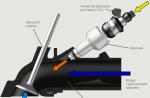
Consider engine injector(its device and principle of operation), taking as an example an electronic system of distributed injection.
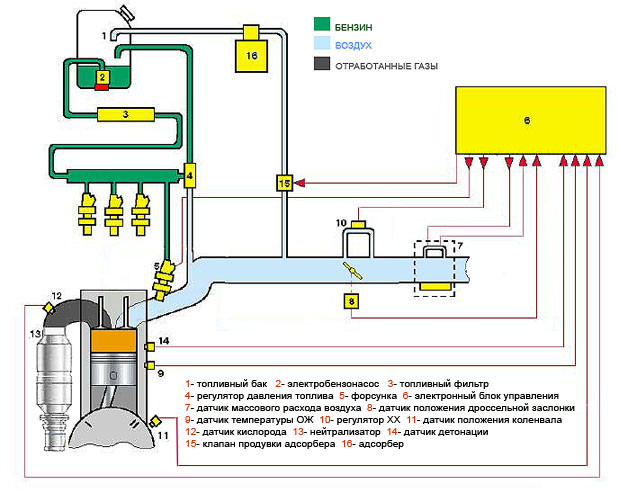
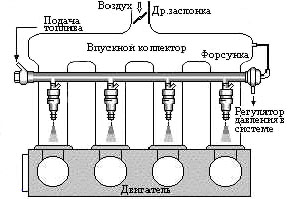
Injection injection engines, which are currently produced, are equipped with individual nozzles for each cylinder. The injectors are connected to the fuel rail, which is pressurized with fuel supplied by an electric fuel pump. Depending on the time during which the injectors are in the open position, the amount of injected fuel changes. An electronic control unit (so-called controller) regulates the opening of the injectors based on information received from various sensors.
Mass air flow sensor necessary for calculating the cyclic filling of cylinders. This sensor measures the mass air flow. Then the received information is recalculated by the program into cylinder cyclic filling. In the event of a sensor failure, its readings are not taken into account by the system, and the calculation is made according to emergency tables.
Throttle position sensor calculates the load factor on the engine injector, as well as its changes depending on engine speed, throttle opening angle and cyclic filling.
coolant temperature sensor necessary to determine the correction of fuel supply and ignition depending on temperature, as well as to control the fan. In the event of a malfunction of this sensor, its readings are not taken into account by the system, and temperature readings are taken in accordance with the table, depending on the operating time of the injector engine.
Crankshaft position sensor performs general synchronization of the system, calculation of engine speed and crankshaft position at certain points in time. DPKV is a polar sensor. If the sensor is not turned on correctly, then injection engine will not start. If the sensor breaks, the system will not work. The crankshaft position sensor is the only sensor in the system, in the event of a breakdown of which the car will not move. Malfunctions in the operation of the remaining sensors are not critical, and without them it is possible to get to a car service on your own.
oxygen sensor determines the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust gases. The sensor sends information to the electronic control unit for further correction of the amount of fuel supplied. This sensor is used exclusively in catalytic converter systems complying with Euro 2 and Euro 3 emission standards. Moreover, for Euro-3, two oxygen sensors are used, one is installed before the catalyst, and the second after it.
Knock sensor necessary to control possible detonation. If a possible threat of detonation is detected, the ECU starts the detonation damping algorithm, while the system corrects the ignition timing.
There are a number of different sensors that are necessary for the normal operation of the system. For various car models, a certain combination of sensors is selected depending on toxicity standards, injection systems, and so on.
The ECU program, based on the surveys of the installed sensors in the program, controls various actuators. These include: an ignition module, a gasoline pump, injectors, an idle speed controller, a cooling system fan, an adsorber valve for a gasoline vapor recovery system, and others, depending on the model of the car.
If there is at least the slightest idea about most of these devices, then a non-specialist rarely heard about the adsorber. An adsorber is an element of a closed circuit for the recirculation of gasoline vapors. According to Euro-2 standards, the contact of the gas tank ventilation with the atmosphere is prohibited, and gasoline vapors must be adsorbed (that is, collected) and sent to the cylinders for further afterburning during the purge process. When the engine is off, gasoline vapors from the tank and intake manifold enter the canister, where they are absorbed. During the engine start, at the command of the ECU, the adsorber begins to be blown by the air flow that is sucked in by the engine. Under the action of the air flow, the vapors are carried away into the combustion chamber and burned there.
Types of injection engines.
Injection systems depend on the place of fuel supply and the number of nozzles. They are of three types:
- single point (single injection). One nozzle is installed on the intake manifold for all cylinders.
- multipoint (distributed). With this type of engine, each cylinder is equipped with its own nozzle that supplies fuel to the manifold)
- direct. In this case, fuel is supplied directly to the cylinders using injectors. An example is diesel injection engines.
Injection systems for injection engines.
Single injection is the simplest kind. It has a small amount of control electronics. The disadvantage is its low efficiency, since the control electronics allows you to control the incoming information from the sensors and, if necessary, influence the injection parameters. The advantage of a single-point spray is the fact that carburetor engines can be easily adapted to it, with virtually no significant design alterations or technological changes in production. Also, a mono-spray has, compared to a carburetor, saves fuel, is more environmentally friendly and is relatively stable and reliable in terms of its parameters. However, single-point injection is inferior to throttle response injection engine. In addition, as a result of the operation of a single injection, about 30% of gasoline remains as a sediment on the collector walls.
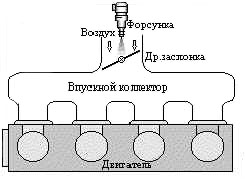
Of course, the mono-injection system is a big breakthrough in comparison with the carburetor power system, but at present it is no longer able to meet modern requirements.
Multi-point injection is a more advanced fuel supply system in which it is supplied separately to each cylinder. This fuel supply system is much more powerful, more economical, but also more complicated. Multi-point injection allows for more power injection engine about 7-10 percent. The main advantages of distributed injection can be considered:
- you can automatically adjust the fuel supply at different speeds and, as a result, improve the filling of the cylinders. As a result, this will allow for the same power of the car to accelerate faster.
- since fuel injection occurs in the immediate vicinity of the intake valve, the amount of fuel that settles on the walls of the intake manifold is significantly reduced. As a result, it becomes possible to more accurately adjust the fuel supply.
It is a more effective tool in optimizing the combustion of the mixture and increasing the efficiency of gasoline injection engine. His work is based on simple principles:
- the fuel is more thoroughly sprayed, which means it mixes better with air and more competently disposes of the finished mixture in different engine operating modes. As a result, injection engine with direct injection consumes less fuel than conventional "injection" engines. This becomes especially noticeable when driving calmly at low speeds;
- with equal working volumes of engines, allows you to accelerate much faster;
- is more environmentally friendly;
- as a result of the higher compression ratio and the simultaneous effect of cooling the air by evaporating the fuel in the cylinders, a higher liter power is guaranteed.
It must be taken into account that this type of injection engine requires high-quality gasoline with a low level of sulfur and other mechanical impurities. This is a prerequisite for ensuring the normal operation of the fuel system.