The Renault Logan ignition coil is of great importance for the performance of the car. If it malfunctions, the car simply cannot be started, which means it will not perform its functions as a vehicle. Unfortunately, the Renault Logan ignition switch in general and the coil in particular often fail. You will learn how to repair them or completely replace them from the article.
[Hide]
Ignition switch and features of its replacement
Structurally, the ignition switch is an electrical element with a contact part and a mechanical lock. It is located to the right of the steering column. A key is used to control this node.
The lock has several components and the release of any of them leaves the machine without energy. Most often, problems arise with the relay and breakage of the return spring.
Instructions for repairing and replacing the ignition coil
Further replacement instructions are intended for a 16 valve engine. But you can adapt it to the 8-valve version to repair it.
You need to do this as follows.
- First, you need to disconnect the power from the coil.
- Then remove the armored wires, also known as night vision devices. Please note that they are marked according to the numbers of the cylinders to which they are connected.
- Now you need to unscrew the three bolts that secure the coil. If it has been installed for a long time, then they may have rusted, so you may need to use force when unscrewing. But be careful.
- Now you just need to install a new coil in the same place. It should have come with three bolts. Although they may be shorter than the old ones, still use them.
- Now simply connect the armor wires according to the numbers on the reel
- All that remains is to connect the block with wires and check the operation of the engine.
If you did everything correctly, there will be no problems with the engine and it will start easily.
Video “Replacing the ignition module on Renault Logan”
This video schematically shows the entire process of replacing the module (the author of the video is Renault Logan DIY Repair).
For Renault Logan and Renault Sandero with 8-valve engines K7J and K7M, produced before 2012, a very common problem is the appearance of engine “triple”. It manifests itself especially strongly after a long stay or in damp weather.
The main and most likely cause, as a rule, is the appearance of cracks in the lower part of the ignition coil. They arise over time due to sudden temperature changes.
The fact is that the ignition coils on Logan and Sandero until 2012 were installed in such a way that, due to their design, the lower part comes into contact with the cylinder head cover. Over time, the plastic of the reel body breaks and cracks form into which moisture gets in. This leads to disruptions in work. Although it is worth noting that on many cars, cracks in the coil do not affect the operation of the engine in any way for many years.


There are several ways to solve the problem.
 The most common option is to install a Bosch coil. Its fundamental difference is the brackets with which it is attached to the cylinder head cover. Due to them, a gap is provided between the coil and the cylinder head cover. The only disadvantage of the design is that when installing this coil, due to its higher position, the length of the standard high-voltage wire of the 2nd cylinder is not enough. Therefore, you will have to either find a replacement for this wire, or purchase a set of longer high-voltage wires. The ideal option is a set of Bosch wires. An alternative may be a set of high-voltage wires NGK.
The most common option is to install a Bosch coil. Its fundamental difference is the brackets with which it is attached to the cylinder head cover. Due to them, a gap is provided between the coil and the cylinder head cover. The only disadvantage of the design is that when installing this coil, due to its higher position, the length of the standard high-voltage wire of the 2nd cylinder is not enough. Therefore, you will have to either find a replacement for this wire, or purchase a set of longer high-voltage wires. The ideal option is a set of Bosch wires. An alternative may be a set of high-voltage wires NGK.


The most budget-friendly way to solve the problem is to purchase a similar ignition coil of an old design. In this case, it is recommended to select slightly longer bolts, similar to those that secure the coil and nuts to them. The nuts are used as spacers, slightly raising the ignition coil housing.

Replacing the Renault Logan ignition coil is required as a result of almost any malfunction. On the other hand, the service life of the part is quite long.
Checking the Renault/Dacha Logan ignition coil
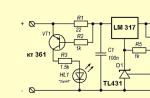
The ignition coil (module) is checked with a conventional tester.
- We connect the probes.
- Before checking the module, we set the measurement limit to 20 kOhm.
- We check the coil in pairs (1-4, 2-3).
Renault Logan ignition coil malfunctions
- Body deformation due to overheating.
- Cracks on the tips, damage to the insulation.
- Short circuit.
Breakdown of ignition coils, of course, can happen at 20-25 thousand kilometers, but usually this part lasts much longer.
If the coil breaks and replacement does not help, you should pay attention to the condition of the spark plugs and high-voltage wires.
Renault Logan: ignition coil repair
The ignition coil is repaired in case of minor damage; more often, if there are malfunctions, the part is replaced.
Now it is possible to replace the tips separately. The manufacturer of original spare parts supplies them in a set with a coil.
If the ignition coil is burst, repairs are not recommended for Logan, but Russian drivers find a way out of the situation. If there are cracks on the body, they are covered with sealant and vibroplast is glued on.
However, many note that this is only a temporary solution to the problem and are planning a replacement in the near future after repairs.
Often, high-voltage wires and a connector are purchased along with the coil.
Replacing the Renault Logan ignition coil step by step
As mentioned above, most often, if the ignition coil is faulty, it needs to be replaced. The procedure is absolutely not difficult.
- We number the wires to facilitate subsequent assembly.
- Disconnect the connector and remove the wires.
- Unscrew the bolts that secure the coil.
- Remove the coil and install a new one.
- We connect the connector and wires.
One of the main problems with “native” ignition coils is their installation close to the engine. This causes the coil body to heat up and become deformed. This type of damage is not expected to affect operation; however, it is best to avoid damage.
The Bosch reel, which has a special spacer, does not have this problem. Largely because of this, it is often preferred to the original, although the price is almost the same.
On many Renault Logan and Sandero, the ignition coil is deformed due to temperature.
Owners may not be aware of the problem; it is not visible visually.
Deformation of the ignition coil can only be seen after removal.
The reason for this deformation is due to a design miscalculation by the engineers. The coil fits very tightly to the motor and the plastic cracks due to temperature. In addition, moisture accumulates under the coil and enters the coil body.
It is worth noting that on many cars this problem does not affect operation in any way.
There are two ways to solve the problem.
1. Installation of a Bosch coil, which has a spacer and is not in close contact with the engine. When installing a Bosch coil, new wires will be required, since the wire of the 2nd cylinder will not reach the connector.
Bosch coil number F000ZS0221 (cost 2500-2700 rubles)
Plus wires about 1200 rubles.
2. In order not to end up with replacing the coil with a Boshevskaya one (2600 rubles) + replacing wires (about 1200 rubles), it’s easier to immediately raise the standard coil by about 10 mm, placing nuts of the appropriate thickness under the mounting bolts, as high as the high-voltage wire of the 2nd one will allow cylinder.
How to remove the ignition coil on a Logan

Disconnect the connector

Removing the wires

unscrew the three coil mounting bolts

we remove the coil, we observe (possibly) such a picture

install the new Bosch coil in place

The coil comes with bolts that are shorter than the original ones, we take the short ones and tighten them with a 10mm wrench



report: JuniorLawyer (drive2.ru)
Complexity
LiftNot marked
We check the ignition coil and its electrical circuits when a malfunction is detected in the ignition system - the absence of sparking on the spark plugs.
The ignition coil and fuel pump are supplied with power from the battery through fuse F03 (25 A) and then through relay K5 (power circuit) installed in the mounting block of the engine compartment (see “Electrical equipment”).
The voltage to the relay coil (control circuit) K5 is supplied from the ignition switch through fuse F02 (5 A), located in the mounting block in the passenger compartment.
To check the power circuit of the ignition coil, disconnect (with the ignition off) the engine control system wiring harness block from the coil (see “Removing the ignition coil”). We connect the tester probes to terminal “C” of the wiring harness block and engine ground. Immediately after turning on the ignition (while the fuel pump is running)…
...the device should record a voltage approximately equal to the battery voltage.
If there is no voltage at terminal “C” of the wiring harness block, then the following may be faulty: fuses, contact group of the ignition switch, relay K5 or their electrical circuits.
With the ignition off, remove relay K5 from the mounting block in the engine compartment. We connect the tester probes to the sockets of the relay power circuits: “positive” - to socket “3”, and “negative” - to socket “5” (the number of the socket corresponds to the number of the relay output). With the ignition on...

...the tester should show the battery voltage.
If this is the case, then the relay or its control circuit is faulty.
If there is no voltage, check whether socket “5” of the relay is connected to ground and whether “+12 V” is supplied to socket “3”. We check the connection of the relay socket to ground with a tester in ohmmeter mode - the resistance should be zero.
To check the “+12 V” voltage supply to socket “3” of the relay...

...we connect the “positive” probe of the tester to the relay socket, and the “negative” probe to the “–” terminal of the battery.
If there is no voltage, check fuse F03 (25 A). If the fuse is good, check the circuit from the fuse socket to the relay socket.
To do this, remove the fuse...

...and connect the tester probes (in ohmmeter mode) to the socket (shown in the photo) of the fuse and to socket “3” of the relay.
If the tester shows “infinity”, there is a break in the circuit. If the circuit is working properly, check whether “+12 V” is supplied from the battery to the other fuse socket.
For this…

...we connect the “positive” probe of the tester to another socket (shown in the photo) of the fuse, and the “negative” probe to the negative terminal of the battery.
The tester should show the battery voltage. Otherwise, the circuit from the battery to the fuse socket is faulty (open or short to ground).
To check the K5 relay control circuits, disconnect (with the ignition off) the engine control system wiring harness block from the ECU.
We connect the tester probes (in ohmmeter mode) to socket “2” of the relay and terminal “69” of the ECU wiring harness block. If the tester shows “infinity”, this means a break in the control “negative” relay circuit.
If the “negative” control circuit of the relay is working, check whether “+12 V” is supplied to socket “1” of the relay.
For this…

...connect the “positive” probe of the tester to socket “1” of the relay, and the “negative” probe to the “negative” terminal of the battery.
The tester should show the battery voltage. If there is no voltage, check fuse F02 installed in the mounting block in the passenger compartment. If the fuse is intact, check the circuit from the fuse socket to socket “1” of the relay and the circuit from the other fuse socket to terminal “3” of the ignition switch wiring harness block.

Numbering of terminals of the ECU wiring harness block
To test the ignition coil control circuits, you can use a probe with a 1–2 W lamp.
We relieve the pressure in the engine power supply system and do not connect the engine control system wiring harness block to the fuel module cover. Disconnect the wiring harness block from the ignition coil and connect the probe probes to terminals “C” and “A” of the wiring harness block. If the probe probes do not fit into the terminal sockets of the block, insert pieces of bare wire into the sockets (pins can be used).
If the coil power supply circuit and the control circuit are working properly, when the crankshaft is cranked by the starter...

...the probe light should blink frequently.
Otherwise, check the wire connecting terminal “A” of the coil wiring harness block to terminal “32” of the ECU wiring harness block for open circuit and short to ground.
Similarly, by connecting the probe probes to terminals “C” and “B” of the ignition coil wiring harness block, and then to terminal “B” of the coil wiring harness block and to terminal “1” of the ECU wiring harness block, we check the other ignition coil control circuit.
You can check the serviceability of the ignition coil itself on the engine by disconnecting the wiring harness block and high-voltage wires from it.
To check one of the primary windings of the ignition coil, connect the tester probes to terminals “C” and “A” of the coil.

Using an ohmmeter, we check the winding for an open circuit.
If the tester shows infinity, there is a break in the winding. Similarly, by connecting the tester probes to terminals “C” and “B” of the coil, we check the other primary winding of the coil for an open circuit.
To check for a break in the secondary winding of the ignition coil, connect the tester probes to the paired high-voltage terminals of the coil (terminals 1–4 or 2–3 cylinders).

For a working ignition coil, the tester should record a resistance of about 7.0 kOhm.
If the secondary winding breaks, the tester will show “infinity”.
Similarly, we check the other secondary winding of the ignition coil.
We check the secondary windings of the ignition coil for breakdown on the engine. We relieve the pressure in the engine power supply system and do not connect the wiring harness block to the fuel module cover. To test, you will need two known good spark plugs.

We tie the candle bodies together with a piece of uninsulated wire (“massage”).
We connect the paired terminals of the ignition coil with the spark plugs using serviceable high-voltage wires and place the spark plugs on the cylinder head cover. We turn the crankshaft with the starter.
To avoid electric shock, do not touch spark plugs or high-voltage wire tips.
If the ignition coil is working properly, sparks should regularly jump between the electrodes of the spark plugs. Similarly, by connecting the high-voltage wires to the other two paired terminals of the coil, we check the other secondary winding for breakdown.