The injector was a logical development of the car's injection system, when the subsequent improvement of the carburetor to meet environmental standards was impractical. Forced dosing of injected fuel is superior to the carburetor in terms of economy, environmental friendliness and power characteristics. Consider the principle of operation of the injector, as well as the design of the injector power system.
System types
The fuel injection system got its name from a device that is responsible for spraying gasoline - an injector (from the English. Injection - injection, injector - nozzle). A power supply system of this type was installed on aircraft as early as the 20s of the last century. Remarkably, even then it was direct fuel injection into the engine cylinders. We will focus on the development of variations of the Motronic system, in which the fuel supply and ignition angle adjustment are responsible (hereinafter referred to as the ECU or ECU).
Single Point Fuel Injection
Single-point injection, more commonly known as mono-injection, is a transitional technology that has allowed many automakers to switch from a carbureted fuel system to an injection system at a low cost. 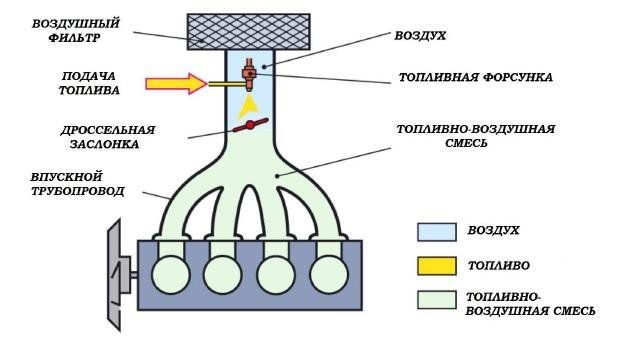
In other words, instead of a carburetor, a central fuel injection unit began to be installed above the intake manifold. The system had a number of advantages, since the ECU allowed for more accurate dosing of gasoline.
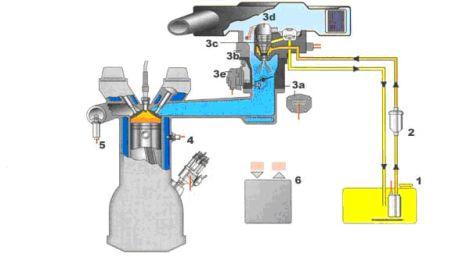 The principle of operation of the injector is based on the following elements:
The principle of operation of the injector is based on the following elements:
- – a fuel tank with the fuel pump located in it;
- – filter element for fuel cleaning;
- – central injection unit. 3a - throttle position sensor (TPS); 3b - regulator responsible for fuel pressure; 3c - injector nozzle; 3e - temperature sensor of the air entering the intake manifold; 3e - throttle position regulator (in the simplest design options, the damper drive was connected to the accelerator pedal by a cable drive);
- – coolant temperature sensor (DTOZH);
- – lambda probe (oxygen sensor);
- - electronic engine control unit.
Principle of operation
The diagram does not show one element, without which the operation of the mechanism would be impossible - the crankshaft position sensor. It is the DPKV that allows the ECU to calculate the amount of air entering the engine. Recall that the amount of fuel supplied depends entirely on the mass of air entering the cylinders, otherwise it is impossible to regulate the composition of the air-fuel mixture (TPVS) for the normal operation of a gasoline engine. At the stage of creating an engine, designers calculate how much air passes under a certain load, that is, the degree of throttle opening, and at certain engine speeds. The data is entered into the fuel card of the engine, which will be recorded in the ECU. Subsequently, when the engine is running, the control unit fixes the speed using the DPKV, the load is determined by the throttle potentiometer, which allows you to take a value from the fuel map that corresponds to the required amount of fuel. But the system can ideally work only in laboratory conditions, since in practice atmospheric pressure depends not only on the position above sea level, but also on temperature, the air filter clogs over time, passing less air through itself, and the throttle assembly itself becomes clogged. An air temperature sensor is used for correction, but its role is small. The lambda probe, which measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases, really affects the composition of the mixture. If there is too much oxygen, the ECU understands that the mixture needs to be enriched, and vice versa.
Characteristic
The main advantage of single-point injection is the low cost of implementation. Flaws:
- uneven filling of the cylinders, due to the location of the nozzle;
- wet collector. When the injector is opened, the gasoline travels a long way to the combustion chamber. When the collector is cold, the fuel does not evaporate, but settles on the walls, as a result of which the mixture must be greatly enriched;
- Although the lambda probe allows you to adjust the TPVS, the method for measuring the mass of air is generally inefficient.
Multi-point fuel injection
Multi-point injection was a significant step forward compared to single-point injection, as it allowed cars to invest in EURO-3 emission standards.
Single-point injection, due to incurable diseases due to design features, could only fulfill the requirements of EURO-2.
The history of the evolution of automotive injection systems is extremely interesting, but it is not the main topic of this article. That is why we will not pay attention to the intricacies of the operation of such engine management systems with distributed injection as D-Jetronic, KE-Jetronic, K-Jetronic and L-Jetronic. The listed variations were no longer installed on cars in the early 90s, and therefore it is extremely difficult to meet a car with a “live” distribution injection system of this type. 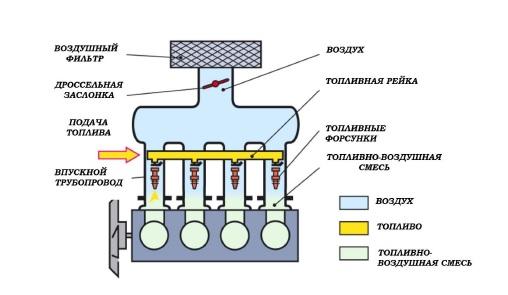
The main difference between a full-fledged injector and a single injection is the presence of 4 nozzles located near the intake valves. Injection Engine Components: 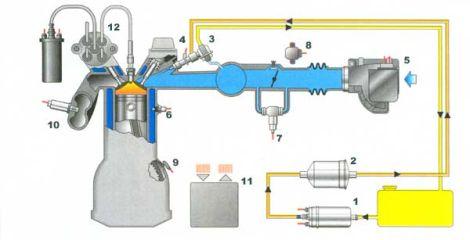
- - the fuel pump, which in the vast majority of cases is located in the tank;
- – coarse fuel filter;
- - a fuel pressure regulator, from which a return line goes to the tank to drain excess fuel. In some cars, there is no return line as such, and the fuel regulator is located next to the pump in the tank;
- - nozzle. The picture above shows how all the injectors are connected by a fuel rail;
- – air flow meter;
- – Coolant temperature sensor;
- - idle speed regulator (IAC);
- - a potentiometer that fixes the actual position of the throttle valve (TPDZ);
- – the gauge of frequency of rotation of a cranked shaft (DPKV);
- - oxygen sensor;
- - ECU;
- - Ignition distributor.
Air Mass Calculation
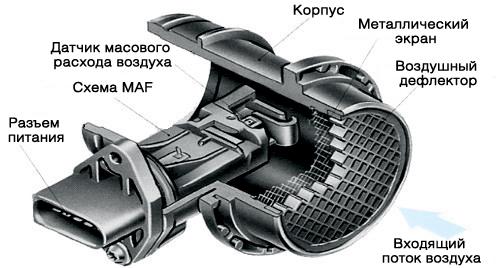
In addition to nozzles, a feature of the system is the way the air mass is calculated. There are only 5 ways to measure the amount of air passing through the throttle:
Characteristic
Advantages of distributor injection on valves:
- uniform filling of cylinders;
- the use of a DMRV or a MAP sensor allows you to accurately calculate the air flow, which gives you more options for adjusting the TPVS in all engine operating modes.
That is why cars with a full-fledged injector are always more powerful and more economical than cars with single-point injection.
Direct injection, which is a type of distributor injection system, is the last word in gasoline engine power systems. The main feature of direct injection is the supply of fuel directly into the combustion chamber. 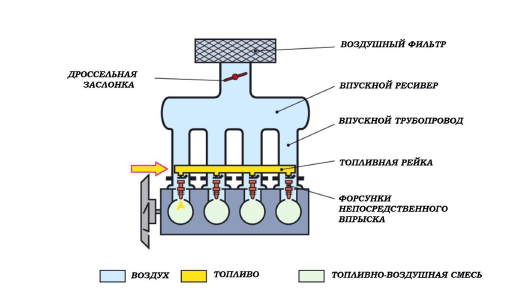
GDI, FSI, D4 are abbreviations used by Mitsubishi, Volkswagen and Toyota respectively for direct injection engines. The power supply system of such internal combustion engines is more like diesel engines than the usual Otto cycle internal combustion engines. Device: 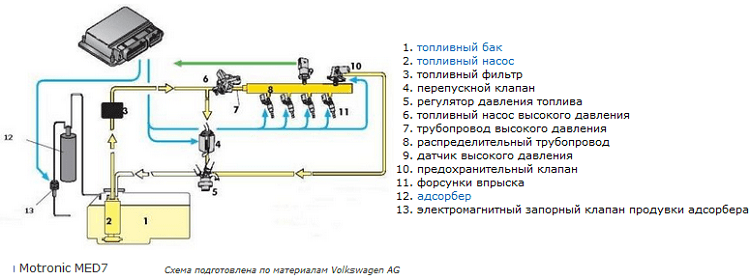
What determines the efficiency
The high cost and complexity of production, which are the main disadvantages of direct injection, are more than compensated by the extreme efficiency and power characteristics. This is achieved due to the fact that the engine can run on 3 main options for the fuel mixture (the GDI system is chosen as an example):
- super blend. Fuel is injected at the end of the compression stroke and burns in close proximity to the spark plug, while around the combustion zone in the combustion chamber there is mainly clean air or a mixture of air with exhaust gases, which is supplied by the EGR;
- stoichiometric. Fuel is supplied at the intake stroke, it mixes well with air, forming a mixture close to the ideal proportional ratio (14.7 / 1) in the entire combustion chamber;
- power mode, in which TPVS is prepared in two stages. A small amount of fuel is injected on the intake stroke, but most of it is injected at the end of the compression stroke.
By supplying fuel in the liquid phase directly to the combustion chamber, direct injection engines are less prone to compression, which allows for higher compression ratios and higher engine efficiency.