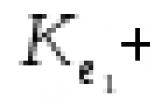This post is dedicated entirely to API CF (API CF-2, API CF-4). What's interesting about the CF API? What unites API CF-2 and API CF-4 under the API CF flag, and what is the difference between them? Let's start with the fact that API CF is a class of motor oils in the API classification, finally introduced in 1994 (API CF-4 was introduced and was valid for engines manufactured in 1990, and API CF-2 approved only in 1994).
API CF class are engine oils for diesel engines with split injection using fuel with a high sulfur content (more than 0.5%). The ratio of engine oil to API CF class implies the presence of additives that are more effective (compared to the obsolete and canceled API CD class) in preventing deposits and deposits on pistons and piston groups, and provide increased protection for plain bearings containing copper.
API CF-2
A feature of API CF-2 is that this class refers to two-stroke (2 - in the abbreviation) diesel engines operating in severe operating conditions. Oils of API CF-2 class provide enhanced protection of piston rings and the entire group from deposits and soot (“bedding” of rings, etc.), contain “reinforced” additives against coking and sludge in a diesel engine.
API CF-4
As for API CF-4, this class, which came into effect since 1990, combined engine oils for high-speed and powerful four-stroke (this is indicated by 4 in the API CF-4 abbreviation) diesel engines operating in various operating conditions. Ideally, these are powerful mainline tractors “charged for an endless run” along the highway. Both with and without turbocharging. Moreover, the additives used in API CF-4 oils provide increased protection of the piston group from carbon deposits and overheating, even on uprated engines (this was an API CE class privilege, but API CF-4 successfully replaced it). Another feature of API CF-4. Oils in this class often meet the API SJ (i.e. gasoline) class. In this case, it is necessary to coordinate the use of such oil in a gasoline engine with the manufacturer.
Feature API CF
I forgot to mention the CF API feature. The fact is that the CF API is the most "ancient" of the current API classes. But "longevity" does not detract from its merits. The presence of API CF on the market today only emphasizes its specificity. API CF grade motor oils will provide the best protection of the piston group against carbon deposits when using high-sulphur fuels, as well as protection against wear and corrosion for copper-containing bearings. Oils certified by API CF provide oil pumpability, both conventionally and with the help of a compressor or supercharger.
API motor oil classification was established in 1969 by the American Petroleum Institute. The API classification is called the quality classification of motor oils.
This classification divides engine oils into:
oils for gasoline engines;
oils for diesel engines;
oils for two-stroke engines;
transmission oils;
For each of these types, quality classes are provided that describe a specific set of properties and qualities of automotive oils of each class.
On the label, information on assigning an API class to engine oil is provided in the following form: API SM, API CF, or API SM/CF.
If an engine oil can be used in both types of engines, then two classes are assigned to such an oil - for diesel and for gasoline engines. On the oil label, these classes are separated by a slash, such as API SJ/CF-4. At the same time, the class of oil that corresponds to the more preferred (according to the manufacturer of the oil) application is put first. That is, in the above case, the main purpose of the oil is for gasoline engines, but the manufacturer also allows its use in diesel engines.
It should be noted that the lack of information on the engine oil label regarding compliance with any of the API classes clearly means that this car oil either does not have an API certificate at all, or the quality class assigned to it is outdated.
What do the symbols of the API code mean?
The alphanumeric code is the designation of the oil class.
In this case, the first letter of the encoding means the type of oil:
"S" - for gasoline engines (service / spark ignition)
"C" - for diesel engines (commercial / compression ignition)
"T" - for two-stroke engines (two-stroke)
API Engine Oil Grades: Gasoline Engines
API SN
The new SN class was created by the American Petroleum Institute (API) in conjunction with the American professional association ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers).
The differences between the API SN class and the previous SM specification are much larger than the differences between the SM class and SL. The main difference between API SN and previous API classifications is the limitation of phosphorus content for compatibility with modern exhaust gas aftertreatment systems, as well as comprehensive energy savings. That is, oils classified according to API SN will approximately correspond to ACEA C2, C3, C4, without correction for high temperature viscosity.
For the new API SN category, the Lubrication Committee has proposed to follow the same development path as with the earlier API and ILSAC categories. This means that all API and ILSAC engine oil performance will be equivalent, except that the proposed API SN requirements do not include Sequence IIIG wear protection tests on aged oils. These tests and the Sequence VID fuel economy tests are important benchmarks for oils applying for ILSAC GF-5.
The main differences between ILSAC GF-5 and the previous GF4 classification are the ability to work with biofuels, improved wear and corrosion protection, greater fuel efficiency, improved compatibility with sealing materials and improved protection against sludge formation.
The requirements of API SN and ILSAC GF-5 are quite close and low viscosity oils are likely to be classified under these two classifications.
Oils meeting API SN can be used to replace API SM and earlier.
API SM
engines
since 2004 release.
The API SM class describes engine oils for modern gasoline (multi-valve, turbocharged) engines. Compared to API SL, motor oils meeting API SM requirements must provide better protection against oxidation and premature wear of engine parts. In addition, standards regarding the properties of the oil at low temperatures have been raised. Engine oils in this class can be certified to the ILSAC energy saving class.
Engine oils meeting the requirements of API SM can be used in cases where API SL or earlier is recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
API SL
Motor oils for gasoline engines
since 2000 release.
In accordance with the requirements of car manufacturers, API SL class motor oils are used in multi-valve, turbocharged engines running on lean fuel mixtures that meet modern increased environmental requirements, as well as energy saving.
Engine oils meeting API SL requirements may be used where API SJ or earlier is recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
API SK
Due to the fact that one Korean motor oil manufacturer uses the abbreviation "SK" as its corporate name, the letter "K" is not used to indicate the category of motor oils for gasoline engines to avoid possible confusion.
API SJ
Motor oils for gasoline engines
since 1996 release.
Automotive oils of this class are designed for use in gasoline engines of cars and sports cars, minibuses and light trucks, which are serviced in accordance with the requirements of car manufacturers. SJ has the same minimum standards as SH and additional requirements for carbon build-up and low temperature operation. Oils are certified under the API SJ / EC energy saving category.
Engine oils meeting the requirements of API SJ may be used where SH or earlier is recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
API SH
Motor oils for gasoline engines
since 1993 release.
Motor oils of this class are intended for use in gasoline engines of cars, minibuses and light trucks manufactured in 1996 and older, in accordance with the recommendations of their manufacturers. Engine oils of this class have been tested in accordance with the requirements of the Chemical Manufacturers Association (CMA).
The class is characterized by higher requirements compared to the SG class, and was developed as a substitute for the latter, to improve anti-carbon, antioxidant, anti-wear properties of oils and increased corrosion protection.
The API SH class corresponds to the ILSAC GF-1 category in all respects, except for the mandatory energy saving, and, depending on the degree of fuel economy, belongs to the API SH / EC and API SH / ECII categories.
Engine oils in this grade may be used where API SG or earlier is recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
API SG
Motor oils for gasoline engines
from 1989 to 1993 release.
Designed for use in gasoline engines of passenger cars, minibuses and light trucks of 1993 and older models, running on unleaded gasoline with oxygenates. Motor oils of this class have properties that provide improved protection against carbon deposits, oil oxidation and engine wear, in comparison with previous classes, and also contain additives that protect against rust and corrosion of internal engine parts.
API SG engine oils meet the requirements for engine oils for API CC and CD diesel engines. Can be used where API classes SF, SE, SF/CC or SE/CC are recommended.
API SF
Motor oils for gasoline engines from 1980 to 1989.
These engine oils were used in 1980-1989 gasoline engines running on leaded gasoline, subject to the recommendations and instructions of the engine manufacturer.
Provide enhanced resistance to oxidation, rust and corrosion, improved protection against wear of parts, in comparison with the basic characteristics of API SE class motor oils, as well as more reliable protection against carbon deposits and slag.
API SF grade motor oils could be used as substitutes for previous API SE, SD or SC grades.
API SE
Motor oils for gasoline engines from 1972 to 1980.
These motor oils were used in gasoline engines of 1972-1979 models, as well as in some 1971 models.
Additional protection compared to API SC and SD motor oils. Can be used as substitutes for API SC and SD.
API SD
Motor oils for gasoline engines from 1968 to 1971.
Motor oils of this class were used in gasoline engines of passenger cars and some trucks manufactured in 1968-70, as well as some models of 1971 and later.
Improved protection compared to API SC motor oils, also used only when recommended by the engine manufacturer.
API SC
Motor oils for gasoline engines from 1964 to 1967.
They were usually used in the engines of cars and some trucks manufactured in 1964-1967. Reduce high and low temperature deposits, wear and protect against corrosion.
API SB
Motor oils for low-power gasoline engines.
Motor oils of the 30s of the 20th century, which provided fairly light protection against wear and oxidation, as well as anti-corrosion protection of bearings in motors that are operated in light load conditions.
API SB engine oils may only be used if they are specifically recommended by the engine manufacturer.
API SA
Motor oils for gasoline and diesel engines.
An outdated class of oils for use in old engines operating in conditions and modes in which protection of parts with additives is not needed.
API SA grade engine oils may only be used if recommended by the engine manufacturer.
API Engine Oil Grades: Diesel Engines
API СJ-4
Engine oils for diesel engines
since 2006 release.
The API CJ-4 classification has been licensed since October 2006.
API CJ-4 is designed for heavy duty diesel engines that meet key NOx and particulate emissions requirements for 2007 and 2007 engines. recommended for engines equipped with particulate filters, as well as other systems to reduce the toxicity of exhaust gases.
The API CJ-4 standard is undergoing significant changes in response to the needs of new engine manufacturers that meet the new environmental standards that have been introduced since 2007. API CJ-4 oils are subject to limits for certain indicators: ash content less than 1.0%, sulfur 0.4%, phosphorus 0.12%.
The API CJ-4 classification exceeds the requirements of the earlier API CI-4 PLUS, CI-4 categories and can be used as a replacement.
API CI-4PLUS
An additional performance class of motor oils API CI-4 PLUS for diesel engines was introduced in 2004.
Compared to API CI-4, the requirements for specific soot content, as well as volatility and high-temperature oxidation, are increased. When certified in this classification, engine oil must be tested in seventeen engine tests.
API CI-4
Engine oils for diesel engines
since 2002 release.
API CI-4 class introduced in 2002.
These engine oils are used in modern diesel engines with various types of injection and supercharging, as well as in engines with an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system.
The API CI-4 class was introduced in connection with the emergence of new, more stringent requirements for ecology and exhaust gas toxicity, which apply to engines manufactured from October 1, 2002. The requirements for soot formation, deposits, viscosity indicators, and TBN value limitation have been tightened.
Engine oil meeting API CI-4 must contain appropriate detergent/dispersant additives and has, in comparison with API CH-4, increased resistance to thermal oxidation, as well as higher dispersant properties. In addition, such motor oils provide a significant reduction in engine oil waste by reducing volatility and reducing evaporation at operating temperatures up to 370 ° C, under the influence of gases. The requirements for cold pumpability have been tightened, the resource of gaps, tolerances and motor seals has been increased by improving the fluidity of the motor oil.
The API CI-4 classification replaces API CD, CE, CF-4, CG 4 and CH-4 oils.
API CH-4
Engine oils for diesel engines
since 1998 release.
Engine oils of this class are used in four-stroke diesel engines that operate in high speed conditions and meet the requirements of the 1998 emission standards and standards.
API CH-4 motor oils meet the fairly stringent requirements of both American and European diesel engine manufacturers. Class requirements are specifically designed for use in engines running on high-quality fuels with a specific sulfur content of up to 0.5%. At the same time, unlike the API CG-4 class, the resource of these motor oils is less sensitive to the use of diesel fuel with a sulfur content of more than 0.5%, which is especially important for the countries of South America, Asia, and Africa.
API CH-4 engine oils meet increased requirements and must contain additives that more effectively prevent valve wear and the formation of carbon deposits on internal surfaces.
API GH-4 oils may be used as replacements for API CD, CE, CF-4 and CG-4 engine oils, as recommended by the engine manufacturer.
API CG-4
Engine oils for diesel engines
since 1995 release.
API class CG-4 introduced in 1995.
Engine oils of this class are recommended for four-stroke diesel engines of buses, trucks and tractors of the main and non-main line type, which are operated in high load and high speed modes.
API CG-4 engine oil is suitable for engines that use high quality fuels with a specific sulfur content of not more than 0.05%, as well as for engines for which there are no special requirements for fuel quality (specific sulfur content can reach 0.5% ).
API CG-4 certified motor oils should more effectively prevent wear of internal engine parts, the formation of deposits on internal surfaces and pistons, oxidation, foaming, and soot formation (these properties are especially needed for engines of modern long-distance buses and tractors).
The API CG-4 class was created in connection with the approval in the USA of new requirements and standards for the ecology and toxicity of exhaust gases (revised in 1994). The main drawback that limits the mass use of motor oils of this class, for example, in Eastern Europe and Asia, is the significant dependence of the motor oil resource on the quality of the fuel used.
API CG-4 engine oils can be used in engines where API CD, CE and CF-4 grades are recommended.
API CF (CF-2, CF-4)
Motor oils for diesel engines with indirect injection.
A hyphenated number means a two- or four-stroke engine.
The API CF class describes motor oils recommended for use in diesel engines with indirect injection, as well as other types of diesel engines that operate on fuels of various qualities, including those with a high sulfur content (for example, more than 0.5% of the total mass) .
API CF certified engine oils contain additives to improve the prevention of piston deposits, wear and corrosion of copper (copper-containing) bearings, which are of great importance in these types of engines, and can be pumped in the usual way, as well as with turbocharger or compressor.
API CF engine oils may be used where API CD quality is recommended.
API CF-2 (CF-II)
Engine oils for diesel engines
since 1994 release.
API class CF-2 introduced in 1994.
Motor oils of this class are usually used in two-stroke diesel engines that operate under increased stress. API CF-2 oils must contain additives that provide enhanced performance protection against wear on internal engine parts such as cylinders and rings. In addition, these motor oils must prevent the accumulation of deposits on the internal surfaces of the motor, that is, these oils are characterized by an improved cleaning function.
API CF-2 certified engine oil has improved properties and can be used in place of older similar oils when recommended by the manufacturer.
API CF-4
Engine oils for diesel engines
since 1990 release.
API class CF-4 introduced in 1990.
Engine oils of this class can be used in four-stroke diesel engines, the operating conditions of which are associated with high-speed modes.
API CF-4 motor oils must contain appropriate additives that provide a reduction in car oil burnout, as well as protection against carbon deposits in the piston group. The main purpose of motor oils of this class is the use in diesel engines of heavy duty tractors and other vehicles that are used for long trips on highways.
In addition, these engine oils are sometimes assigned the dual API CF-4/S grade. In this case, subject to the availability of relevant recommendations from the engine manufacturer, these motor oils can also be used in gasoline engines.
The quality requirements for API CF-4 oils exceed the capabilities of the previous API CE class, so API CF-4 engine oils can be used instead of API CE oils, if the engine manufacturer recommends it.
API CE
Engine oils for diesel engines
since 1983 release.
API CE class motor oils were intended for use in some heavy duty turbocharged engines, characterized by a significantly increased operating compression. The use of such oils was allowed for engines with both low and high shaft speeds.
API CE engine oils have been recommended for low and high speed diesel engines manufactured since 1983 that operate under heavy duty conditions. Subject to the relevant recommendations of the engine manufacturer, these motor oils could also be used in engines for which API CD class engine oils were recommended.
API CD-II ( CD-2)
Engine oils for two-stroke diesel engines engines
since 1985 release.
The API CD-II class was introduced in 1985 for use in two-stroke diesel engines and is, in fact, an evolutionary development of the previous API CD class. The main purpose of using such motor oils was the use in heavy powerful diesel engines, which were installed mainly on agricultural machinery.
Engine oils of this class meet all the performance standards of the previous API CD class, in addition, the requirements for highly effective engine protection against carbon deposits and wear have been significantly increased.
API CD+
Engine oils for diesel engines
Japanese production.
The oils are highly resistant to oxidation and thickening under the influence of soot build-up, as well as increased wear protection of the valve assembly.
API CD
Engine oils for diesel engines
since 1955 release.
The API CD class was introduced in 1955 for general use in some diesel engines, both naturally aspirated and turbocharged, with increased cylinder compression, where effective protection against carbon deposits and wear is essential. Motor oils of this class were commonly used in agricultural machinery.
API CD engine oils may be used in cases where no additional fuel quality requirements (including fuels with a high sulfur content) have been put forward by the engine manufacturer.
API CD motor oils were supposed to provide increased protection against bearing corrosion and high-temperature soot in diesel engines compared to previous classes. Often, engine oils in this class were called "Caterpillar Series 3", due to the fact that they met the requirements of the Superior Lubricants (Series 3) certification developed by the Caterpillar Tractor Company.
API CC
Engine oils for diesel engines
since 1961 release.
The API CC class was introduced in 1961 for use in some engines, both naturally aspirated and turbocharged, which were characterized by increased compression. Engine oils of this class were recommended for engines that were operated in moderate and high load modes.
Compared to earlier grades, API CC motor oils were required to provide a higher level of protection against high temperature deposits and bearing corrosion in diesel engines, as well as rust, corrosion and low temperature deposits in gasoline engines.
API CB
Engine oils for diesel engines from 1949 to 1960.
Engine oils for diesel engines operating under medium load on sour fuels.
The class was approved in 1949 as an evolutionary development of the API CA class, using fuel with a high sulfur content, without special quality requirements. API CB motor oils were also intended for use in supercharged engines that were operated in light and moderate conditions. This grade was often referred to as "Annex 1 Motor Oils" to indicate compliance with military regulation MIL-L-2104A Annex 1.
API CA
Motor oils for diesel engines from 1940 to 1950.
Motor oils for light duty diesel engines.
Car oils of this class are designed for use in diesel engines operating in light and moderate conditions on high-quality low-sulphur diesel fuel.
The class was widely used in the 40s and 50s of the last century and cannot be used in modern conditions unless it is required by the engine manufacturer.
API CA engine oils must have properties that provide protection against carbon deposits on piston rings, as well as against bearing corrosion in supercharged engines, for which there are no special requirements for the quality of the fuel used.
API Engine Oil Grades: Two-Stroke Engines
API TD
Oils for outboard two-stroke engines of motor boats.
API TC
Oils for engines with high requirements for oil quality, except for motor boats, for example, motorcycle engines, snowmobiles. It is possible to use the TC API in cases where the TA or TB API class is required.
API TB
Oils for high-speed two-stroke engines with a volume of 50-200 cm3, operating under heavy loads, such as scooters, chainsaws, motorcycles.
API TA
Oils for air-cooled two-stroke engines up to 50 cm3, e.g. mopeds, lawn mowers.
API Engine Oil Grades: Gear Oils
API GL-6
Gear oils for high displacement hypoid gears operating under high speed, high torque and shock loading conditions.
API GL-5
Gear oils for hypoid gears with performance level MIL-L-2105 C/D. These oils are preferably used in hypoid bevel gears and helical bevel gears for final drives in automobiles, motorcycle cardan drives and motorcycle speed gearboxes.
Oils are used specifically for hypoid gears with high axle misalignment. For the most severe operating conditions with shock and alternating loading. Recommended for hypoid gears operating at high speeds with low torques and shock loads on gear teeth.
API GL-4
High performance gear oils with MIL-L-2105 performance levels. These oils are used preferably in manual gearboxes and steering gears, final drives and low displacement hypoid gears in automobiles and trackless vehicles for the transport of goods and passengers and for non-transport applications.
Oils are used for hypoid gears operating at high speeds at low torques and at low speeds at high torques.
Highly effective extreme pressure additives are required.
API GL-3
High performance gear oils with MIL-L-2105 performance. These oils are used preferably in speed gearboxes and steering gears, in final drives and hypoid gears with low displacement in automobiles and trackless vehicles for the transport of goods, passengers and for non-transport work.
The oils are used for spiral bevel gears operating in moderately severe conditions, as well as for conventional transmissions with spiral bevel gears operating in moderately severe conditions in terms of speeds and loads.
They have better anti-wear properties than API GL-2.
API GL-2
Gear oils for worm gears operating under GL-1 conditions at low speeds and loads, but with higher requirements for anti-friction properties.
API GL-1
Mineral oils without additives or oils with antioxidant and antifoam additives, but without EP components, for use in manual transmissions with low specific pressures and sliding speeds.
Oils are used in spur, worm and helical bevel gears operating at low speeds and loads.
API MT-1
Oils for highly loaded units.
Designed for non-synchronized manual transmissions of powerful commercial vehicles (tractors and buses).
Equivalent to API GL-5 oils but with improved thermal stability.
API PG-2
Oils for transmissions of driving axles of powerful commercial vehicles (tractors and buses) and mobile equipment.
Equivalent to API GL-5 oils but with improved thermal stability and improved elastomer compatibility.
Oil quality- this is a set of properties that is necessary for the performance of the oil for its intended purpose. To facilitate the selection of an oil of the required quality for a specific type of engine and operating conditions, an API engine oil classification system has been created.
This classification was created and is being developed in collaboration with API (American Petroleum Institute), ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and SAE. It determines the limits of various parameters (eg piston cleanliness, piston ring wear, etc.) using various test motors.
According to the API system, 2 operational categories of purpose and quality are established
- For gasoline engines where SE, SF, SG, SH, SJ, SL, SM, SN classes apply.
- For diesel engines where CC, CD, CE, CF, CG, CH, CI, CJ classes apply.
Universal oils for gasoline and diesel engines are indicated by two symbols of the corresponding categories: the first symbol is the main one, and the second indicates the possibility of using this oil for another type of engine. For example, API CG-4/SH is an oil optimized for use in diesel engines, but it can also be used in gasoline engines for which an oil of API SH and lower categories (SG, SF, SE, etc.) is prescribed.
Categories of oils for gasoline engines of passenger cars
Oil group |
Vehicle Years |
||
SN |
Current | Engine oil in this category provides better protection against high temperature piston deposits, reduction of low temperature deposits (tar) and enhanced compatibility with sealing parts. The API SN Resource Conserving category combines API SN performance with improved fuel economy, turbocharger component protection, emission control compatibility, and additional engine protection when using ethanol-containing fuels up to E85. Thus, this category can be equated with ILSAC GF-5 | Introduced in October 2010 for vehicles 2011 and older. |
SM |
Current | Introduced in November 2004. | For vehicles 2004 and older |
SL |
Current | API planned to develop the PS-06 project as the next API SK category, but one motor oil supplier in Korea uses the abbreviation “SK” as part of its corporate name. To eliminate possible confusion, the letter “K” will be omitted for the next category “S”. - stability of energy-saving properties; - reduced volatility; - extended replacement intervals; |
For vehicles 2001 and older |
SJ |
Current | The category was approved on 11/06/1995, licenses began to be issued from 10/15/1996. Automotive oils in this category are designed for all currently used gasoline engines and completely replace the oils of all previously existing categories in older engine models. The maximum level of operational properties. API SJ/EC Energy Saving Certification Possibility. | since 1996 |
SH |
obsolete | Licensed category approved in 1992. To date, the category is conditionally valid and can only be certified as an additional category to API C categories (for example, API AF-4 / SH). According to the requirements, it meets the ILSAC GF-1 category, but without mandatory energy saving. Automobile oils in this category are designed for gasoline engines of 1996 and older models. When carrying out certification for energy saving, depending on the degree of fuel economy, API SH / EC and API SH / ECII categories were assigned. | since 1993 |
SG |
obsolete | Licensed category approved in 1988. The issuance of licenses ceased at the end of 1995. Automotive oils are designed for engines of 1993 and older models. Fuel - unleaded gasoline with oxygenates. Satisfies the requirements for automotive diesel engine oils of API CC and API CD categories. They have higher thermal and oxidation stability, improved anti-wear properties, reduced tendency to form deposits and sludge. API SG automotive oils replace API SF, SE, API SF/CC and API SE/CC oils. |
1989-1993 |
SF |
obsolete | Automobile oils in this category are designed for engines of 1988 and older models. Fuel - leaded gasoline. They have more effective than the previous categories, antioxidant, antiwear, anticorrosion properties and have a lower tendency to form high and low temperature deposits and slag. API SF automotive oils replace API SC, API SD and API SE oils in older engines. |
1981-1988 |
SE |
obsolete | Should not be used in gasoline engines of vehicles manufactured after 1979. | 1972-1980 |
SD |
obsolete | Should not be used in gasoline engines of vehicles manufactured after 1971. Use in more modern engines may result in poor performance or breakdowns. | 1968-1971 |
SC |
obsolete | Should not be used in gasoline engines of vehicles manufactured after 1967. Use in more modern engines may result in poor performance or breakdowns. | 1964-1967 |
SB |
obsolete | Should not be used in gasoline engines of vehicles manufactured after 1951. Use in more modern engines may result in poor performance or breakdowns. | - |
SA |
obsolete | Does not contain additives. Should not be used in gasoline engines of vehicles manufactured after 1930. Use in more modern engines may result in poor performance or breakdowns. | - |
Categories of oils for diesel engines of commercial vehicles
Oil group |
||
CJ-4 |
Current | Introduced in 2006. For high-speed four-stroke engines designed to meet 2007 emission standards on main roads. CJ-4 oils allow the use of fuels with sulfur content up to 500 ppm (0.05% by weight). However, operation with fuels containing more than 15ppm (0.0015% by weight) sulfur may affect the performance of exhaust aftertreatment systems and/or oil change intervals. CJ-4 oils are recommended for engines equipped with diesel particulate filters and other aftertreatment systems. Oils with the CJ-4 specification exceed the performance properties of CI-4, CI-4 Plus, CH-4, CG-4, CF-4 and can be used in engines for which oils of these classes are recommended. |
CI-4 |
Current | Introduced in 2002. For high-speed four-stroke engines designed to meet the 2002 exhaust emission regulations. CI-4 oils allow the use of fuels with a sulfur content of up to 0.5% by weight, and are also used in engines with an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system. Replaces CD, CE, CF-4, CG 4 and CH-4 oils. In 2004, an additional API category, CI-4 PLUS, was introduced. The requirements for soot formation, deposits, viscosity indicators, and the limitation of the TBN value have been tightened. |
CH-4 |
Current | Introduced in 1998. For high speed 4-stroke engines that meet U.S. emission regulations since 1998. CH-4 oils allow the use of fuels with a sulfur content of up to 0.5% by weight. Can be used instead of CD, CE, CF-4 and CG-4 oils. |
СG-4 |
obsolete | Introduced in 1995. For engines of high-speed diesel vehicles operating on fuel with a sulfur content of less than 0.5%. CG-4 oils for engines that comply with the exhaust gas toxicity requirements introduced in the USA since 1994. Replaces CD, CE and CF-4 oils. |
CF-4 |
obsolete | Introduced in 1990. For high-speed four-stroke diesel engines with and without turbocharging. Can be used instead of CD and CE oils. |
CF-2 |
obsolete | Introduced in 1994. Improved performance, used instead of CD-II for two-stroke engines |
CF |
obsolete | Introduced in 1994. For diesel engines with two-cavity combustion chambers (indirect injection) and others installed on off-highway vehicles, including engines that operate on fuel with a sulfur content of more than 0.5% by weight. Can be used instead of CD oils. |
CE |
obsolete | Introduced in 1985. For high speed naturally aspirated and supercharged 4-stroke engines. Can be used instead of CC and CD. |
CD-II |
obsolete | Introduced in 1985. For two stroke engines. |
CD |
obsolete | Introduced in 1955. For some naturally aspirated and supercharged engines. |
CC |
obsolete | Should not be used in diesel engines manufactured after 1990. |
CB |
obsolete | Should not be used in diesel engines manufactured after 1961. |
SA |
obsolete | Should not be used in diesel engines manufactured after 1959. |
Oh yes - the age-old question "what kind of oil to pour .."
In principle, the answer to it is in the competence of the manufacturer of a particular motorcycle model. The fact is that the engine and exhaust system are designed to work with a certain type of oil.
In order for the consumer not to rack his brains if he chooses the oil himself, each model has a list of parameters that allow you not to get confused: oil viscosity according to the standard SAE(American Association of Automotive Engineers) for example 10w40 and its classification according to the system API(Engine Service Classification System), for example SG. Data can be found in the User Manual.
This information is almost enough to choose an oil.
AN650 from 2002 to 2005 - API: SF or SG, SAE10W-40
AN650 from 2006 to 2013 - API: SF or SG or SH or SJ, SAE10W-40
AN400 from 1998 to 2006 - API: SF or SG, SAE10W-40
AN400 from 2007 to present - API: SF or SG or SH or SJ, SAE10W-40
AN250 from 1998 to 2006 - API: SF or SG, SAE10W-40
AN250 from 2007 to present - API: SF or SG or SH or SJ, SAE10W-40
in the same manual, Suzuki does not recommend the use of energy-saving oils according to API classification, some of the SH, SJ, SL and SM that have the EC (Energy Conserving) badge.
Another factor influencing the choice of oils is the presence of additives for clutch operation in an oil bath. This is important for all AN650 years. Those. only motorcycle oil needs to be poured into these devices. In AN400 and AN250, it is even permissible to fill in automotive oil that is suitable for viscosity and API classification.
Oil classes according to API:
| For gasoline engines - oil classes on the S scale | |||
| Oil group | Recommended area of application | Vehicle Years | Qualitative indicators |
| SM | Introduced in November 2004. Trends in the development of technology are aimed at improving their environmental safety, increasing maintenance intervals while maintaining reliability. Naturally, this makes its own adjustments to the process of improving engines, being reflected in the qualities of lubricants. Following these trends, in November 2004, a class for engine oils for gasoline engines appeared in the API classification - SM, suggesting, compared to SL, increased requirements for lubricants regarding oxidation resistance, protection against deposits, wear, etc. Since October 2006, the category for diesel oils of the CJ-4 class has been replenished. |
since 2004 | - |
| SL | (active). API planned to develop the PS-06 project as the next API SK category, but one motor oil supplier in Korea uses the abbreviation "SK" as part of its corporate name. To eliminate possible confusion, the letter "K" will be omitted for the next category "S". - stability of energy-saving properties; - reduced volatility; - Extended drain intervals. |
since 2001 | - |
| SJ | (active). The category was approved on 11/06/1995, licenses began to be issued from 10/15/1996. Automotive oils in this category are designed for all currently used gasoline engines and completely replace the oils of all previously existing categories in older engine models. The maximum level of operational properties. API SJ/EC Energy Saving Certification Possibility. | since 1996 | - |
| SH | (Conditionally active). Licensed category approved in 1992. To date, the category is conditionally valid and can only be certified as an additional category to API C categories (for example, API AF-4 / SH). According to the requirements, it meets the ILSAC GF-1 category, but without mandatory energy saving. Automobile oils in this category are designed for gasoline engines of 1996 and older models. When carrying out certification for energy saving, depending on the degree of fuel economy, API SH / EC and API SH / ECII categories were assigned. | since 1993 | higher for models from 1995 onwards |
| SG | Licensed category approved in 1988. The issuance of licenses ceased at the end of 1995. Automotive oils are designed for engines of 1993 and older models. Fuel - unleaded gasoline with oxygenates. Satisfies the requirements for automotive diesel engine oils of API CC and API CD categories. They have higher thermal and oxidation stability, improved anti-wear properties, reduced tendency to form deposits and sludge. API SG automotive oils replace API SF, SE, API SF/CC and API SE/CC oils. |
1989-1993 | higher for four-stroke engines |
| SF | Automobile oils in this category are designed for engines of 1988 and older models. Fuel - leaded gasoline. They have more effective than the previous categories, antioxidant, antiwear, anticorrosion properties and have a lower tendency to form high and low temperature deposits and slag. API SF automotive oils replace API SC, API SD and API SE oils in older engines. |
1981-1988 | higher for two-stroke engines |
| SE | High performance engines operating under severe conditions. | 1972-1980 | higher |
| SD | Medium boosted engines operating in difficult conditions. | 1968-1971 | average |
| SC | Engines operating with increased loads. | 1964-1967 | - |
| SB | Motors operating at moderate loads are used only at the request of the manufacturer. | - | - |
| SA | Engines operating in light conditions are used only at the request of the manufacturer. | - | - |
The API classification of engine oils was developed in 1969. It is quite widespread all over the world.
She labels products of well-known manufacturers, such as Castrol, Motul, Shell. The marking indicates the type of car engine into which it is possible to fill the oil fluid. Its decryption is quite simple. According to the classification of oils according to API, all lubricants are divided into:
- S - motor oils for gasoline engines;
- C - consumables for diesels;
- EC - energy-saving motor oils. They are of high quality, low viscosity, fluidity, and are able to reduce fuel costs.
![]()
Lubricants suitable for any motor are marked with a pair of symbols. The 1st character is considered the main one, the 2nd indicates that the oil product can be poured into a different type of engine. Example: API SM/CF oils.
Categories of oils for internal combustion engines on gasoline
The API classification includes the following classes of oil for internal combustion engines on gasoline:
- SN - approved 01.10.2010. Contains a limited amount of phosphorus. Compatible with new emission neutralizing systems, energy saving.
- SM - approved 11/30/2004. The API SM class is for gasoline engines produced today. Better than SL, protects against oxidation and early wear of motor parts. Almost does not change its own characteristics in low-temperature conditions.
- SL. Optimal for cars made in the twenty-first century. According to the tolerances of automakers, this lubricant is used in multi-valve, turbocharged power units that operate on lean fuel. The oil is environmentally friendly, energy-saving.
- SJ. Suitable for gasoline engines manufactured after 1996. Such a car oil is intended for use in cars, sports cars, minibuses, small trucks. When using it, a little soot is formed, the lubricant retains its properties in winter.
- SH. Optimal for gasoline engines made after 1994. Good resistance to soot, oxidation, wear, corrosive attack. It can be poured into cars, minibuses, freight transport. The main thing is to comply with the manufacturer's tolerances. They are listed in the table in the operating manual.
- SG. Suitable for cars manufactured no earlier than 1989. The additives contained in the motor oil protect the engine parts from corrosion and rusting.
- SF. An obsolete category in the API engine oil specification. A lubricant related to it can be poured into internal combustion engines made after 1980.
- SE. Suitable for engines released after 1972.
- SD. Car oil for use in gasoline engines manufactured after 1968 (obsolete category). The oil was used in gasoline internal combustion engines of cars and trucks.
- SC. Oily fluid for engines manufactured after 1964. It was usually used in the engines of passenger cars, trucks manufactured in 1964-1967.
- SB. Lubricant for gasoline engines that have low power. Provided rather weak protection of motor bearings from wear, oxidation, corrosive effects. Such a car oil cannot be poured into a modern car (unless the opposite is stated in the operating manual).
- SA. It differs from previous oils in that it can be used not only in gasoline, but also in diesel engines. A very outdated group of lubricants that are almost never used today. Previously, high-quality protection of motor parts through additives was not particularly required, so SA API oils were quite popular.
Categories of oils for diesel engines
API diesel engine oil may fall into one of the following categories:
- CJ-4. It was introduced on 01.10.2006. It was developed specifically for high load motors. The lubricant meets the basic requirements for the formation of carbon deposits and solid elements for power units manufactured in 2007. There are restrictions on certain characteristics: ash content should be less than one percent, sulfur concentration - less than four tenths of a percent, phosphorus - less than twelve hundredths of a percent. Oils in this API quality class have all the benefits of lubricants from other categories. They are also great for modern powertrains, comply with the introduced environmental standards.
- CI-4PLUS. The lubricant forms little soot, evaporates weakly, and practically does not oxidize at high temperatures. Any oil certified in this API specification class will pass approximately 17 production tests.
- CI-4. This class was introduced into the API specification fifteen years ago. Similar motor oils are used in today's diesel engines with different types of injection and boost. They contain in their composition special dispersing and detergent additives. Consumables are resistant to thermal oxidation, have good dispersing properties. They also significantly reduce the amount of smoke during operation. Volatility is reduced, evaporation begins when the temperature reaches three hundred and seventy degrees Celsius. The oil is very fluid, perfectly passes through the entire lubrication complex in severe frosts. This reduces the wear of the sealing elements of the power unit.
- CH4. The class was introduced on 01.12.1998. Lubricants are used in four-stroke diesel engines operating in high speed mode. They meet all requirements for the content of toxic substances in the exhaust. These requirements were adopted nineteen years ago. Oily fluids belonging to this category are recommended to be poured into the motor by automakers from Europe and the United States of America. Lubricants are designed for use in engines that run on very high quality fuel containing no more than five tenths of a percent of sulfur. However, they can be poured at a sulfur concentration that exceeds the established limit. This is especially important for South American, Asian and African states. Consumables contain additives that protect valves well from wear and prevent the appearance of carbon deposits on motor parts.
- CG-4. This API oil class was introduced twenty-two years ago. Petroleum products included in this category must be poured into four-stroke diesel engines (buses, trucks, tractors - vehicles operated under highly loaded conditions and at high speeds). The level of sulfur in the fuel must not exceed five hundredths of a percent. You can also fill this oil into power units for which there are no special requirements for fuel quality (sulfur concentration can reach up to five tenths of a percent). Lubricants that are certified in this class do not allow wear of motor parts, the appearance of carbon deposits in the piston system. The elements of the power unit are less oxidized, little foam and soot are formed (such characteristics are very significant for the engines of today's buses and tractors). The main disadvantage, which limits the mass use of such consumables, for example, in Eastern European and Asian countries, is that oils significantly depend on the quality of the fuel being poured.
- CF-2. API CF 2 oils are intended for use in two-stroke diesel engines operating in difficult conditions. The class was introduced twenty-three years ago. Such motor oils are usually poured into highly loaded engines.
- CF-4. This includes lubricants designed to be filled in four-stroke diesel engines manufactured after 1990. Unless the automaker indicates otherwise in the owner's manual, the oil can be used in gasoline internal combustion engines.
- CE. Motor oils for use in diesel engines manufactured no earlier than 1983. They were used in very powerful turbo engines, which are characterized by a significantly increased working pressure compared to others.
- CD. The class was introduced in 1955. Such oils were often used in agriculture (tractors, combines).
- CC. This class appeared in 1961. This includes oil products that can be poured into medium-loaded engines.
- CB. The class was adopted in 1949. It was an improved CA class.
- ca. Lubricants were poured exclusively into lightly loaded diesel power units.
Categories of oils for transmissions
It is necessary to familiarize yourself with the classification of gear oils in order to be able to decipher the marking when choosing a lubricant for the transmission. By means of the designations on the canister, it is possible to understand what the performance of the product is, what additives and base oils it consists of.
- GL-1. Designed for cone-spiral, worm and mechanical gearboxes (without synchronizers) installed in trucks and special equipment.
- GL-2. Optimal for worm gearboxes that operate in low-speed and light-loaded mode. Usually used in tractor equipment.
- GL-3. Suitable for cone-helical transmissions operating in medium conditions. Designed to lubricate spiral and other truck gearboxes. Do not pour into hypoid transmissions.
- GL-4. Oils for hypoid transmissions operating in high speed/low torque/low speed/high torque applications. Today, these lubricants are often used in synchronized gearboxes.
- GL-5. Lubricants are suitable for hypoid gearboxes that operate under conditions of heavy load on the gear teeth and high speeds. Usually they are poured into transmissions with offset axles. For synchronized manual transmissions, you must use petroleum products approved by the automaker.
- GL-6. Car oils are intended for filling in hypoid gearboxes with a large displacement. Today they are not used due to their complete displacement by GL-5 oils.