An injection engine (engine with an injector, English electronic fuel injection engine) is a modern type of internal combustion engine, equipped with an injection fuel injection system, which replaced engines with a carburetor. Today, new gasoline cars are equipped exclusively with an injector, since this solution is able to ensure that the power plant meets the strict standards regarding efficiency and toxicity of exhaust gases.
The carburetor loses to the injector in terms of overall efficiency, since injection engines work more stable, the car gets improved acceleration dynamics. The injection unit consumes less fuel, the content of harmful substances in the exhaust is reduced, as the fuel burns more fully. The system control is fully automated (unlike the carburetor), that is, it does not require manual adjustment during operation. As for diesel engines, the diesel fuel injection system on such engines has a number of design differences, although the general principle of operation of the diesel injector remains similar to gasoline counterparts.
How the injector works
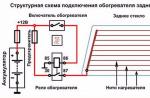
The injection system includes several additional elements, including sensors, a controller, a gasoline pump, and a pressure regulator. The controller receives information from numerous sensors that inform the electronics about air consumption, crankshaft speed, coolant temperature, auto network voltage, throttle position and many other important data. Based on the information received, the controller (or ECU - an electronic control unit) doses the fuel supply and controls other systems, auto devices, ensuring the most optimal engine operation.
The injector operation scheme can also be considered in a different way: an electric pump pumps fuel, a pressure regulator provides a pressure difference in the injectors and the intake manifold, and the controller, receiving information from sensors, controls engine systems, incl. fuel supply, ignition distribution.
Pros and cons of an injector

One of the main advantages is lower fuel consumption compared to a carburetor engine, due to point injection. Also, accurate dosing ensures almost complete combustion of fuel in the cylinders, which reduces the toxicity of exhaust gases. As a result of the operation of the injector, the motor operates in the most optimal mode, which increases its power (by about 5-10%) and extends its service life.
Other advantages include easier starting in winter (heating is not required) and a quick response to load changes, which improves the dynamic properties of the car. But there were some drawbacks: the injector is more expensive than the carburetor system, and its repair is quite complicated and expensive. If the maintenance of the carburetor often comes down to flushing, purging, then only high-quality diagnostics of the injector requires special equipment, which, given the Russian specifics, is not available in every car service. 
Scheme of the injector
If you don’t get into the jungle of the “electronic brain” of our car, then the injector operation scheme is as follows. Numerous sensors receive information about: crankshaft rotation, air consumption, engine coolant temperature, throttle valve, engine knocking, fuel consumption, speed mode, vehicle on-board network voltage, and so on.
The controller, receiving this information about the parameters of the car, controls systems and devices, in particular: fuel supply, ignition system, idle speed controller, diagnostic system, and so on. The change in the operating parameters of the injector injection system is changed systematically, based on the received data.
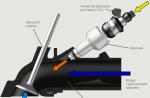
The device of the simplest injector
The injector includes such actuating elements as:
- fuel pump (electric),
- ECU (controller),
- pressure regulator,
- sensors,
- nozzle (injector).
Accordingly, the injector circuit: the electric fuel pump supplies fuel, the pressure regulator maintains the pressure difference in the injectors (nozzles) and the intake manifold air. The controller processes information from sensors: temperature, detonation, camshaft and crankshaft, and controls the ignition, fuel supply systems, and so on.
The fuel injection system is good for everyone, but it was not without its own characteristics. Adherents of carburetors call them shortcomings. The features of the injector can be safely called: the rather high cost of the injector components, low maintainability, high requirements for the quality and composition of the fuel, the need for special equipment for diagnostics, and the high cost of repair work.
Now, let's move from a story about how the injector works and looks to a visual aid. You will see in the video the principle of operation of the injector, and everything that is written above will immediately become clear to you.
A LITTLE HISTORY
Such a power system has been actively installed on cars since the mid-80s, when environmental emission standards began to be introduced. The very idea of an injection power system appeared much earlier, back in the 30s. But then the main task was not in environmentally friendly exhaust, but in increasing power.
The first injection systems were used in combat aviation. At that time, it was a completely mechanical design, which performed its functions quite well. With the advent of jet engines, injectors have practically ceased to be used in military aircraft. On cars, the mechanical injector was not particularly widespread, since it could not fully perform the assigned functions. The fact is that the modes of the car engine change much more often than that of an airplane, and the mechanical system did not have time to adapt to the operation of the engine in a timely manner. In this regard, the carburetor won.
But the active development of electronics gave a "second life" to the injection system. And an important role in this was played by the struggle to reduce the emission of harmful substances. In search of a replacement for the carburetor, which no longer met environmental standards, the designers returned to the injection system, but radically revised its operation and design.
TYPES OF INJECTORS
The first injectors that were massively used on gasoline engines were still mechanical, but they already began to have some electrical elements that contributed to better engine performance.
The modern injection system includes a large number of electronic elements, and the entire operation of the system is controlled by a controller, also known as an electronic control unit.
In total, there are three types of injection systems that differ in the type of fuel supply:
- Central;
- distributed;
- Immediate.
1. CENTRAL
The central injection system is now obsolete. Its essence is that the fuel is injected in one place - at the inlet to the intake manifold, where it is mixed with air and distributed over the cylinders. In this case, its operation is very similar to a carburetor, with the only difference being that the fuel is supplied under pressure. This ensures its atomization and better mixing with air. But a number of factors could affect the uniform filling of the cylinders.
The central system was distinguished by its simple design and quick response to changes in the operating parameters of the power plant. But it could not fully perform its functions. Due to the difference in the filling of the cylinders, it was not possible to achieve the desired combustion of fuel in the cylinders.
2. DISTRIBUTED
The distributed system is currently the most optimal and is used on many vehicles. With this injector, fuel is supplied separately for each cylinder, although it is also injected into the intake manifold. To ensure separate supply, the elements that supply fuel are installed near the head of the block, and gasoline is supplied to the valve area.
Thanks to this design, it is possible to achieve compliance with the proportions of the air-fuel mixture to ensure the desired combustion. Cars with such a system are more economical, but at the same time the power output is greater, and they pollute the environment less.
The disadvantages of a distributed system include a more complex design and sensitivity to fuel quality.
3. DIRECT
The direct injection system is currently the most advanced. It differs in that the fuel is injected directly into the cylinders, where it is already mixed with air. This system is very similar in principle to diesel. It allows you to further reduce gasoline consumption and provides more power output, but it is very complex in design and very demanding on the quality of gasoline.
ELECTRONIC COMPONENT
The main element of the electronic part of the system is an electronic unit consisting of a controller and a memory unit. The design also includes a large number of sensors, based on the readings of which the ECU controls the system.
For its work, the ECU uses the readings of the sensors:
- Lambda probe. This is a sensor that detects the remaining unburned air in the exhaust gases. Based on the readings of the lambda probe, the ECU evaluates how mixture formation is observed in the required proportions. It is installed in the exhaust system of the car.
- Mass air flow sensor (abbr. DMRV). This sensor determines the amount of air passing through the throttle assembly when it is sucked in by the cylinders. Located in the air filter element housing;
- Throttle position sensor (abbr. TPS). This sensor gives a signal about the position of the accelerator pedal. Installed in the throttle assembly;
- Power plant temperature sensor. Based on the readings of this element, the composition of the mixture is regulated depending on the temperature of the motor. Located near the thermostat;
- Crankshaft position sensor (abbr. DPKV). Based on the readings of this sensor, the cylinder is determined into which it is necessary to supply a portion of fuel, the time for supplying gasoline, and sparking. Installed near the crankshaft pulley;
- Knock sensor. It is necessary to detect the formation of detonation combustion and take measures to eliminate it. Located on the cylinder block;
- Speed sensor. It is needed to create impulses, according to which the speed of the car is calculated. Based on his testimony, the fuel mixture is adjusted. Mounted on the gearbox;
- Phase sensor. It is designed to determine the angular position of the camshaft. May not be available on some vehicles. If this sensor is present in the engine, phased injection is performed, that is, the opening impulse is received only for a specific injector. If this sensor is not present, then the injectors operate in pair mode, when the opening signal is sent to two injectors at once. Installed in the block head;
Now briefly on how everything works. The electric fuel pump fills the entire system with fuel. The controller receives readings from all sensors, compares them with the data stored in the memory block. If the readings do not match, it corrects the operation of the power system in such a way as to achieve the maximum coincidence of the received
data stored in the memory block.
As for the fuel supply, based on the data from the sensors, the controller calculates the opening time of the injectors to ensure the optimal amount of gasoline supplied to create the air-fuel mixture in the required proportion.
If one of the sensors fails, the controller goes into emergency mode. That is, it takes the average value of the readings of the faulty sensor and uses them to work. In this case, a change in the functioning of the motor is possible - consumption increases, power drops, interruptions in work appear. But this does not apply to the DPKV, if it breaks down, the engine cannot function. 
What is the difference between an injection engine and a carburetor
The injector is a fundamentally different way of supplying fuel to the combustion chamber compared to a carburetor. In other words, in the injection engine, the largest design changes affected the power supply and fuel supply systems. In a carbureted engine, gasoline is mixed with a certain amount of air in an external device (carburetor). After the resulting fuel-air mixture is sucked into the engine cylinders. The injection engine has special injection nozzles that meteredly inject fuel under pressure, after which a portion of the fuel is mixed with air. If we compare the efficiency of fuel supply by an injector and a carburetor, an engine with an injector is up to 15% more powerful. Significant fuel savings are also noted in different engine operating modes.
Frequent malfunctions of the injector
Since the injector is a complex multi-component system, individual elements may fail over time. The main task of the injector is the highest possible efficiency of fuel combustion, which is achieved by maintaining a strictly defined composition of the working mixture of fuel and air. As a result, any failure in the operation of electronic sensors leads to an imbalance in the operation of the entire injection system, speeds may float at idle or in motion, the engine may triple or not start, a change in the color of the exhaust is noted, etc.
In some cases, the ECU can put the engine into emergency mode. The power unit in such a situation does not gain momentum, “check” is lit on the dashboard, etc. Another cause of injector malfunctions is contamination of the filter elements in the fuel supply system or the injection nozzles themselves as a result of the use of poor quality gasoline. To maintain performance, the fuel filter must be changed in a timely manner. No less attention, especially on cars with a mileage of more than 50-70 thousand km, deserves a fuel pump mesh filter. The specified mesh of the fuel pump is recommended to be changed or cleaned.
It is also desirable to wash the fuel tank once every few years in parallel with the replacement or cleaning of said fuel pump coarse filter. Note that it is important to identify and fix the malfunction of the injector in a timely manner, since failures in its operation can significantly worsen the general condition of the internal combustion engine and lead to other breakdowns. With regard to clogged fuel injectors, in this case, the engine starts worse, loses power and starts to consume more fuel. Violation of the shape of the fuel spray jet (especially in engines with direct injection) leads to local overheating, engine detonation, valve burnout, etc.
Also, the injectors can “pour” fuel, that is, they do not close after the impulse from the ECU stops. In this case, excess fuel enters the combustion chamber, then can penetrate into the exhaust system and into the engine lubrication system through leaks at the piston ring installation sites. In such situations, the entire engine suffers greatly, as gasoline dilutes the oil and the lubrication of loaded parts deteriorates. The presence of fuel in the exhaust system disables the catalytic converter (catalyst), which cleans the exhaust gases from harmful compounds.
To prevent malfunctions of the injector, the nozzles must be cleaned periodically. The fact is that the presence of fractions and impurities in gasoline gradually pollutes the injectors, which reduces their performance, and also violates the quality of the fuel spray. There are two ways to clean the nozzles: with removal or directly on the machine. The procedure for cleaning injector nozzles on a car assumes that a special flushing liquid is passed through the injectors to clean the injector.
The method consists in the fact that the fuel line is disconnected from the fuel rail, after which, instead of the gasoline pump, a special compressor instead of the gasoline pump starts pumping the flushing fluid into the system. Another option for cleaning the injector is cleaning with the removal of nozzles in an ultrasonic bath or on a special washing stand. As for ultrasound, the nozzles are placed in a special apparatus or bath, where the wave vibrations "break" the deposits. Flushing of injectors with removal on the stand is a procedure when the operation of the injectors in the engine is simulated, while washing liquid is passed through them instead of gasoline.