For a real car enthusiast, a car is not just a means of transportation, but also an instrument of freedom. With the help of a car, you can get to anywhere in the city, country or continent. But having a license is not enough for a true traveler. After all, there are still many places where the mobile does not catch, and where tow trucks cannot reach. In such cases, in the event of a breakdown, the entire responsibility falls on the shoulders of the motorist.
Therefore, every driver should at least a little understand the device of his car, and you need to start with the engine. Of course, modern car companies produce many cars with different types of engines, but most often manufacturers use internal combustion engines in their designs. They have high efficiency and at the same time provide high reliability of the entire system.
Attention! In most scientific articles, internal combustion engines are abbreviated as internal combustion engines.
What are ICEs
Before proceeding to a detailed study of the internal combustion engine device and their principle of operation, we will consider what internal combustion engines are. One important remark needs to be made right away. Over more than 100 years of evolution, scientists have come up with many varieties of designs, each of which has its own advantages. Therefore, to begin with, we highlight the main criteria by which these mechanisms can be distinguished:
- Depending on the method of creating a combustible mixture, all internal combustion engines are divided into carburetor, gas and injection devices. Moreover, this is a class with external mixing. If we talk about the internal, then these are diesels.
- Depending on the type of fuel, internal combustion engines can be divided into gasoline, gas and diesel.
- Cooling of the engine device can be of two types: liquid and air.
- cylinders can be located both opposite each other, and in the shape of the letter V.
- The mixture inside the cylinders can be ignited by a spark. This happens in carburetor and injection internal combustion engines or due to self-ignition.
In most automotive magazines and among professional auto exporters, it is customary to classify internal combustion engines into the following types:
- Gas engine. This device runs on gasoline. Ignition is forced by a spark generated by a candle. The carburetor and injection systems are responsible for the dosage of the fuel-air mixture. Ignition occurs on compression.
- Diesel . Engines with this type of device work by burning diesel fuel. The main difference compared to gasoline units is that the fuel explodes due to an increase in air temperature. The latter becomes possible due to the increase in pressure inside the cylinder.
- Gas systems operate using propane-butane. Ignition is forced. Gas with air is supplied to the cylinder. Otherwise, the device of such an internal combustion engine is similar to a gasoline engine.
It is this classification that is most often used, pointing to the specific features of the system.
Device and principle of operation
Internal combustion engine device

It is best to consider the internal combustion engine device using the example of a single-cylinder engine. The main part in the mechanism is the cylinder. It contains a piston that moves up and down. In this case, there are two control points for its movement: upper and lower. In professional literature, they are referred to as TDC and BDC. The decoding is as follows: upper and lower dead points.
Attention! The piston is also connected to the shaft. The connecting link is the connecting rod.
The main task of the connecting rod is to convert the energy that is generated as a result of the up and down movement of the piston into rotational energy. The result of such a transformation is the movement of the car in the direction you need. This is what the ICE device is responsible for. Also, do not forget about the on-board network, the operation of which becomes possible thanks to the energy generated by the engine.
The flywheel is attached to the end of the engine shaft. It ensures the stability of the rotation of the crankshaft. The intake and exhaust valves are located at the top of the cylinder, which, in turn, is covered with a special head.
Attention! The valves open and close the appropriate channels at the right time.
In order for the internal combustion engine valves to open, they are acted upon by the camshaft cams. This happens through transmission parts. The shaft itself moves with the help of crankshaft gears.
Attention! The piston moves freely inside the cylinder, freezing for a moment either at the top dead center or at the bottom.
In order for the internal combustion engine device to function in normal mode, the combustible mixture must be supplied in a clearly calibrated proportion. Otherwise, fire may not occur. A huge role is also played by the moment at which the filing occurs.
Oil is necessary in order to prevent premature wear of parts in the internal combustion engine. In general, the entire device of an internal combustion engine consists of the following main elements:
- spark plugs,
- valves,
- pistons
- piston rings,
- connecting rods,
- crankshaft,
- crankcase.
The interaction of these system elements allows the internal combustion engine device to generate the energy necessary for the movement of the car.
Principle of operation

Consider how a four-stroke internal combustion engine works. To understand how it works, you must know the meaning of the concept of tact. This is a certain period of time during which the action necessary for the operation of the device is carried out inside the cylinder. It could be compression or ignition.
The internal combustion engine cycles form a working cycle, which, in turn, ensures the operation of the entire system. During this cycle, thermal energy is converted into mechanical energy. Due to this, the movement of the crankshaft occurs.
Attention! The working cycle is considered completed after the crankshaft makes one revolution. But this statement only works for a two-stroke engine.
There is one important explanation to be made here. Now in cars, the device of a four-stroke engine is mainly used. Such systems are characterized by greater reliability and improved performance.
It takes two revolutions of the crankshaft to complete a four-stroke cycle. These are four up and down piston movements. Each measure performs actions in the exact sequence:
- inlet,
- compression,
- extension,
- release.
The penultimate cycle is also called the working stroke. You already know about the top and bottom dead centers. But the distance between them indicates another important parameter. Namely, the volume of the internal combustion engine. It can fluctuate on average from 1.5 to 2.5 liters. The indicator is measured by plus the data of each cylinder.

During the first half revolution, the piston moves from TDC to BDC. The intake valve remains open while the exhaust valve is tightly closed. As a result of this process, a vacuum is formed in the cylinder.
A combustible mixture of gasoline and air enters the gas pipeline of the internal combustion engine. There it is mixed with exhaust gases. As a result, a substance ideal for ignition is formed, which can be compressed in the second act.
Compression occurs when the cylinder is completely filled with the working mixture. The crankshaft continues its rotation, and the piston moves from bottom dead center to top.
Attention! As the volume decreases, the temperature of the mixture inside the internal combustion engine cylinder increases.
On the third cycle, expansion occurs. When compression comes to its logical conclusion, the candle generates a spark and ignition occurs. In a diesel engine, things are a little different.
Firstly, instead of a candle, a special nozzle is installed, which injects fuel into the system on the third cycle. Secondly, air is pumped into the cylinder, and not a mixture of gases.
The principle of operation of a diesel internal combustion engine is interesting in that the fuel in it ignites on its own. This happens due to an increase in the temperature of the air inside the cylinder. A similar result can be achieved due to compression, as a result of which pressure increases and temperature rises.
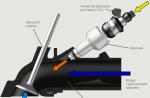
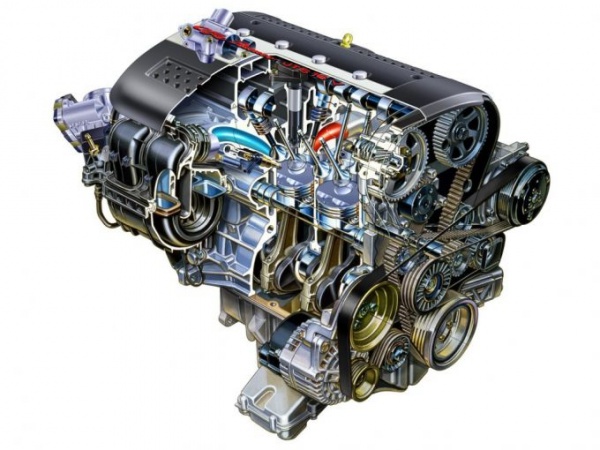
When fuel enters the internal combustion engine cylinder through the nozzle, the temperature inside is so high that ignition occurs by itself. When using gasoline, this result cannot be achieved. This is because it ignites at a much higher temperature.
Attention! In the process of piston movement from the microexplosion that occurred inside, the ICE part makes a reverse jerk, and the crankshaft scrolls.
The last stroke in a four-stroke internal combustion engine is called the intake. It occurs on the fourth half-turn. The principle of its operation is quite simple. The exhaust valve opens, and all combustion products enter it, from where it enters the exhaust gas pipeline.
Before being released into the atmosphere, exhaust gases from usually go through a filter system. This allows minimizing the damage to the environment. Nevertheless, the design of diesel engines is still much more environmentally friendly than gasoline ones.
Devices to increase the performance of internal combustion engines
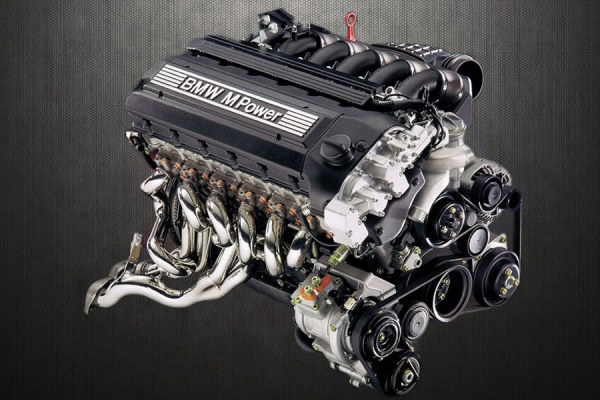

Since the invention of the first internal combustion engine, the system has been constantly improved. If we recall the first engines of production cars, they could accelerate to a maximum of 50 miles per hour. Modern supercars easily overcome the mark of 390 kilometers. Scientists managed to achieve such results by integrating additional systems into the engine device and some structural changes.
A large increase in power at one time was given by the valve mechanism introduced into the internal combustion engine. Another step in the evolution was the location of the camshaft at the top of the structure. This allowed to reduce the number of moving elements and increase productivity.
Also, the usefulness of a modern internal combustion engine ignition system cannot be denied. It provides the highest possible stability. First, a charge is generated that enters the distributor, and from it to one of the candles.
Attention! Of course, we must not forget about the cooling system, consisting of a radiator and a pump. Thanks to it, it is possible to prevent timely overheating of the internal combustion engine device.
Results
As you can see, the device of the internal combustion engine is not particularly difficult. In order to understand it, you do not need any special knowledge - a simple desire is enough. Nevertheless, knowledge of the principles of operation of the internal combustion engine will definitely not be superfluous for every driver.