If you are into patchwork and quilting, then the Husqvarna Sapphire series (eg model 870) or the Pfaff Expression 4.0 are your best bet. We can also recommend the Janome Memory Craft 6600 Professional.
Adherents of the Japanese approach to technology - sophisticated electronics and outstanding functionality for moderate money - can safely recommend the older Brother models: NV 600 and NV 400. Janome 4900 QC has similar capabilities.
Among the machines in this class, it is worth highlighting the novelty of 2009 - Janome Memory Craft 5200. This machine uses a unique needle plate, the hole in which automatically decreases when you sew with a straight line. This innovation has a very positive effect on the quality of the straight stitch, especially on thin fabrics, and also reduces the likelihood of skipped stitches when sewing stretch fabrics.
In the segment of electromechanical machines, the situation with the prices and functionality of machines is similar to the situation with computer machines. Just as European cars are of high quality workmanship and reliability, just like Japanese cars have more features at lower prices.
Among mechanical machines with modern types of shuttles, we can safely recommend Pfaff Select 3.0 and older models. Family has very good Gold Line models - 7123, 7023 and 7018, as well as new Gold Master series machines (8124e, 8024a and 8018a) And from Janome we can recommend the time-tested very successful models Janome 1221 and Janome w23u.
Sewing machine device
The device of industrial sewing machines
Industrial sewing machines have increased speed characteristics and slightly different kinematic relationships in comparison with household sewing machines operating at low speeds. These kinematic relationships are discussed below using the example sewing machines 22-A And 97-A classes having a corresponding shaft speed of 3500 and 5000 rpm.
Sewing machine 22-A class PMZ
needle mechanism(Fig. 12). This mechanism is typically crank, converting the rotational movement of the main shaft 6 through the crank 7 and the connecting rod 8 into the reciprocating movement of the needle bar 4 with the needle 1 fixed in the needle holder 2. The needle bar can be moved in height using regulatory screws R leash (studs).
Thread take-up mechanism(Fig. 13). This is a hinge-rod type mechanism. It is a lever 3, put on the inner shoulder of the crank pin (see Fig. 12, 7), pivotally connected to the connecting link, which is pivotally connected to the body cars using pin 2. The outer arm of the lever is equipped with an eyelet for threading. As the main shaft crank rotates, the thread take-up eye follows a complex curve, slowly lowering to feed the thread and quickly rising to tighten the stitch. Adjustment missing from the mechanism.

Shuttle mechanism(Fig. 14). The mechanism of the shuttle is rotating. The shuttle receives its movements from the main shaft through the means of two pairs of bevel gears 2 with a total gear ratio of 1 = 1:2. The shuttle is mounted on the shuttle shaft with 4 screws, so if necessary it can be rotated or moved (when adjusting cars).

Tissue Engine Mechanism(Fig. 15) consists of two nodes, one of which informs the rail of the vertical movement, and the second - horizontally.
Node of vertical movements of the rail has the following device. A double eccentric is attached to the main shaft. When the main shaft rotates, the eccentric tells the connecting rod 3 vertical movements. In this case, the connecting rod, pivotally connected by the rear head to the rear rocker arm 8 of the lifting shaft 9, vibrates this shaft in the center screws. The rocker arm 10 fixed at the front end of the shaft raises and lowers the cloth feed lever 11 with the rack through the roller and, if necessary, can be turned on the shaft ( adjustment R).

Node of horizontal movements of the rail. When the main shaft rotates, the eccentric through the cuff informs the connecting rod-fork 2 oscillatory movements, while the rocker arm 14 oscillates together with the advance shaft 13. The front rocker arm 12 informs the lever-fork 11 with the rack reciprocating movements horizontally. The magnitude of these movements can change, and consequently, the amount of tissue advancement will change. To do this, it is enough to bring the connecting link 5 closer to the connecting rod-fork 2. For this purpose, screw 4 is screwed in ( adjustment R). In this case, the upper arm of the lever-fork 6 moves in the direction from the worker, and the lower one, together with the connecting link 5, moves in the direction of the worker. The amount of advance decreases. To increase the amount of advancement, this screw is turned out. To change the direction of movement of the fabric when fastening the stitch, it is enough to move the connecting link to the other side of the connecting rod-fork 2. For this purpose, lower the front shoulder of the two-arm reverse stroke lever 7. The roller, together with the lever-fork 6 and the connecting link, will move to the working one. The lower the lever is lowered, the more the connecting link moves to the worker. If you lower the reverse stroke lever, the coil spring will return the connecting link to its previous position and the fabric under the needle will move away from the working one. By turning the eccentric 1 ( adjustment P) on the main shaft, the timing of tissue advancement changes. By turning the rocker 14 ( adjustment P) the position of the teeth of the feed dog in the slot of the needle plate is changed.

The general layout of the mechanisms is shown in Figure 16. The main places are marked on the kinematic diagram adjustments mechanisms and arrows show lubrication points.
Sewing machine 97-A class
Car 97-A class refers to modern high-speed equipment and has more complex kinematic connections.

Needle mechanism (Fig. 17). In principle, it does not differ from a similar mechanism 22-A class, however, it is structurally more perfect: a shortened, lightweight, thin needle bar 8 in its movement is guided not only by the bushings 4, but also by the guide for the insert 7, put on the pin of the pin 11. This guide is equipped with automatic lubrication. The upper head of the connecting rod 9 is mounted on a needle bearing.

Thread take-up mechanism(Fig. 18). The single rotating mechanism consists of a crank pin 1, a disk of the thread take-up lever 3, rigidly fixed with screws 2 on the pin, and the thread take-up itself - a part of a peculiar shape that is screwed to the lever. Adjustment mechanism is shown in the figure by arrows (P). The mechanism does not require lubrication.

Shuttle mechanism(Fig. 19). Unlike the machine shuttle mechanism 22-A class shuttle mechanism 97-A class made with automatic lubrication. From the main shaft, the rotation of the shuttle shaft 7 is transmitted by a system of toothed drums 1 and gears 4 and 5 through the transmission shaft 3, which is supported by a ball bearing and a bushing mounted in the holes of the platform tides.
The gear ratio from the main shaft to the transmission shaft is 1=1:1, and to the shuttle shaft 1:2. The gears are located in the crankcase with oil.
Mechanism It has device for automatic oil supply: from the crankcase to the shuttle 8 through the axial hole in the shuttle shaft.

Tissue Engine Mechanism(Fig. 20). The fabric engine 9 is fixed on the lever 8, which is pivotally connected to the rocker arm 7 of the advance shaft 6. The advance shaft receives rocking movements from the transmission shaft through the eccentric. The eccentric is covered by the head of the connecting rod 2, connected by means of a connecting link 3 with the rear rocker arm of the advance shaft. Device 4-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17 allows regulate stitch size and moving fabric from forward to reverse.
The fabric motor receives vertical movements from the lift shaft 21, which also receives rocking movements from the eccentric 18, mounted on the transmission shaft. The eccentric is covered by the head of the connecting rod 19, the other head of which is pivotally connected to the rocker arm 20 of the lift shaft.
The mechanism is characterized by the use of needle bearings, short articulated links.
For adjustments stitch value, press the platform button to the stopper with your left hand, locking the ring, and turn the main shaft of the machine by the flywheel with your right hand. Locations are marked on the diagram. adjustments(R). Dotted arrows show lubrication points.
Electric drive for industrial sewing machine
Unlike household sewing machines with manual or foot drive (some household machines supplied with electric drives), each industrial sewing machine equipped with an individual friction electric drive, which serves to turn on and off cars And adjustments her speed.

In universal sewing machines sewing speed changes smoothly. To do this, use the transmission of motion by friction: the wheels are brought together so that they are in close contact with each other. When the force pressing one wheel against another is weakened, one wheel begins to slip, the speed decreases! This is the principle of operation of the friction electric drive, it consists of an electric motor, a friction clutch, a transmission system, control equipment and electrical protection.
The kinematics of an individual friction drive is shown in Figure 21. When you press the foot pedal 12, the lever 10 rotates with the help of a chain. At the same time, the sleeve 5, thanks to its slot 3, moves translationally towards the electric motor 9 relative to the fixed finger 4. The disk 7, mounted on the shaft 2, engages with the disk 8Г fixed on the motor shaft, and begins to rotate, transferring rotation through the pulley to the main shaft cars. The lower the foot pressure of the worker on the pedal, the greater the slippage between discs 7 and 8, the lower the speed of the machine. When the pedal is lowered, the spring 11 returns the lever 10 and the sleeve 5 to their initial position, the disks 7 and 8 diverge and break the connection with the motor shaft. Brake 6 stops disc 7.
In special sewing machines And semi-automatic machines having an automatic stop, a frictionless electric drive is used.
Article based on site materials
With and increased stitch length. This model is designed to work with light and medium fabrics. The stitch length is adjustable from 1 to 5 mm. Installation step - 0.5 mm. The maximum sewing speed is 5,000 sti/min.
Minerva M5550-JDE is manufactured under license from the German company Dürkopp-Adler, on a similar mechanical base, with identical component quality and excellent build quality. The sewing machine is equipped with a silent built-in servo motor with energy-saving Eco-Drive™ technology. High-quality electronics provide quick start and precise stop of the main shaft, for stable and smooth stitching. The control panel is built into the head of the machine. The lubrication system is represented by an open oil sump with an automatic oil pump. For the productive work of a seamstress, there are: needle positioning options, a soft start function, a function for setting sewing speed limits, LED illumination of the working area and a built-in bobbin winder. There is also a button for adding one stitch in the needle bar area.
Speed control
By equipping the machine with a servo motor, the possibility of flexible setting of the sewing speed is available. The minimum starting speed is 300 rpm. The motor speed is regulated by 100 revolutions. Using the function of setting the sewing speed limits, it is also possible to set the speed range of the motor, and by pressing the start pedal, the servomotor will only run within the specified numbers.
Smooth start
The soft start function allows you to realize a smooth start of the stitching with a gradual increase in sewing speed. To do this, you need to activate the corresponding option on the control panel and set the number of initial stitches that will be performed at the minimum engine speed
Economic Servo Motor
Modern servo
The latest noise reduction technology and a modern servo drive built into the head of the machine made it possible to reduce the level of vibration and noise by 50% compared to industrial sewing machines of this class. In turn, the energy-saving Eco-Drive™ technology saves up to 450 kWh* of electricity annually

Integrated panel
A convenient control panel is built into the head of the sewing machine, allowing you to make all sewing settings in one place, including setting the motor speed and soft start functions.
Adding a stitch

Adding a stitch
This option allows you to add a stitch at the right place in the stitching with just one touch of a button. The function will be useful when attaching small parts and finishing stitches to the butt

Versatility
The increased stroke of the comb and the ability to adjust the height and angle of the feed teeth, makes it easy to debug the material feed mechanism for sewing various types of light and medium fabrics, with the same high stitch quality
LED backlight

LED backlight
The built-in LED light is conveniently placed directly above the needle bar, providing excellent illumination of the entire work area. Two-position brightness adjustment available

Built-in bobbin winder
The winder is practically integrated into the head of the sewing machine, allowing you to carry out the preparatory work of winding the thread onto the bobbins as quickly as possible. The bobbin winder is powered by a servomotor. There is also a thread cutter.
Automatic lubrication
The Minerva M5550-JDE is equipped with a new lubrication system with an automatic oil pump, providing fast oil supply to the friction units in the minimum amount required for high-speed operation. Replaceable oil filter reliably removes dust, keeping oil clean

Automatic lubrication
The Minerva M818-JDE is equipped with a new lubrication system with an automatic oil pump, providing fast oil supply to the friction units in the minimum amount required for high-speed operation. Replaceable oil filter reliably removes dust, keeping oil clean
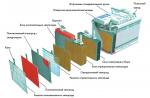
In this article, you will learn how the engine of a modern household sewing machine, located inside its body, works. In order to replace or perform preventive maintenance on this sewing motor, it is often necessary to disassemble the body of the sewing machine.
For an ordinary user, this article will be useful only as information about the device of a household sewing machine, since only a master (electrician) should disassemble the body of a sewing machine, and even more so, disassemble the electric drive.
In any case, after repairing the electric motor or sewing machine pedal, never leave it connected to the mains unattended for a long time.

It looks like the electric motor of a household sewing machine disassembled.
Video how to disassemble the electric drive of a household sewing machine.
How to remove the motor pulley

The motor pulley is most often fixed to the shaft with a screw. There is a saw cut on the shaft, into which this screw rests.

But there are other types of fastening the pulley to the motor shaft, which complicates the replacement of such a drive. In this case, you will have to buy an original (branded) drive or have it repaired if possible.
Motor brushes

Sometimes brushes can cause engine failure. In such a case, replacing them may restore the operation of the sewing motor.

Most often, they can be removed without disassembling the motor housing. It is enough to unscrew the plastic similar bushings and pull out the brushes along with the springs.

In this case, the brushes are already worn out, but they are quite functional and do not need to be changed.
How to disassemble the sewing motor housing

After you have removed the brushes, you can begin to inspect other parts of the engine inside.
Usually, this requires unscrewing two nuts at the front and two at the back, tightening the two ladles of the body together.

Carefully remove the front half of the case.

Please note that this motor model does not have bearings. Instead, bushings are installed, the inner surface of which must be lubricated.

Be sure to pay attention to the number and sequence of installation of washers on the shaft.

Now you can carefully pull the motor rotor out of the stator and inspect it.
Preventive inspection of internal engine parts

The winding turns should be light, not have melted and burned areas.
The collector surface must be smooth and clean.

The turns of the stator winding must also be light and clean, without melted and darkened areas.

The sleeve located on the back of the case also needs to be lubricated with one or two drops of sewing oil.

The polluted (burned) surface of the collector must be cleaned with a piece of ordinary thick paper (not sandpaper).
Electric motor contacts

If the sewing machine is quite old and has "worked" a lot, the wiring and various kinds of contacts connecting the motor to the network may be the cause of the malfunction of the electric drive.
Firstly, the contacts can be highly oxidized and need to be cleaned, now with sandpaper.

Contacts with screw fastening can also oxidize and even break off.

Make sure that everything is in order in the wiring, sewing pedal, connectors before disassembling the sewing machine motor.
Many household sewing machines are equipped with the TUR-2 brand electric drive. This is a reliable engine, but sometimes it needs preventive maintenance.
The device of the sewing electric drive of friction type. How to choose the right type and power of the engine for an industrial machine.
Each sewing machine has its own instructions different from other brands of machines, but most economy class machines with a swinging shuttle (like the Seagull sewing machine): Brother, Jaguar, Singer, Veritas, Janome, Husqvarna and other brands have almost the same device.
Instructions for use, threading, switching operations, installing the bobbin case, lubrication and maintenance, etc. in the instructions for such sewing machines are almost the same.

The main parts of the sewing machine:
1. Knob for selecting the type of stitch. With this knob, you set the type of stitch you want: straight, darning, zigzag or offset needle for sewing on a zipper, sewing a buttonhole, etc.
2. Buttonhole fine adjustment screw. Not every machine has such an adjustment. It is designed to equalize the frequency (density) of the zigzag stitch when sewing a buttonhole. That is, in one of the directions the zigzag will be less frequent, so before making a loop, check it on a trim of the same fabric. And make adjustments if necessary.
3. Thread take-up lever.
4. Removable table with storage compartment for accessories.
5. Upper thread tension dial.

6. Button for moving the fabric in the opposite direction.
7. Thread trimmer. A very convenient device, but requires a certain habit. Usually they are rarely used, just forgetting about it, cutting the thread with scissors.
8. Presser foot adapter assembly.
9. Presser foot holder screw.
10. Presser foot.
11. Needle plate.
12. Shuttle knot.
13. Bobbin case.
14. Combs (rake) of the fabric conveyor.
15. Sewing needle.
16. Needle clamp screw.

17. Shuttle cover.
18. Rod for installing the coil.
19. Bobbin winder.
20. Flywheel.
21. Pedal socket.
22. Presser foot lever.
23. Power switch and backlight bulbs.
24. Built-in carrying handle.
25. Thread guide, thread tension regulator when winding on the bobbin.
Sewing machine accessories and accessories

1. Buttonhole foot. A special foot with which it is convenient to make buttonholes. The size of the buttonhole depends on the size of the button inserted into it. In inexpensive models of sewing machines, the buttonhole is sewn in 4 steps.
2. Zipper foot.
3. Foot for sewing on buttons.
4. A set of needles.
5. Double needle.
6. Bobbins.
7. Darning plate. This plate replaces the lever that lowers the toast. The plate is simply put on over the rail, hiding the teeth so that the fabric does not advance when the machine is running.
8. Screwdriver
9. Additional core for the coil. This pin is needed when using a twin needle, its purpose is to install a second spool of thread.
The accessories listed above are stored in a specially designed case inside the side table. These accessories are designed to make most sewing tasks easier.
Needle Installation Instructions

Before installing the needle, be sure to turn off the sewing machine from the mains. This must be done especially for inexperienced, just beginning seamstresses.
1. Unplug the power cord from the electrical outlet.
2. Raise the needle bar to its highest position.
3. Lower the presser foot.
4. If the needle is already installed, remove the needle o by loosening the needle clamp screw with your hand or a screwdriver and pulling the needle down.
5. Insert a new needle with the flat side facing the rear of the machine, sliding it as high as possible until it stops.
6. Tighten the needle clamp screw.

1. For high-quality sewing, the sewing needle must be straight and sharp.
2. To check the straightness of the needle, place it flat side down on a flat surface as shown.
3. If the needle is bent or dull, replace it. Never try to straighten or sharpen it. The metal from which the needle is made is not intended for this.
See Do-it-yourself sewing machine repair.

Depending on your work, you may need to replace the presser foot. Turn the power switch to the "O" position.
2. Detach the presser foot by lifting the lever on the back of the presser foot holder assembly.
3. Place the presser foot on the needle plate with the cross bar of the presser foot under the groove at the bottom of the presser foot holder.
4. Lower the presser foot lever, and attach the presser foot to the adapter. When the presser foot is in the correct position, the pin will snap into place in the adapter.
Reverse sewing machine. bartack

To sew in reverse, press the reverse sewing key all the way down and hold it in this position while lightly depressing the foot controller. Release the key to sew in the forward direction. Reverse sewing is used to secure and reinforce seams. You can use reverse feed for decorative stitching and darning of garments.

1. Place the spool of thread on the spool pin and pass the thread around the thread tension knob when winding the bobbin.
2. Pass the end of the thread through the hole in the bobbin from the inside of the bobbin.
3. Place the bobbin on the winder shaft and slide the shaft to the right. Turn the bobbin clockwise by hand until the spring on the shaft fits into its groove on the bobbin.
4. While holding the end of the thread, gently depress the foot controller to wind the thread around the bobbin a few turns. Then stop the car.
5. Trim the excess thread above the bobbin, and while depressing the foot controller, continue winding the thread onto the bobbin. Note: When the bobbin is filled with thread, the machine stops automatically.
6. After the machine stops, cut the thread between the bobbin and the spool, slide the shaft to the left, and remove the wound bobbin from the shaft. Note: When the bobbin winder shaft is shifted towards the pressure roller, the needle bar is stationary, but the handwheel continues to rotate. Therefore, do not touch the handwheel while winding the bobbin.
In this video you will see how to wind a thread on a bobbin using a winder.
Threading the lower thread into the bobbin case

Turn the power switch to the "O" position.
1. Raise the needle to its highest position by turning the handwheel toward you (counterclockwise), then raise the presser foot lever.
2. Open the bobbin cover behind the attachment table at the front of the machine, remove the bobbin case by pulling its latch towards you and removing it from the bobbin.
3. Unwind approximately 10 cm of thread from a fully wound bobbin, and insert the bobbin into the bobbin case. Pass the unwound end of the thread through the slot, then down and to the left until the thread enters the hole under the tension spring.
4. Holding the bobbin case by the latch, insert it into the hook as far as it will go, then release the latch. Make sure that the bobbin case pin fits into the groove on the top of the hook. Note: If the bobbin case is incorrectly inserted into the machine, it will fall out of the hook immediately after sewing starts.

1. Raise the presser foot lever using the appropriate lever, and turn the handwheel toward you (counterclockwise) to raise the thread take-up lever to its highest position.
2. Pull up the spool pin and put the spool of thread on it.
3. Pass the thread through both thread guides, first through the back thread guide and then through the front thread guide.
4. Draw the thread down and around the upper thread tension knob from right to left until the thread catches the thread stop spring. Hold the thread and pull it between the tension discs.
5. Guide the thread to the back of the thread take-up lever and around it from right to left. Pass the thread through the slit, pulling it towards you until it enters the thread take-up eye.
6. Pull the thread down and pass it behind the thread guide.
7. Thread the eye of the needle from front to back and pull out about 5 cm of thread. Note: If the thread is not threaded correctly, it may break, skip stitches, or wrinkle the fabric.
If your sewing machine does not have an instruction manual and you do not know how to use it, then you can use this simplified and universal manual. This manual is suitable for any economy-class sewing machine with an oscillating hook that performs a minimum set of operations.