According to its philosophy, the DSG is a manual gearbox, in which the gear change occurs automatically. The driver has the opportunity to use the manual shift mode, but even in this case, the gear change is carried out by actuators by directing electrical signals. This design does not imply a direct connection between the gearshift lever and the driven gear change forks. The operation of the clutch is based on the same principle. The ICE flywheel is disconnected from the gearbox input shaft by a servo drive at the command of the automatic transmission control unit.
A distinctive feature of the DSG box is the dual clutch. Lightning-fast gearshift speeds were achieved thanks to the fact that when a gear is engaged, the next stage is automatically switched on. For example, when you shift into 1st gear, 2nd gear immediately follows. We can say that two separate clutch baskets work in tandem with a manual gearbox. It will be difficult for you to understand how the DSG works if you are unfamiliar with the car.
At the moment, there are two generations of robotic gearboxes from VW-Group. Each of them has its own characteristics, so the DSG 6 and DSG 7 device should be considered separately.
DQ250
Volkswagen AG launched DSG production in 2003. The gearbox was developed by the American company BorgWarner. According to the assurances of the designers, the mechanical components "digest" up to 350 Nm. This made it possible to meet such a box on a car with an internal combustion engine volume of 1.6-3.2 liters. DQ250 is equipped with VW Golf, Scirocco Jetta, Passat, Sharan, Touran, as well as some Seat and Skoda models . The main components of the automatic transmission:
A dual-mass flywheel is used to transmit torque from the crankshaft. The main feature of the six-speed gearbox is a wet clutch, which in its design resembles a torque converter-type automatic transmission. Inside the housing there are 2 clutch packs, which consist of discs rigidly connected to the engine flywheel, as well as friction discs engaged with the gearbox input shaft. When clutching the gearbox shaft and flywheel is required, the discs are compressed under oil pressure. In idle mode, the discs rotate without engaging. The design uses a hydraulic type oil pump, which provides oil not only for clutch, but also for mechatronics actuators.
DSG 7
In 2008, the seven-speed DQ200, developed by Luk, saw the light. The moment comfortable for the automatic transmission was limited to 250 Nm, so it is equipped with less powerful, light cars with a transverse engine. Of the features of the device, one can single out the clutch arranged in one housing with a two-mass flywheel, which is no longer combined with an oil bath inside the box. The principle of operation of a dry clutch is identical to that used on cars with a manual transmission. This follows already from the device:
Luk also replaced the hydraulic oil pump with an electrically driven system. This made it possible to reduce the filling volume of oil by almost 4 times (1.7 liters versus 6.5 liters for DSG 6).
DQ500
The third generation of automatic transmission was developed by Volkswagen specialists. The manufacturer claims that it is able to “hold” up to 600 Nm, so such gearboxes are installed on the Transporter 4 × 4, Tiguan and many other models from the VW-Group. The designers returned to the wet type of clutch.
Control system
It is Mechatronic that controls the processes occurring inside the DSG. System components:
- input sensors that record the position of the gear forks, shaft rotation speed, oil pressure and temperature readings, throttle opening degree, etc.;
- electronic control unit;
- electrohydraulic unit, which is a complex of actuators. It includes spool valves, solenoid valves, oil pressure control valves, multiplexer.
Assembling the puzzle
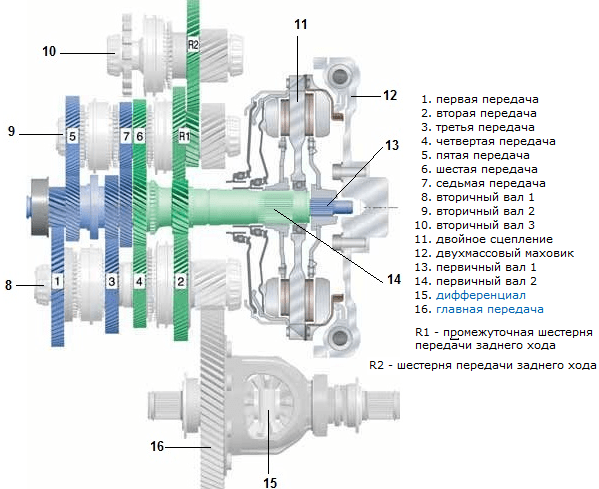
It remains to consider only some features of the DSG device, which make it possible to understand how the preliminary switching on of the next gear is implemented. The main secret is that the gearbox has two input shafts. They are located coaxially (one passes inside the other) and are connected each with its own clutch.
One of the shafts is designed for an even number of speeds, the other for odd steps and reverse gear. In driving mode, the wheels are connected to only one input shaft. The amount of torque, that is, the transmission, is determined by which pinion of the output shaft is currently connected to the input shaft. At the moment when one of the clutches connects the input shaft to one of the output shafts, the second output shaft rotates freely, which allows the next gear to be selected through the synchronizers. When the mechatronic decides that the right moment has come to engage the gear, he will open one clutch and immediately engage the second. Exactly the one whose shaft is already connected to the gear of the next gear.
The type of actuator installed in the vehicle determines the layout of the wet clutch. A more compact version is concentric (friction discs are located in the same plane). For rear-wheel drive cars, a parallel arrangement of couplings is used (located perpendicular to the shaft, the packages are one after the other). The type of the drive axle also determines the layout of the gearbox itself.
Buying danger
It is worth recognizing that the smoothness of switching and the speed of switching are very expensive for many owners of cars with DSG. Major breakdowns:
- DQ250 - quick failure of the dual mass flywheel. The problem here is not the DSG, but the unreliable design of the flywheel element. The appearance of vibrations accelerates the failure of the double clutch;
- DQ200 - Flywheel issue fixed. But a dry clutch wears out much faster. Reducing the amount of oil leads to frequent overheating. The dual clutch does not tolerate constant hard acceleration very well. Designers, trying to extend the life of the automatic transmission, programmatically underestimate the characteristics of the internal combustion engine, smooth out the reactions to a sharp pressing of the accelerator pedal;
- overheating is a common problem for all DSGs, but automatic transmissions with a dry clutch are the worst in this regard;
- mechatronics failure. A typical failure for the DQ200 and DQ250, but there are precedents for the DQ500 as well;
- breakage of the axis of the differential satellites is a problem that has migrated from the manual transmission of new images. Fortunately for the owners, the malfunction is infrequent.
How to be
Jerks or vibrations when switching, kicks, constant sounds and gears that do not turn on can catch the owner of a new car already from 30 thousand km. Trouble-free operation of the DQ200 rarely lasts more than 70 thousand km. The DQ250 is capable of running over 100,000 km in normal use. This situation is really frightening, because the resource of an automatic transmission of a torque converter type is often not limited to 250 thousand km. Some models, with regular oil changes and careful operation, wind up to 400 thousand km. At the moment, the best DSG transmission is the DQ500, which is installed on all-wheel drive cars. The front-wheel drive layout is more prone to overheating. Much, of course, depends on the conditions in which they drive a car. What harms a robotic gearbox:
- long driving in traffic jams (especially in summer);
- dynamic driving with sharp accelerations;
- wrong chip tuning.
Now you know what DSG is. In addition to the above information, owners can be advised to change the oil every 30 thousand km in a wet clutch gearbox. This will significantly extend the service life. Special attention deserves the question of the advisability of buying used cars with DSG.