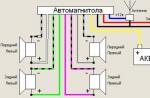
According to the rules of the road (SDA), a moving vehicle during daylight hours must be marked with dipped beam headlights, fog lights (PTF) or daytime running lights (DRL or DRL in English). We will learn about various options for connecting DRLs to automotive wiring through an electromagnetic relay in this reference material prepared by the site.
An example of connecting DRL from a generator

Attention: do not forget to put a fuse in case of a short circuit. No one is safe from accidental short circuits during installation and operation!


DRL connection diagram through 4 contact relay

Some people buy DRL headlights and simply connect them to the dimensions. But it is more correct to make them light up when the ignition is turned on and go out when the side lights of the car are turned on.
You can even connect the DRL lamps to the cigarette lighter, because it is energized only when the ignition is on. It will be better than looking for the ignition wire in the wiring.
Connecting DRL lamps via a 5-pin relay


Many are in no hurry to install daytime LED headlights simply by turning on the dipped beam headlights, but keep in mind that using DRLs instead of dipped beam will allow you to charge the battery faster while driving, since their power consumption is 5 times less.
 15 watt LED DRLs
15 watt LED DRLs DRL connection diagram using a control unit

Some daylights, from the most expensive and modern models, have a control unit that allows you to automatically control their operation (brightness, inclusion, and so on). In this case, the electrical circuit will look like this:

Some auto electronics manufacturers produce running lights control units with the ability to turn off DRLs at the time of one of the functions: parking brake, reverse gear, starter operation when starting the engine. So it's better to overpay a little and buy just such a set of headlights.
Relay- an electrical, electronic or mechanical device - a device designed to close and open various sections of electrical circuits when the input data indicator changes. In other words, the relay has a control part that reacts to changes in input indicators, and a controlled part (contact group) that changes its position to the opposite. Often, relays are also called a variety of devices that make or break contacts when a certain, not necessarily electrical, value changes, for example, devices that are sensitive to temperature (thermal relays), lighting (photo relay), sound pressure level (acoustic relays), etc. Also, various timers are often called relays, for example, a car turn signal timer, on / off timers for various devices and devices, for example, household appliances (time relay).
In the automotive industry, only electrical relays are used., but of various types and purposes. The simplest of them consists of coils with a ferromagnetic armature and a group of contacts connected to it, when an electric current is applied to the relay winding, which generates a magnetic field, the armature changes its position, thereby changing the position of the contact it controls. The first figure on the right shows a relay with one contact group, slightly more complex relays involve several contact groups, and even more complex ones include control of the coil itself (for example, a turn signal control relay, which, with a constant current supply, provides intermittent operation of the coil and contact group , thus turning on the steering column petal of the turn signal, the light is not constantly on but flashes) (second figure).
In terms of applicability, relays are very useful, the fact is that the contact group can work with high voltage and current, but this is not necessary for a coil. Thus, a coil triggered by a voltage of, say, 12 volts is capable of controlling contacts that pass 380 volts, while a small neat button is allowed to control the relay, and a large powerful electric motor will be started from the relay. In this example, we can say that if you needed to start the motor directly through a small, neat button, then it would melt in an instant, and a button or toggle switch capable of withstanding the voltage and current for the operation of the same motor should be far from small and neat! Everything described can be applied to the car engine start system, the ignition switch, supplies electricity with thin wires to the coil, which, when activated, closes the starter power circuit. Surely you have seen at least once when, when lighting up a battery, thin wires heat up so much that in seconds the winding starts to melt, so imagine what kind of wires your car would have been entangled if no one had ever invented a RELAY!
Relays designed to work in the electrical network of a car have approximately the same characteristics:
- Power supply range: 8...16 V
- Rated voltage: 12 V
- Control current: no more 0.2 A
- Trip voltage: not less than 8.0 V
- Release voltage: 1.5...5.0 V
- Maximum current in the power circuit: 30 A
- Active winding resistance: 80±10 ohm
It is also worth noting that some types of relays include not only an electrical board that controls the operation, but also, especially in power ones, elements (diodes or resistors) that protect wiring and other electrical components from overloads that occur when the relay contacts actuate. If there are stabilizing elements (diodes or resistors) inside the relay, this will be reflected on the case.It is necessary to pay attention to the marking and arrangement of contacts on the relay, as some manufacturers produce relays with a non-standard arrangement of contacts. It is also worth noting that during prolonged operation of the relay in maximum load modes, a spark that jumps when switching contacts creates carbon deposits between these contacts, due to which the controlled device may not work or work incorrectly. In the place of poor contact, when the current flows, excess heat is released, the current in the power circuits increases, which entails heating of the place of poor contact in the connected circuit, and subsequently the plastic parts of the attachment points of these contacts are melted.
According to the initial state of the contacts, relays are distinguished with:- normally closed contacts
- Normally open contacts
- changeover contacts

To control various actuating devices, switching circuits, and controlling devices in electronics, an electromagnetic relay is actively used.
The relay device is quite simple. Its basis is coil consisting of a large number of turns of insulated wire.
Installed inside the coil kernel from soft iron. The result is an electromagnet. Also in the design of the relay is present anchor.It is fixed on spring contact. The spring contact itself is fixed on yoke. Together with the rod and armature, the yoke forms a magnetic circuit.
If the coil is connected to a current source, then the resulting magnetic field magnetizes the core. He, in turn, attracts the anchor. The armature is fixed on a spring contact. Next, the spring contact closes with another fixed contact. Depending on the design of the relay, the armature can mechanically control the contacts in different ways.
In most cases, the relay is mounted in a protective housing. It can be either metal or plastic. Consider the relay device more clearly, using the example of an imported electromagnetic relay bestar. Let's take a look at what's inside this relay.

Here is the relay without the protective case. As you can see, the relay has a coil, a rod, a spring contact on which the armature is fixed, as well as executive contacts.
On the circuit diagrams, the electromagnetic relay is indicated as follows.

The symbol of the relay in the diagram consists of two parts, as it were. One part ( K1) is the symbol for an electromagnetic coil. It is designated as a rectangle with two pins. Second part ( K1.1; K1.2) are the groups of contacts controlled by the relay. Depending on its complexity, the relay can have a fairly large number of switched contacts. They are divided into groups. As you can see, the designation shows two groups of contacts (K1.1 and K1.2).
How does a relay work?
The principle of operation of the relay is clearly illustrated by the following diagram. There is a control circuit. This is the K1 electromagnetic relay itself, the SA1 switch and the G1 power battery. There is also an executive circuit, which is controlled by the relay. The executive circuit consists of load HL1 (signal lamp), relay contacts K1.1 and battery G2. The load may be, for example, an electric lamp or an electric motor. In this case, the signal lamp HL1 is used as a load.

As soon as we close the control circuit with switch SA1, the current from the battery G1 will go to the relay K1. The relay will work, and its contacts K1.1 will close the executive circuit. The load will be powered by battery G2 and the lamp HL1 will light up. If you open the circuit with the SA1 switch, then the supply voltage will be removed from the K1 relay and the K1.1 relay contacts will open again and the HL1 lamp will turn off.

Switched relay contacts can have their own design. So, for example, normally open contacts, normally closed contacts and switching contacts (changeover contacts) are distinguished. Let's deal with this in more detail.
Normally open contacts
Normally open contacts - these are relay contacts that are in the open state until current flows through the relay coil. Simply put, when the relay is off, the contacts are also open. On the diagrams, relays with normally open contacts are indicated like this.

Normally closed contacts
Normally closed contacts - these are relay contacts that are in a closed state until current begins to flow through the relay coil. Thus, it turns out that when the relay is off, the contacts are closed. Such contacts on the diagrams are depicted as follows.

Changeover contacts
Changeover contacts is a combination of normally closed and normally open contacts. Switch contacts have a common wire that switches from one contact to another.

Modern widespread relays, as a rule, have changeover contacts, but relays can also be found that include only normally open contacts.
For imported relays, normally open relay contacts are indicated by the abbreviation N.O. A normally closed contacts N.C.. The common contact of the relay has an abbreviation com.(from the word common- "general").
Now let's turn to the parameters of electromagnetic relays.
Parameters of electromagnetic relays.
As a rule, the dimensions of the relays themselves make it possible to apply their main parameters to the case. As an example, consider an imported relay Bestar BS-115C. The following inscriptions are inscribed on its body.
COIL 12V DC- This rated operating voltage relay ( 12V). Since this is a DC relay, the abbreviation for DC voltage is indicated (abbreviation DC stands for direct current/voltage). English word COIL translated as "coil", "solenoid". It indicates that the abbreviation 12VDC refers to the relay coil.

Further, the electrical parameters of its contacts are indicated on the relay. It is clear that the power of the relay contacts can be different. It depends both on the overall dimensions of the contacts and on the materials used. When connecting a load to the relay contacts, you need to know the power for which they are designed. If the load consumes more power than the relay contacts are designed for, then they will heat up, spark, "stick". Naturally, this will lead to an early failure of the relay contacts.
For relays, as a rule, the parameters of alternating and direct current are indicated that the contacts can withstand.
So, for example, Bestar BS-115C relay contacts are capable of switching alternating current of 12A and voltage of 120V. These parameters are encrypted in the inscription 12A 120V AC (reduction AC stands for alternating current).
Also, the relay is capable of switching direct current with a power of 10A and a voltage of 28V. This is evidenced by the inscription 10A 28V DC . These were the power characteristics of the relay, or rather its contacts.
Relay power consumption.
Now let's turn to the power that the relay consumes. As you know, direct current power is equal to the product of voltage ( U) to current ( I): P=U*I. Let's take the values of the nominal operating voltage (12V) and the consumed current (30 mA) of the Bestar BS-115C relay and get its power consumption (eng. - power consumption).
Thus, the power of the Bestar BS-115C relay is 360 milliwatts ( mW).
There is one more parameter - this is the sensitivity of the relay. At its core, this is the power consumption of the relay in the on state. It is clear that a relay that requires less power to operate is more sensitive than one that draws more power. Such a parameter as the sensitivity of the relay is especially important for self-powered devices, since the switched on relay consumes battery power. For example, there are two relays with power consumption 200mW And 360mW. Thus, a 200 mW relay is more sensitive than a 360 mW relay.
How to check the relay?
The electromagnetic relay can be checked with a conventional multimeter in ohmmeter mode. Since the relay coil winding has active resistance, it can be easily measured. The resistance of the relay winding can vary from several tens of ohms ( Ω ), up to several kiloohms ( kΩ). Typically, miniature relays, which are rated at 3 volts, have the lowest winding resistance. For relays whose nominal voltage is 48 volts, the winding resistance is much higher. This is clearly seen from the table, which shows the parameters of the Bestar BS-115C series relays.
| Rated voltage (V, DC) | Winding resistance (Ω ±10%) | Rated current (mA) | Power Consumption (mW) |
| 3 | 25 | 120 | 360 |
| 5 | 70 | 72 | |
| 6 | 100 | 60 | |
| 9 | 225 | 40 | |
| 12 | 400 | 30 | |
| 24 | 1600 | 15 | |
| 48 | 6400 | 7,5 |
Note that the power consumption of all types of relays in this series is the same and is 360 mW.
The electromagnetic relay is an electromechanical device. This is probably the biggest plus and at the same time a significant minus.
With intensive use, any mechanical parts wear out and become unusable. In addition, the contacts of powerful relays must withstand huge currents. Therefore, they are coated with precious metal alloys such as platinum (Pt), silver (Ag) and gold (Au). Because of this, high-quality relays are quite expensive. If your relay is still out of order, then you can replace it.
The positive qualities of electromagnetic relays include resistance to false alarms and electrostatic discharges.
Hi all.
In today's review, I will share with you my impressions of a 5-pin automotive relay purchased on eBay, as well as show one of the possible options for using it.
The relay was ordered almost simultaneously with the DRL kit, which I talked about a few days ago. For what? Because when using a standard connection, when you turn on the dimensions or low / high beam, the DRL still continued to glow. I didn’t find anything good in this, and therefore I began to think about automating their shutdown when the dimensions or dipped beam were turned on. The simplest and most logical option seemed to me to use a relay. 
By the way, this is one of those few purchases, before making which I went to the local auto parts store. Imagine my surprise when I saw the price in the VAZ store: a relay - 5 rubles (about $ 2.5), a block for it - 2.5 rubles ($ 1). In total, we have $ 3.5 for a set offline without waiting, against $ 1.66 for them. The choice is obvious :) I ordered 2 relays at once, since I originally planned to install one for each light bulb.
The seller sent the parcel a few days after payment, assigning it a track, all available events for which you can see.
It took about a month for the parcel to get from China to Belarus, after which it was safely received at my post office. They are delivered in ordinary plastic bags without any identifying marks and inscriptions (except for the barcode sticker). 
Outwardly, the relays are not much different from those that can be seen on the shelves in their native stores. I have no particular complaints about their workmanship. The relays themselves actually look very decent. The contacts are securely sealed with a resin-like sealant: 
As you can see in the photo, each contact is signed, so there should be no connection problems :)
On top of the relay, the principle of operation of the relay is shown, as well as the manufacturer and brief characteristics. 
As you can see, this relay is designed for a voltage of 12-14 V and a maximum current of 40A. Whether it is really capable of surviving such a load, I can’t say, since I didn’t have anything suitable for checking this parameter at the time of connection: (I have a maximum load of about 4A in the network, so there are no problems with this.
To mount the relay, a metal plate is provided in the design, which can be easily removed if necessary. 
The package includes the relay itself and the block to it. The block comes immediately with wires, which greatly simplifies the installation process. The quality of the pads will be somewhat worse. The main disadvantage is the abundance of flash, which was not removed after the block was out. The length of the wires going to the block is about 15 centimeters. 
But here the appearance rather suffers, since this does not affect the functionality in any way. If you believe the description, then each relay is able to work out 10,000 on-off cycles, which is quite good.
In principle, there is nothing more interesting in the appearance of the relay, which means you can proceed to checking their performance. But before doing this, I think it would not be superfluous to recall why these relays are needed at all.
In the normal state, the relay has 2 contacts permanently closed. These are the contacts marked on the relay with the numbers 30 and 87a (in some cases 88). When voltage is applied to contacts 86 and 85, the circuit 30-87a breaks, and 86-85 closes. On the free contact (87) there is a free plus (we do not need it). So we remove the wire from the block that goes to pin 87. 
So let's get started. First of all, we cut the positive wire going to the DRL. Since it is common in mine, you can get by with one relay by installing it near the place of its connection. In the cut, we connect the wires going to contacts 30 and 87a. 86 pin connected to ground, and 85 to the positive wire going to the parking lights. We isolate the wire connection points and fasten the relay somewhere under the hood. It turned out something like this for me (I brought the ground wire to the mounting bolt): 
It remains the case for small things - to check how everything works. We turn on the ignition and see that our DRLs glow. So it didn't get any worse. 
Next, turn on the dimensions / dipped beam: 
As you can see, everything works as intended. When you turn on the dimensions / dipped beam, the DRL bulbs turn off. For greater clarity, I made a short video on the topic of how it looks live:
Summing up everything that was written here, I can say that I was satisfied with the purchase. First, everything works the way I wanted it to. Secondly, the price of a purchased relay with a block is two times lower than ours. Thirdly, one more relay was left in reserve :) And the idea arose to power the DRL from the generator so that they start working only after the engine is started, and not when the ignition is turned on. Since if you are waiting for someone sitting in the car and listening to the radio, then the DRLs glow. True, with a total load of 0.4A, they should not plant the battery, but somehow I don’t really like it anyway ...
If desired, the relay can be used in a wide variety of variations. As far as I know, some of them even assemble anti-theft devices :)
On this, perhaps, everything. Thank you for your attention and your time.
I plan to buy +14 Add to favorites Liked the review +23 +37Many improvements in the electrical equipment of the car include the use of power relays. This article discusses the principle of operation and several examples of relays used in cars. This article is useful to all lovers of tuning improvements in terms of car electrical equipment.
Here are the main characteristics of domestic relays:
- Rated voltage: 12V
- Control current: no more than 0.2A
- Operation voltage: not less than 8.0V
- Release voltage: 1.5 - 5.0V
- Maximum switching current: 30A
- Control winding resistance: 80±10 ohm
Versions of domestic relays:
- 90.3747-10 - plastic housing without fastening lug
- 90.3747 - plastic housing with eyelet
- 113.3747 - metal case with fastening eye
- 113.3747-10 - metal case without fastening lug
- 111.3747 - metal case with fastening eye
- 111.3747-10 - metal case without fastening lug.
The relay must be used in cases where switching of high load currents (20-40A) is required, and this is more than the control output produces (the winding of the relay control circuit usually consumes no more than 0.2A)
Relays with 4 and 5 contacts are produced.
Power relays have winding contacts that control the operation of power contacts (85 and 86 contacts), and power contacts themselves (30, 87 and 87a). 
The principle of operation of the power relay is as follows. Voltage is applied to the control contacts of the relay (winding), the winding attracts the power contacts of the relay to each other, the relay operates and closes (or opens) the electrical circuit with its power contacts. If there is no voltage on the contacts of the control winding of the relay, contact number 30 is permanently closed to contact number 87a. If voltage is applied to the control winding of the relay, then contact number 30 is disconnected from contact number 87a and connected to contact number 87. One of the contacts, 87a or 87, may be missing. In this case, the relay works either only for closing or for opening the power circuit.
Some imported relays between the 85th and 86th contacts have quenching diodes or resistors, and sometimes both. These elements protect the control circuits from overloads during the operation of the relay contacts.

If the diode symbol is applied on the relay case, this means that when connecting such a relay, it is necessary to observe the polarity of the control contacts.
It is necessary to pay attention to the marking and arrangement of contacts on the relay, as some manufacturers produce relays with a non-standard arrangement of contacts.
It should be noted that during long-term operation of the relay in maximum load modes, a spark that jumps when switching contacts creates carbon deposits between these contacts, due to which the controlled device may not work or work incorrectly. In the place of poor contact, when the current flows, excess heat is released, the current in the power circuits increases, which entails heating of the place of poor contact in the connected circuit, and subsequently the plastic parts of the attachment points of these contacts are melted. The attachment points of the relay contacts are melted, which leads to their displacement relative to their standard position, and sparking begins due to the appearance of gaps between the contacts, and as a result of these processes, the contact point heats up even more.
Imported relays are considered more reliable, domestic relays are less hermetic and wear-resistant.
When choosing a relay, pay attention to the coating of the relay contacts and the connector where the relay is inserted. The most preferred are relays with tinned contacts.