, the CEO of Daimler said that special sensors will soon appear on Mercedes cars that “will monitor the parameters of the body of passengers and correct the situation ...
Named the average price of a new car in Russia
If in 2006 the weighted average price of a car was about 450 thousand rubles, then in 2016 it was already 1.36 million rubles. Such data are provided by the analytical agency Avtostat, which has studied the situation on the market. Like 10 years ago, foreign cars remain the most expensive on the Russian market. Now the average price of a new car...
Named the regions of Russia with the oldest cars
At the same time, the youngest vehicle fleet is in the Republic of Tatarstan (average age is 9.3 years), and the oldest is in the Kamchatka Territory (20.9 years). Such data are provided by the analytical agency Avtostat in their study. As it turned out, in addition to Tatarstan, only in two Russian regions the average age of cars is less than...
Photo of the Day: Giant Duck Vs Drivers
The path to motorists on one of the local highways was blocked by ... a huge rubber duck! Photos of the duck instantly went viral on social networks, where they found a lot of fans. According to The Daily Mail, the giant rubber duck belonged to one of the local car dealers. Apparently, he demolished an inflatable figure on the road ...
GMC SUV turned into a sports car
Hennessey Performance has always been famous for its ability to generously add additional horses to a “pumped” car, but this time the Americans were clearly modest. GMC Yukon Denali could turn into a real monster, fortunately, that the 6.2-liter "eight" allows you to do this, but the mechanics of Hennessey limited themselves to a rather modest "bonus", increasing the engine power ...
HOW to choose and buy a car, Buying and selling.
How to choose and buy a car The choice of cars, both new and used, on the market is huge. And not to get lost in this abundance will help common sense and a practical approach to choosing a car. Do not give in to the first desire to buy the car you like, carefully study everything ...
The most expensive car in the world
There are a huge number of cars in the world: beautiful and not very, expensive and cheap, powerful and weak, our own and others. However, there is only one most expensive car in the world - this is the Ferrari 250 GTO, it was produced in 1963 and only this car is considered ...
The cheapest car in the world - TOP-52018-2019
Crises and the financial situation are not very conducive to buying a new car, especially in 2017. Only everyone has to drive, and not everyone is ready to buy a car in the secondary market. There are individual reasons for this - to whom the origin does not allow to travel ...
Rating TOP-5: the most expensive car in the worldYou can treat them as you like - admire, hate, admire, feel disgust, but they will not leave anyone indifferent. Some of them are just a monument to human mediocrity, made of gold and rubies in full size, some are so exclusive that when you...
What car to buy for a beginner When the long-awaited driver's license is finally obtained, the most pleasant and exciting moment comes - buying a car. The auto industry vying with each other offers customers the most sophisticated novelties and it is very difficult for an inexperienced driver to make the right choice. But often it is from the first ...
Rating 2018-2019: DVRs with a radar detectorThe requirements for additional equipment in the passenger compartment are growing at a rapid pace. Up to the fact that in the cabin there is simply not enough space to accommodate all the necessary equipment. If earlier only video recorders and air flavors interfered with the review, today the list of devices ...
Where can I buy a new car in Moscow? The number of car dealerships in Moscow will soon reach a thousand. Now in the capital you can buy almost any car, even a Ferrari or Lamborghini. In the struggle for a client, salons go to all sorts of tricks. But your task...
The most bought cars in 2018-2019 in Russia
How to choose a new car? In addition to taste preferences and technical characteristics of the future car, a list or rating of the best-selling and popular cars in Russia in 2016–2017 can help you. If the car is in demand, then it deserves your attention. The obvious fact is the Russians ...
- Discussion
- In contact with
The manual transmission is no longer the most common type of transmission used in cars today. However, it still remains quite in demand due to its reliability, simplicity of design and maintainability. The manual transmission gets its name from the "manual" (or mechanical) way of shifting gears. The transmission refers to stepped gearboxes in which the torque is changed by steps (gears). A manual transmission is considered the most reliable, but also the most difficult to manage, especially for a novice driver.
The principle of operation of a manual transmission
Manual TransmissionThe principle of operation of a manual transmission is as follows: the torque from the engine is transmitted through the input shaft of the gearbox, then converted using pairs of interacting gears and then transmitted to the wheels. Each pair of gears (stage) has a specific gear ratio that converts the rotational speed and torque of the engine crankshaft. Moreover, if the transmission increases the torque, then the rotation speed decreases and vice versa. In the first case, the transmission will be called downshifting, and in the second - upshifting.
The gear ratio is determined by the ratio of the number of teeth on the output and input gears in a pair. In turn, the number of teeth directly depends on the size of the gear itself: the more teeth, the larger the diameter of the gear. For example, first gear has the largest gear ratio, and therefore the input gear (on the input shaft) is the smallest and the output gear is the largest. Gear shifting in a manual transmission occurs only when you press , because it is necessary to interrupt the power flow transmitted from the engine.
The movement of a car equipped with a manual transmission always starts in first gear. The exception is heavy trucks - there it can be done from second gear. To do this, you must manually move the lever selector to the appropriate position. The transition to higher gears is carried out by sequential gear shifting one after another. The very moment of switching speed depends on the readings of the speedometer and tachometer, since each gear is designed to operate in a certain range of engine speeds.
Types of manual gearboxes
According to the number of steps, a manual transmission is mainly divided into:
- 4-speed;
- 5-speed;
- 6-speed.
The most common mechanics is the 5MT transmission, i.e. five-speed gearbox.
Depending on the number of shafts, the following types of gearboxes are distinguished:
- two-shaft mechanical transmissions installed on passenger front-wheel drive vehicles;
- three-shaft manual transmissions, which are used mainly on rear-wheel drive vehicles, as well as on trucks.
Manual transmission device
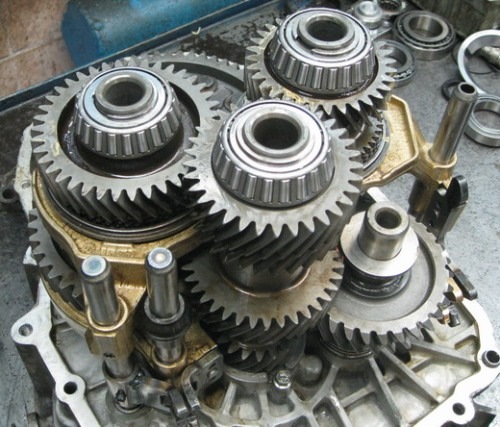 Manual transmission device
Manual transmission device Structurally, a manual gearbox consists of the following elements:
- drive or input shaft;
- driven or output shaft;
- intermediate shaft (for 3-shaft manual transmission);
- gears of primary and secondary shafts;
- gear selection mechanism;
- synchronizer clutches (synchronizers);
- crankcase;
- main gear;
- differential.
At the same time, the device and principle of operation of two-shaft and three-shaft transmission differ from each other.
Two-shaft gearbox: device and principle of operation
 Scheme of a two-shaft manual transmission
Scheme of a two-shaft manual transmission This type of box is the most common. through the clutch is transmitted to the input shaft. Depending on the design of a particular gearbox, some of the gears on the primary and secondary shafts are rigidly fixed to them, and some rotate freely. Also, at least one synchronizer is located on each shaft. The gears of the primary and secondary shafts are in constant engagement with each other. Understanding which of them are fixed and which rotate is very simple: the gears near the synchronizers always rotate on the shaft.
The final drive gear is rigidly fixed to the driven shaft. Torque is transmitted from the secondary shaft to the wheels of the vehicle. The latter ensures the rotation of the wheels with different angular speeds.
The gear selection mechanism in a two-shaft gearbox is located in the box body and consists of forks and rods that move. The mechanism is equipped with protection against simultaneous engagement of two gears.
The principle of operation of a two-shaft transmission is as follows:
- In the neutral position of the gear lever, the torque from the engine is not transmitted to the drive wheels, the gears on the shafts scroll freely.
- When moving the lever, the driver moves the synchronizer sleeve with the corresponding fork through a system of cables or rods.
- The clutch synchronizes the angular speeds of the corresponding gear and the shaft on which the synchronizer is located.
- The synchronizer clutch engages with the gear and torque begins to be transmitted from the input shaft to the secondary.
- There is a transmission of torque from the engine to the drive wheels with a given gear ratio.
For reversing, an additional shaft with an intermediate reverse gear is used.
Torque transmission schemes for each of the gears:
Three-shaft gearbox: device and principle of operation
The difference between three-shaft mechanics and two-shaft mechanics is that three types of shafts are used here. In addition to the driven and leading, an intermediate shaft is also used.
The input shaft connected to the clutch transmits torque to the intermediate. The transmission takes place through the corresponding gear - thus, the shafts are in constant mesh.
 Three-shaft manual transmission device
Three-shaft manual transmission device The intermediate shaft is parallel to the primary, all the gears on it are rigidly fixed.
On the same axis with the primary is the secondary shaft. The thrust bearing on the drive shaft, which includes the output shaft, is responsible for this. In this case, the gears of the driven shaft can rotate freely and do not have a rigid fixation with the shaft. The output shaft gears are in constant mesh with the countershaft gears. Therefore, in the neutral position of the gearbox, the torque from the input shaft is transmitted to the intermediate and then to the gears of the output shaft. But since they rotate freely on the shaft, the car does not move.
Between the gears of the secondary shaft there are synchronizers, the work of which is to align the angular velocities of the gears of the secondary shaft with the angular velocity of the shaft itself due to friction forces.
Synchronizers are rigidly fixed on the shaft and, due to the spline connection, can move along it in the axial direction.
Unlike a two-shaft gearbox, the shift mechanism in a three-shaft transmission is located on the box body and consists of a control lever and rods with forks. The mechanism is also equipped with a locking device to prevent the simultaneous engagement of two gears.
It may also have a remote control. In this case, the remote switching mechanism is provided by a link or hinged cables.
The principle of shifting gears in a three-shaft gearbox is similar to the principle of operation of a two-shaft transmission.
A little about the manual transmission synchronizer
The synchronizer is used for shockless gear engagement due to the alignment of the angular velocities of the shaft and gear. Structurally, the synchronizer consists of a clutch, two locking rings, three crackers and two wire rings.
In the process of engaging the gear, the fork moves the clutch to the desired gear, where the blocking ring first moves. The resulting friction force due to the difference in the angular velocities of the elements rotates the blocking ring until it stops. Further movement of the synchronizer clutch and engagement occurs only after the alignment of the angular velocities. You can read more about the synchronizer in our article.
Advantages and disadvantages of manual transmission
For clarity, the positive and negative sides of a manual transmission are presented in the form of a comparative table.
| Advantages | Flaws |
|---|---|
| The cost and weight of the box is lower compared to other types of gearboxes | Less driver comfort compared to other gearboxes |
| High acceleration dynamics, fuel economy and efficiency | Driver tiring shifting process |
| High reliability due to simple design | The need for periodic clutch replacement |
| Simple and inexpensive maintenance | Lower smoothness of the car in comparison with other types of gearboxes |
| Possibility of more efficient off-road driving | |
| Ability to tow a car |
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, the operation of a manual transmission is accompanied by many advantages. One economic side of using the box is worth it! And coupled with the reliability of the transmission and a more "driver's" driving experience, the manual transmission is an excellent solution for lovers of fast driving or off-road driving. If comfort is not paramount for you, then the choice in favor of manual transmission is obvious.
Today we will consider the device of a manual transmission, its positive and negative sides, as well as the most common malfunctions. Despite the very wide choice of cars equipped with automatic transmission, vehicles with manual transmission are still relevant. This is due to the fact that the reliability and resource reserve of mechanics is significantly higher than that of automatic analogues. In addition, cars with mechanics are much more frisky, and their control requires more activity from the driver when driving.
In the photo - the handle of the 7-speed gearbox
The transmission is designed to change the frequency of the torque transmitted from the internal combustion engine. In a manual unit, the driver himself decides which gear ratio should be included in a particular situation.
Modern passenger cars are usually equipped with five speed transmissions: four base and one overdrive. This is perhaps the best option for most drivers. These models include domestic and many imported vehicles, such as. However, there are models with a large number of steps. Manual transmissions with six or seven gears usually have five base stages and two or one overdrive.
Overdrive, or overdrive, has a gear ratio less than one. In other words, when overdrive is engaged, the driven shaft rotates faster than the drive shaft.
More expensive vehicles are equipped with six or seven speed manuals. For example, a gearbox or has six gear positions, and the latest generation Porsche 911 is equipped with a seven-speed manual.
It is worth noting that budget models, for example, Kia Rio or Hyundai Solaris 2016-2017, are already equipped with a 6-speed gearbox.
Advantages of a six-speed transmission
Naturally, a six or seven-speed gearbox compares favorably with five-speed units. First of all, it is worth noting that the switching process exhausts the internal combustion engine resource much less, since the transition from one speed mode to another is smoother. In addition, the fuel consumption of six-speed manual transmissions is somewhat lower, especially in the extra-urban driving cycle. Acceleration dynamics are much higher due to the fact that the gears are short.

In every modern car equipped with a six-speed manual, there is electronic equipment that notifies the driver of the need to shift. There is a similar thing in cars with a five-speed gearbox, but not always.
Manual transmission device
The transmission of a car is a multi-stage gearbox, the principle of operation of which is to alternately mesh individual gear pairs.

Clutch
The smoothness of switching from one gear to another in mechanics occurs due to the presence of a clutch assembly. It allows you to interrupt the connection of the transmission with the power unit for the time of switching. Its mechanism is an intermediate link between the car engine and gearbox. In addition to ensuring smooth shifting, the clutch assembly reduces vibrations transmitted from the internal combustion engine.
The clutch is divided according to the type of design and three types: friction, hydraulic, and electromagnetic.
The friction type is the most popular and can be single-disk, double-disk, multi-disk.
Today's vehicles are usually equipped with single disc models.
The principle of operation of the node is quite simple. The flywheel mounted on the crankshaft of the internal combustion engine acts as a drive disk. The driven disk is pressed against it with the help of a pressure plate, and pressing the clutch weakens this connection. The diaphragm spring provides optimal compression of the driven disc with the flywheel.

The pressure plate with the diaphragm is a one-piece design - the clutch basket. Baskets are both push and pull, but the first type is the most common.
With the help of splines, the driven disk is joined to the primary axis of the manual transmission. The smoothness of the transmission is due to the damper springs located on the disc hub. In addition, the slave is equipped with friction linings that are able to withstand high temperatures for a short time, when the clutch is engaged.
Gear shift
In each gearbox, shafts are located in parallel, on which gears are located. There are three-shaft and two-shaft transmissions. The shafts are called driving (primary), driven (secondary), also in the three-shaft type there is also an intermediate one.

Three-shaft type
The input shaft receives from the internal combustion engine, and from its axis, with the help of a rigid engagement with the drive shaft gear, the rotation is transmitted to the intermediate shaft. The secondary and primary axles are in the same plane and are joined together by a bearing. Due to this, their rotation occurs either completely independently or through an intermediate shaft. The gears on the secondary shaft do not have a rigid fixation, and are separated from each other by synchronizers that fit tightly on the shaft, but can walk along its axis with the help of splines. The end face of the synchronizer has gear rims that allow it to engage with similar rims on the gear wheel.
In the neutral position, the wheels rotate freely on the shaft, and the synchronizers are open. When the gear is engaged, the fork displaces the clutch and engages it with a certain gear.
From the secondary axis, the rotation goes to, or and in front-wheel drive cars. To enable reverse gear, an intermediate wheel is installed in the gearbox, which changes the rotation from the intermediate axle to the opposite.
Three-axle units are the most popular and are installed in almost every modern car.

Twin shaft type
The input shaft of a two-axle unit has many gears, not just one. Since there is no intermediate axle, its place is taken by the driven one with synchronizer couplings and gears installed on it. By and large, the difference lies in the presence of only one pair of engagements between the axles for each stage, and not two.
Switching is carried out in a similar way - a fork, controlled by a shift knob using a rod, shifts the clutch along the secondary shaft to the appropriate position.
The two-shaft type is characterized by high efficiency, but is limited in increasing the gear ratio, which is why this type of design is used extremely rarely. Due to the possibility of combining the gearbox, clutch assembly, and the internal combustion engine itself into a single unit, almost all small cars are equipped with this particular type of transmission. An example of the use of two-axle mechanics in a car with a front-mounted power unit can be considered the Citroen C3.

Important to remember!
Due to the fact that the intermediate gear that provides reverse rotation of the reverse output shaft does not have a synchronizer, the reverse gear should only be engaged after the vehicle has come to a complete stop. Otherwise, the gearbox will fail after such a switch.
Synchronizer clutch
Every modern transmission has synchronizer clutches. Their presence is important to simplify the switching mode. Without synchronizers, shifting would have to do a double clutch release in order to equalize the speed of the axles. On some types of special equipment, where gearboxes have a large number of steps, couplings are not used, since this is impossible.

On the inner circumference of the hub are splined grooves that allow the synchronizer to move along its own axis. When switching, the fork shifts the synchronizer along the splines until it mates with its pair at the end of a certain gear. When switching a stage, a significant force is applied to one of the blocking rings. Ultimately, the locking ring turns all the way.
 In the photo - removing the synchronizer clutch
In the photo - removing the synchronizer clutch
Further displacement of the synchronizer clutch without switching the stage is not possible. When the synchronizer engages with the gear ring, the elements are securely fixed.
Pros and cons of mechanics
The manual unit has both its advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
Less costly transmission maintenance.
High efficiency.
Does not require separate cooling.
Cars with manual transmission are less voracious and have better dynamics.
The simplicity of the mechanics significantly increases the reliability of the unit.
Wider range of driving mode selection.
The vehicle is allowed to be towed.
Minuses:
Smooth starting and shifting require driving skills that only come with time.
A small resource of the clutch assembly.
During long trips, the driver of a vehicle with mechanics is much more tired than the driver of a car with automatic transmission.
The limited steps do not allow you to smoothly change the gear ratio.
Possible problems
Despite the simplicity of the design, the unit can break. If abnormal operation of the gearbox is detected, it is recommended to contact a car service as soon as possible. You can try to solve the problem yourself, but this will require both appropriate tools and certain skills.
The first thing worth stopping at is the occurrence of extraneous noise when the neutral gear is turned on. This can happen if the oil in the box has long exhausted its resource or it is not left at all. Usually, drivers change it extremely rarely, but if the transmission does not work correctly, the first thing you should pay attention to is the condition of the oil.

It can also leak due to the poor condition of the seals and gaskets. In this case, when changing the oil, other defective elements should also be changed. However, worn out bearings, gears, misalignment of the shaft axes can also be the cause of this problem. In this case, the box should be dismantled and completely sorted out, replacing worn-out structural elements.
There are situations when the driver has to make more effort to change gear than usual. This may be due to the failure of the switching mechanism itself or the incomplete disengagement of the clutch. However, damage to the stem lever may have caused the problem. To eliminate it, it is necessary to adjust the shifting or clutch mechanism, and it may also be necessary to replace damaged elements.
Some drivers have experienced transmission problems. This is often associated with wear of gears, forks, rods, bearings of the driven or intermediate shafts, as well as weakening their fixation. Since there can be quite a few reasons, in order to get rid of a manual transmission malfunction, it is necessary to completely sort out with the replacement of all defective structural elements.
Incompletely depressing the clutch pedal or driving the car with the clutch partially depressed is fraught with damage to the assembly parts. There is rapid wear of the clutch disc, and the petals of the diaphragm spring can simply break off. In addition, incomplete disengagement of the clutch when switching will soon lead to licking of the gear wheels.
It is also worth mentioning that the strong vibration of the transmission when the internal combustion engine is running indicates that the docking of the two units is unreliable. Most likely, in this case, the weakening of the bolted connections is to blame; in this case, it will be enough to tighten them only more strongly. However, it is possible that the vibration is associated with the destruction of the supports, and then a very time-consuming repair will be required.
The occurrence of incorrect noise when shifting gears is most often associated with a clutch malfunction. The output shaft bearing may also be the culprit.
Careful use of any mechanism is a guarantee of its durability. The unpretentiousness of the mechanical unit attracts car owners. And yet, there are some recommendations regarding the use of manual transmission.
The first thing to remember is the importance of fully depressing the clutch pedal before changing gear. This is perhaps the most important moment in the use of mechanics. Also, the included gear must correspond to the driving mode. In addition, it is worth remembering that before switching to a lower gear, the speed must be reduced.
Despite the fact that, unlike the automatic machine, the mechanics can work without oil at all, this has a rather strong effect on its general condition. It is recommended to check the level and condition of the lubricant after passing 20,000 km. Despite the fact that most even experienced car owners never change the oil in mechanics at all, this is still completely wrong. It is advisable to change it at least after every 70,000 km of run.